목표
- DirectionalLight, PointLight 클래스 작성
- 프래그먼트 쉐이더에서 각 라이트에 맞는 계산 수행
1. Directional Light
- 위치에 관계 없이 방향으로만 작용하는 직광 만들기
DirectionalLight 클래스 작성
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
class DirectionalLight
{
private:
glm::vec3 direction; // 빛의 방향과 반전된 L 벡터 방향
glm::vec3 color;
float intensity;
public:
DirectionalLight(const glm::vec3& direction, const glm::vec3& color, const float& intensity = 1.f)
{
// NOTE : 직광의 방향은 라이트벡터로 사용하기 위해 반전시켜 전달
this->direction = -glm::normalize(direction);
this->color = color;
this->intensity = intensity;
}
~DirectionalLight() {}
void SendToShader(Shader& shader, const std::string& structVariableName)
{
shader.SetVec3f((structVariableName + ".direction").c_str(), this->direction);
shader.SetVec3f((structVariableName + ".color").c_str(), this->color);
shader.SetFloat((structVariableName + ".intensity").c_str(), this->intensity);
}
};
프래그먼트 쉐이더 작성
-
위에서 작성한 DirectionalLight와 동일한 형태의 구조체를 작성한다.
-
라이트가 여러개일 때를 고려하여, 라이팅 계산을 함수화한다.
-
쉐이더 내에서 사용할 월드 벡터(Pos, Normal, View)들을 구조체화하여 글로벌 변수로 사용한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
#version 440
#define saturate(x) clamp(x, 0., 1.)
struct WorldVectors
{
vec3 pos;
vec3 normal;
vec3 view;
};
struct Material
{
vec3 ambient;
vec3 diffuse;
vec3 specular;
sampler2D diffuseMap;
};
struct DirectionalLight
{
vec3 direction;
vec3 color;
float intensity;
};
// ====================== Global Variables =================
WorldVectors world;
in vec3 vs_position;
in vec3 vs_color;
in vec2 vs_texcoord;
in vec3 vs_normal;
out vec4 fs_color;
// ====================== Uniforms =========================
uniform Material material;
uniform DirectionalLight mainLight;
uniform sampler2D wallTex;
uniform vec3 cameraPos; // Camera World Position
// ====================== Method Prototypes ================
vec3 CalculateDirectionalLight(DirectionalLight dLight, vec3 diffColor, vec3 specColor);
void main()
{
vec3 col = vec3(0.);
// ====================== World Vectors =========================
world.pos = vs_position;
world.normal = normalize(vs_normal);
world.view = normalize(cameraPos - world.pos);
// ====================== Textures ==============================
vec3 diffMapCol = texture(material.diffuseMap, vs_texcoord).xyz;
vec3 diffMapMask = step(vec3(0.01), diffMapCol);
vec3 wallMapCol = texture(wallTex, vs_texcoord).xyz;
// ====================== Colors ================================
vec3 diffCol = mix(wallMapCol, diffMapCol * material.diffuse, diffMapMask);
vec3 specCol = material.specular;
// ====================== Lighting ==============================
// Ambient Light
vec3 ambient = material.ambient;
// Main Light
vec3 diffuseMainLight = CalculateDirectionalLight(mainLight, diffCol, specCol);
// ====================== Final Colors ==========================
col += diffuseMainLight;
col += ambient;
fs_color = vec4(col, 1.);
}
// Diffuse + Specular(BP)
vec3 CalculateDirectionalLight(DirectionalLight dLight, vec3 diffColor, vec3 specColor)
{
float diff = saturate(dot(world.normal, dLight.direction));
vec3 wHalf = normalize(world.view + dLight.direction);
float sNDH = saturate(dot(world.normal, wHalf));
float spec = pow(sNDH, 300.);
return (diff * diffColor + spec * specColor) * dLight.color * dLight.intensity;
}
main.cpp - 라이트 정보 전달
1
2
3
DirectionalLight mainLight(glm::vec3(0.0f, -1.0f, -1.0f), glm::vec3(1.0f), 0.5f);
mainLight.SendToShader(shader, "mainLight");
실행 결과

2. Point Light
- 포인트 라이트는 디렉셔널 라이트와 다르게, 위치와 범위가 존재한다.
