개념
- 유니티에서 안전한 멀티스레딩을 구현하는 시스템
- 스레드를 별도로 생성하지 않으며, 유니티의 워커스레드에 작업을 지시할 수 있게 한다.
- 잡 대기열에 잡을 배치하면 워커 스레드가 잡 대기열에서 항목을 가져와 실행한다.
- Native Container를 이용해 잡의 수행 결과를 메인 스레드와 공유한다.
- 버스트 컴파일러를 이용하여 추가적인 성능 향상을 기대할 수 있다.

장점
- 다수의 작은 작업들을 처리하기에 좋으며, 속도가 빠르다.
- 스레드를 추가로 만들고 관리하지 않아도 되므로 메모리를 절약할 수 있다.
- 유니티 콘솔을 이용해 디버깅할 수 있다.
- 메인 스레드의 데이터를 잡의 스택에 깊은 복사를 하여 복사본으로 사용하므로 Race Condition이 발생하지 않는다.
단점
- 워커 스레드를 이용하기 때문에 일반 스레드처럼 Sleep을 사용할 수 없다.
- 메인 스레드에서 관리하는 데이터에 접근할 수 없다.
- 값형 필드만 사용할 수 있다.
NativeContainer
-
각 복사본 내에 격리되는 잡의 처리 결과를 메인 스레드와 공유하기 위한 공유 메모리 타입
-
NativeArray : ECS가 아닌, 모노에서도 사용할 수 있는 타입
-
엔터티 컴포넌트 시스템(ECS) 확장
- NativeList : 크기 변경이 가능한 NativeArray
- NativeHashMap : 키값 쌍 컨테이너
- NativeMultiHashMap : 키 당 여러 개의 값을 갖는 컨테이너
- NativeQueue : 선입선출(FIFO) 컨테이너
NativeContainer Safety System
- DisposeSentinel
- 메모리 누수를 검사한 후, 메모리를 잘못 할당한 경우 오류를 표시한다.
- AtomicSafetyHandle
- 스크립트에서 NativeContainer의 소유권을 이전할 수 있다.
- 두 개의 예약된 잡이 동일한 NativeArray에 동시에 접근하게 되면 안전 시스템을 통해 예외가 발생한다.
- 이 경우, 종속성을 이용해 잡을 예약할 수 있다.
- 첫 번째 잡이 NativeContainer에 쓰기를 마친 뒤 다음 잡에 동일한 NativeContainer에 안전하게 이어 쓰도록 예약할 수 있다.
- 잡 내에서 정적 데이터에 액세스하면 모든 안전 시스템을 우회하므로 유니티에 충돌이 발생할 수 있다.
NativeContainer Allocator
- NativeContainer를 생성할 때는 필요한 메모리 할당 타입을 지정해야 하며, 할당 타입에 지정된 수명 내에 Dispose() 메소드를 통해 메모리를 해제해야 한다.
| 할당자 | 수명 | 설명 |
| Allocator.Temp | 1프레임 | 가장 빠르지만 Temp를 사용하여 잡 내에 NativeContainer 할당을 전달하면 안된다. |
| Allocator.TempJob | 4프레임 | 대부분의 경우 사용한다. |
| Allocator.Persistent | 필요한 만큼 | 성능이 중요한 상황에서는 사용하지 않는다. |
Attributes
-
잡 내부에서 NativeArray를 사용하는 경우 NativeContainer에 읽기, 쓰기를 모두 수행할 수 있으므로 성능 저하가 발생할 수 있다.
따라서 용도에 따라 [ReadOnly], [WriteOnly]를 명시함으로써 성능을 향상시킬 수 있다.
1 2
[ReadOnly] public NativeArray<int> input; [WriteOnly] public NativeArray<int> output;
-
잡 구조체 상단에 [BurstCompile]을 명시함으로써 버스트 컴파일링의 대상으로 예약하여 성능을 향상시킬 수 있다.
1 2 3 4 5
[BurstCompile] public struct SomeJob : IJob { // .. }
Interfaces
IJob
- 하나의 잡 내에서 하나의 작업만 수행하는 경우에 사용한다.
- 하나의 잡 내에서 하나의 Execute()를 호출한다.
IJobParallelFor
- 기본적으로 NativeArray를 필드로 사용하여 배열 작업을 수행한다.
- 하나의 잡 내에서 배열의 크기만큼 Execute(int index)를 호출한다.
IJobParallelForTransform
- 잡 내에서는 값 타입만 사용할 수 있지만, 이것을 사용하면 예외적으로 참조 타입인 트랜스폼에 접근할 수 있다.
- 트랜스폼에 접근할 수 있는 TransformAccess 타입의 배열을 받아 작업을 수행한다.
- 하나의 잡 내에서 TransformAccess 배열의 크기만큼 Execute(int index, TransformAccess transform)을 호출한다.
How To Use
패키지 임포트(선택)
- Burst
네임스페이스
1
2
3
4
using Unity.Collections; // NativeArray
using Unity.Jobs; // IJob, IJobParallelFor
using UnityEngine.Jobs; // IJobParallelForTransform
using Unity.Burst; // BurstCompile
잡 구조체 만들기
- 잡 인터페이스를 구현하는 구조체 정의
- 해당 잡이 사용할 필드 및 잡의 결과를 저장할 공유 메모리 타입 필드(Blittable 또는 NativeContainer) 작성
- 구조체 내의 Execute() 메소드에 잡의 동작 구현
- 구조체 상단에 [BurstCompile] 명시하여 버스트 컴파일링 예약 가능
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
[BurstCompile]
public struct MyJob : IJob
{
public float a;
public float b;
[WriteOnly] public NativeArray<float> result;
public void Execute()
{
result[0] = a + b;
}
}
잡 생성, 예약, 대기, 해제
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
// 1. 결과를 받아올 NativeContainer 할당
NativeArray<float> result = new NativeArray<float>(1, Allocator.TempJob);
// 잡 생성
MyJob jobData = new MyJob();
jobData.a = 10;
jobData.b = 10;
jobData.result = result;
// 잡 예약(실행)
JobHandle handle = jobData.Schedule();
// 메인스레드가 잡의 종료 대기
handle.Complete();
// 결과 확인
float aPlusB = result[0];
// 잡 해제
result.Dispose();
예제 - IJobParallelForTransform
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
