소스 코드
메소드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
/// <summary> 바이트 버퍼를 읽어서 구조체로 변환하기 </summary>
public static T? ByteBufferToStruct<T>(byte[] buffer, int offset) where T : struct
{
int size = Marshal.SizeOf(typeof(T));
if (buffer.Length - offset < size)
return null;
// Unmanaged Heap에 size만큼 메모리 할당
IntPtr ptr = Marshal.AllocHGlobal(size);
// buffer[offset]부터 size만큼 읽어서 ptr이 가리키는 메모리에 복사
Marshal.Copy(buffer, offset, ptr, size);
// ptr이 가리키는 위치의 메모리를 T 타입으로 변환하여 새롭게 할당
T obj = Marshal.PtrToStructure<T>(ptr);
// ptr 메모리 해제
Marshal.FreeHGlobal(ptr);
return obj;
}
예제
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
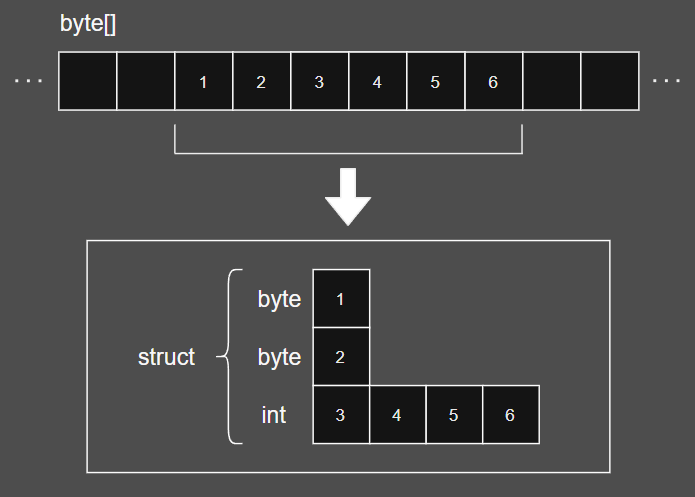
[StructLayout(LayoutKind.Explicit)]
public struct Data
{
[FieldOffset(0)] public byte byte0;
[FieldOffset(1)] public byte byte1;
[FieldOffset(2)] public int int2;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
buffer[4] = 1; // byte0
buffer[5] = 2; // byte1
// int2 (Little Endian)
buffer[6] = 3; // 0x00000003
buffer[7] = 4; // 0x00000400
buffer[8] = 5; // 0x00050000
buffer[9] = 6; // 0x06000000
Data? val = ByteBufferToStruct<Data>(buffer, 4);
if (val != null)
{
Console.WriteLine(val.Value.byte0);
Console.WriteLine(val.Value.byte1);
Console.WriteLine(val.Value.int2);
Console.WriteLine(0x00000003 + 0x00000400 + 0x00050000 + 0x06000000);
// = 100992003
}
}
설명
byte*포인터를T*포인터로 변환하여 할당하는 것과 같다.C#에서는fixed구문에서도T*포인터를 만들 수는 없기 때문에, 위의 방법으로만 가능하다.