- 따라서 다음처럼 클래스를 작성한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
class PointLight
{
private:
glm::vec3 position;
glm::vec3 color;
float range;
float intensity;
public:
PointLight(const glm::vec3& position, const glm::vec3& color, const float& range, const float& intensity = 1.0f)
{
this->position = position;
this->color = color;
this->range = range;
this->intensity = intensity;
}
void SendToShader(Shader& shader, const std::string& structVariableName)
{
shader.SetVec3f((structVariableName + ".position").c_str(), this->position);
shader.SetVec3f((structVariableName + ".color").c_str(), this->color);
shader.SetFloat((structVariableName + ".range").c_str(), this->range);
shader.SetFloat((structVariableName + ".intensity").c_str(), this->intensity);
}
};
- 그리고 프래그먼트 쉐이더에서 동일한 형태의 구조체를 작성한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
struct PointLight
{
vec3 position;
vec3 color;
float range;
float intensity;
};
- 포인트 라이트는 여러 개를 사용할 것이기 때문에 배열로 선언하고, 미리 쉐이더 내에서 허용할 최대 라이트 개수를 define으로 정의한다.
- 그리고 실제로 전달받는 포인트 라이트의 개수 역시 유니폼 변수로 받을 수 있게 한다.
1
2
3
4
#define MAX_POINT_LIGHTS 10
uniform PointLight pointLights[MAX_POINT_LIGHTS];
uniform int pointLightCount;
- 디렉셔널 라이트와 마찬가지로 포인트 라이트 계산도 함수화하여 작성한다.
- 포인트 라이트의 범위와 라이트와 정점 사이 거리를 이용해 감쇄도 계산한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
vec3 CalculatePointLight(PointLight pLight, vec3 diffColor, vec3 specColor)
{
float dist = distance(world.pos, pLight.position);
// 라이트 범위를 벗어나는 경우 색상 0
if(dist > pLight.range) return vec3(0.);
float distAtten = 1. - saturate(dist / pLight.range);