// XZ 평면 회전
[BurstCompile]
public struct RotateJob : IJobParallelForTransform
{
public float t;
public float speed;
public float radius;
public void Execute(int index, TransformAccess transform)
{
Vector3 pos = transform.position;
transform.position = new Vector3(
pos.x + Mathf.Sin(t * speed) * radius,
pos.y,
pos.z + Mathf.Cos(t * speed) * radius
);
}
}
public Transform[] _transformArray; // 대상 트랜스폼들 등록
private TransformAccessArray _transformAccessArray;
private void Start()
{
// Transform 배열을 이용해 TransformAccessArray 초기화
_transformAccessArray = new TransformAccessArray(_transformArray);
}
private void Update()
{
// 잡 생성
RotateJob rJob = new RotateJob { t = Time.time, speed = 2f, radius = 0.05f };
// 잡 예약(실행)
JobHandle handle = rJob.Schedule(_transformAccessArray);
}
private void OnDestroy()
{
// 메모리 해제
_transformAccessArray.Dispose();
}
성능 테스트 - 단순/복합 계산
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
// IParallelForJob을 이용한 성능 테스트
const int Size = 15000000;
// 1. 단순 덧셈
static float JustAdd(in float a, in float b)
{
return a + b;
}
// 2. 복합 계산
static float SomeCalc(in float a, in float b)
{
return a * 123 + b / 85 + a * b * Mathf.Pow(a, 2.5f) / Mathf.Pow(b, 0.25f)
* Mathf.Sin(a) * Mathf.Cos(b) * Mathf.Sqrt(a) * Mathf.Abs(b);
}
// 두 배열의 동일 인덱스에 있는 값 계산하기
[BurstCompile]
public struct ParallelCalcJob : IJobParallelFor
{
[ReadOnly] public NativeArray<float> a; // 읽기 전용
[ReadOnly] public NativeArray<float> b;
[WriteOnly] public NativeArray<float> result; // 결과 저장
public void Execute(int i)
{
//result[i] = JustAdd(a[i], b[i]);
result[i] = SomeCalc(a[i], b[i]);
}
}
// 일반적인 수행
private void TestCommon()
{
// 배열 생성
float[] a = new float[Size];
float[] b = new float[Size];
float[] result = new float[Size];
// 배열 초기화
for (int i = 0; i < Size; i++)
{
a[i] = i;
b[i] = i * 2;
}
Stopwatch sw = new Stopwatch();
sw.Start();
// 계산
for (int i = 0; i < Size; i++)
{
//result[i] = JustAdd(a[i], b[i]);
result[i] = SomeCalc(a[i], b[i]);
}
sw.Stop();
Debug.Log($"Common : {sw.ElapsedMilliseconds}");
}
// 잡으로 수행
private void TestJob(int batch)
{
// 배열 생성
float[] a = new float[Size];
float[] b = new float[Size];
// 배열 초기화
for (int i = 0; i < Size; i++)
{
a[i] = i;
b[i] = i * 2;
}
// 네이티브 배열 생성
NativeArray<float> arrayA = new NativeArray<float>(a, Allocator.TempJob);
NativeArray<float> arrayB = new NativeArray<float>(b, Allocator.TempJob);
NativeArray<float> result = new NativeArray<float>(Size, Allocator.TempJob);
Stopwatch sw = new Stopwatch();
sw.Start();
// 계산
ParallelCalcJob job = new ParallelCalcJob { a = arrayA, b = arrayB, result = result };
JobHandle handle = job.Schedule(result.Length, batch);
handle.Complete();
sw.Stop();
Debug.Log($"Job [Batch {batch} ] : {sw.ElapsedMilliseconds}");
// 해제
arrayA.Dispose();
arrayB.Dispose();
result.Dispose();
}
private void Start()
{
// 테스트 이전에 한 번씩 실행
TestCommon();
TestJob(1);
// 테스트
TestCommon();
TestJob(1);
TestJob(2);
TestJob(4);
TestJob(8);
TestJob(16);
TestJob(32);
}
결과
-
[1] 단순 덧셈
-> 첫 수행에는 잡이 느린듯 보이나, 수행이 거듭될수록 결국 비교도 안되게 빠르다.

-
[2] 복합 연산
-> 잡이 훨씬 빠르다.

-
추가 1: 버스트 컴파일을 하지 않은 경우(복합 연산)
-> 버스트 컴파일을 사용한 경우보다 두 배 정도 느리다.
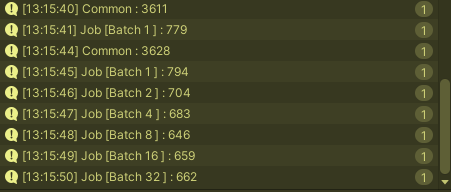
- 추가 2: ParallelJob의 배치는 4~8 정도가 적당한 듯하다.
References
- https://docs.unity3d.com/kr/2020.2/Manual/JobSystem.html
- https://www.raywenderlich.com/7880445-unity-job-system-and-burst-compiler-getting-started
- http://blog.naver.com/PostView.nhn?blogId=canny708&logNo=221557618976