요약
array[(int)enumValue],dict[enumValue]의 참조 성능을 비교한다.
테스트 코드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
public enum MyEnum
{
Zero, One, Two, Three, Four, Five, Six, Seven, Eight, Nine
}
public float[] targetArray;
public Dictionary<MyEnum, float> targetDict;
[GlobalSetup]
public void GlobalSetup()
{
targetArray = new float[10];
targetDict = new Dictionary<MyEnum, float>(10);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
targetArray[i] = i;
targetDict.Add((MyEnum)i, i);
}
}
[Benchmark(Baseline = true)]
public void TestArray()
{
float res;
res = targetArray[(int)MyEnum.Zero];
res = targetArray[(int)MyEnum.One];
res = targetArray[(int)MyEnum.Two];
res = targetArray[(int)MyEnum.Three];
res = targetArray[(int)MyEnum.Four];
res = targetArray[(int)MyEnum.Five];
res = targetArray[(int)MyEnum.Six];
res = targetArray[(int)MyEnum.Seven];
res = targetArray[(int)MyEnum.Eight];
res = targetArray[(int)MyEnum.Nine];
}
[Benchmark]
public void TestDict()
{
float res;
res = targetDict[MyEnum.Zero];
res = targetDict[MyEnum.One];
res = targetDict[MyEnum.Two];
res = targetDict[MyEnum.Three];
res = targetDict[MyEnum.Four];
res = targetDict[MyEnum.Five];
res = targetDict[MyEnum.Six];
res = targetDict[MyEnum.Seven];
res = targetDict[MyEnum.Eight];
res = targetDict[MyEnum.Nine];
}
결과
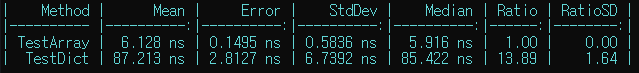
결론
-
(int)로 캐스팅하는 번거로움이 있더라도, 딕셔너리보다 배열을 사용하는 경우의 성능이 압도적으로 좋다. -
enum의 값들이 중복되지 않고 연속적일 경우, 배열을 사용하는 것이 좋다. -
심지어 저장되는 데이터가 구조체 타입일 경우, 딕셔너리는 인덱서에 의해 복제되지만 배열은 복제되지 않은 구조체 객체를 직접 참조할 수 있다는 장점이 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
public struct StructType
{
public float value;
}
public StructType[] arr;
public Dictionary<MyEnum, StructType> dict;
public void Test()
{
arr[(int)MyEnum.Zero].value = 2f; // 가능
dict[MyEnum.Zero].value = 2f; // 불가능
}
추가 - Enum 요소의 개수
1
int len = Enum.GetNames(typeof(MyEnum)).Length;
-
Enum.GetValues()도 있지만 가비지를 더 많이 생성한다. -
참고 : https://stackoverflow.com/questions/856154/total-number-of-items-defined-in-an-enum