vec3 lightDir = normalize(pLight.position - world.pos);
float diff = saturate(dot(world.normal, lightDir));
vec3 wHalf = normalize(world.view + lightDir);
float sNDH = saturate(dot(world.normal, wHalf));
float spec = pow(sNDH, 300.);
return (diff * diffColor + spec * specColor) * pLight.color * pLight.intensity * distAtten;
}
- 계산으로 얻은 결괏값들을 반복문을 통해 더해준다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
// Point Lights
vec3 diffusePointLights = vec3(0.);
for(int i = 0; i < pointLightCount; i++)
{
diffusePointLights += CalculatePointLight(pointLights[i], diffCol, specCol);
}
// ====================== Final Colors ==========================
//col += diffuseMainLight;
col += diffusePointLights;
col += ambient;
- 이제 메인에서 포인트 라이트들을 하나의 배열로 선언하고 쉐이더에 전달한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
PointLight pointLights[] =
{
PointLight(glm::vec3(-1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f), COLOR_RED, 3.0f),
PointLight(glm::vec3(-0.0f, 0.5f, 0.0f), COLOR_GREEN, 3.0f),
PointLight(glm::vec3( 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f), COLOR_BLUE, 3.0f),
};
unsigned int pointLightCount = sizeof(pointLights) / sizeof(*pointLights);
for (int i = 0; i < pointLightCount; i++)
{
pointLights[i].SendToShader(shader, "pointLights[" + std::to_string(i) + "]");
}
shader.SetInt("pointLightCount", pointLightCount);
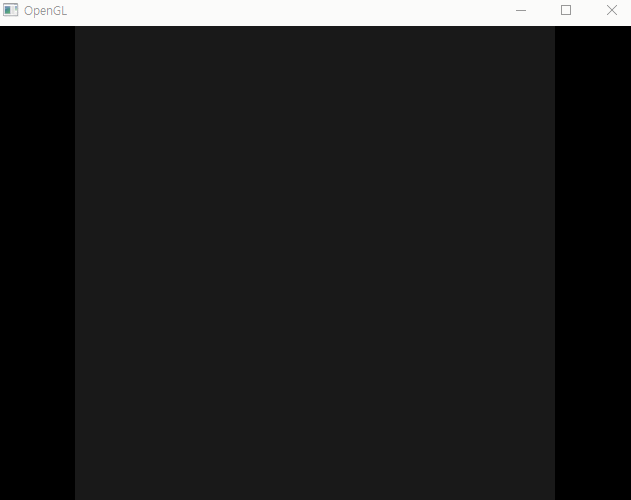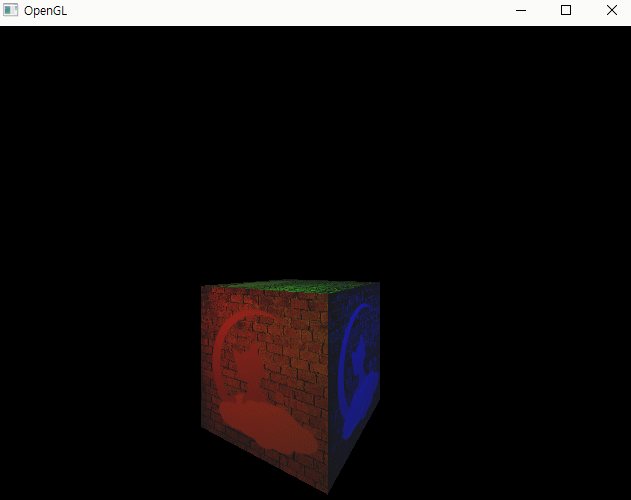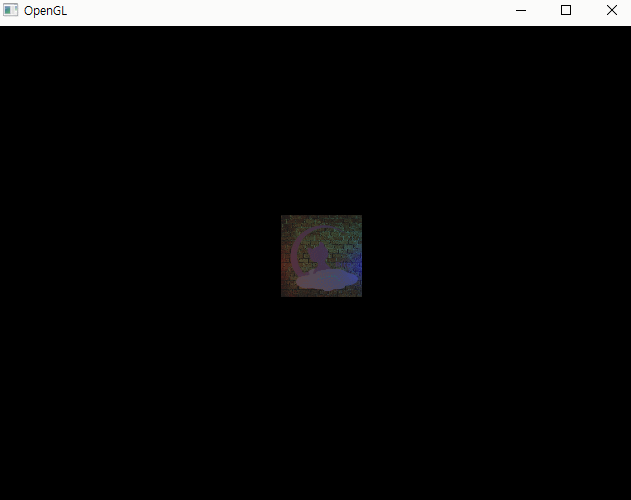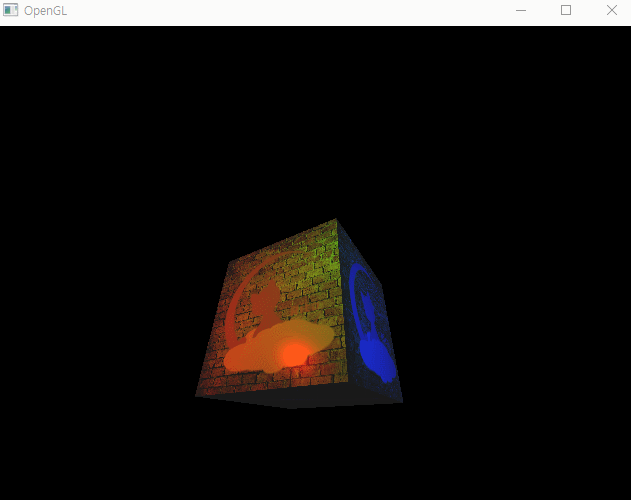
실행 결과
1. 포인트 라이트 + 앰비언트 연산
2. 메인 라이트 + 포인트 라이트 + 앰비언트 연산
