목표
- 프래그먼트 쉐이더 수정
- Mesh 클래스 작성
- GameObject 클래스 작성
- 여러 개의 게임오브젝트 렌더링
1. 프래그먼트 쉐이더 수정
-
각각의 계산이 독립적이고 순차적으로 수행될 수 있도록 변경한다.
-
바뀐 구조
-
1. 색상 계산(텍스쳐, 버텍스 컬러 등)
-
2. 라이트 계산(디퓨즈, 스페큘러, 앰비언트 독립적으로)
-
3. 최종 색상 조립(디퓨즈, 스페큘러, 앰비언트 독립적)
-
소스코드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
// fragment_core.glsl
#version 440
#define saturate(x) clamp(x, 0., 1.)
#define MAX_POINT_LIGHTS 10
struct WorldVectors
{
vec3 pos;
vec3 normal;
vec3 view;
};
struct Material
{
vec3 ambient;
vec3 diffuse;
vec3 specular;
sampler2D diffuseMap;
};
struct DirectionalLight
{
vec3 direction;
vec3 color;
float intensity;
};
struct PointLight
{
vec3 position;
vec3 color;
float range;
float intensity;
};
// ====================== Global Variables =================
WorldVectors world;
in vec3 vs_position;
in vec3 vs_color;
in vec2 vs_texcoord;
in vec3 vs_normal;
out vec4 fs_color;
// ====================== Uniforms =========================
uniform Material material;
uniform DirectionalLight mainLight;
uniform PointLight pointLights[MAX_POINT_LIGHTS];
uniform int pointLightCount;
uniform sampler2D wallTex;
uniform vec3 cameraPos; // Camera World Position
// ====================== Method Prototypes ================
vec3 CalculateDirectionalLightDiffuse(DirectionalLight dLight);
vec3 CalculateDirectionalLightSpecular(DirectionalLight dLight);
vec3 CalculatePointLightDiffuse(PointLight pLight);
vec3 CalculatePointLightSpecular(PointLight pLight);
void main()
{
vec3 col = vec3(0.);
// ====================== World Vectors =========================
world.pos = vs_position;
world.normal = normalize(vs_normal);
world.view = normalize(cameraPos - world.pos);
// ====================== Textures ==============================
vec4 albedo = texture(material.diffuseMap, vs_texcoord);
vec3 diffMapCol = albedo.xyz;
vec3 diffMapMask = vec3(albedo.a);
vec3 wallMapCol = texture(wallTex, vs_texcoord).xyz;
// ====================== Colors ================================
vec3 diffCol = mix(wallMapCol, diffMapCol * material.diffuse, diffMapMask);
vec3 specCol = material.specular;
// ====================== Lights ================================
// Ambient Light
vec3 ambient = material.ambient;
// Main Light
vec3 diffuseMainLight = CalculateDirectionalLightDiffuse(mainLight);
vec3 specularMainLight = CalculateDirectionalLightSpecular(mainLight);
// Point Lights
vec3 diffusePointLights = vec3(0.);
vec3 specularPointLights = vec3(0.);
for(int i = 0; i < pointLightCount; i++)
{
diffusePointLights += CalculatePointLightDiffuse(pointLights[i]);
specularPointLights += CalculatePointLightSpecular(pointLights[i]);
}
// ====================== Final Colors ==========================
vec3 finalDiffuse = diffCol * (diffuseMainLight + diffusePointLights);
vec3 finelSpecular = specCol * (specularMainLight + specularPointLights);
col += finalDiffuse;
col += finelSpecular;
col += ambient;
fs_color = vec4(col, 1.);
}
// Directional Light : DIffuse
vec3 CalculateDirectionalLightDiffuse(DirectionalLight dLight)
{
float diff = saturate(dot(world.normal, dLight.direction));
return diff * dLight.color * dLight.intensity;
}
// Directional Light : Blinn Phong Specular
vec3 CalculateDirectionalLightSpecular(DirectionalLight dLight)
{
vec3 wHalf = normalize(world.view + dLight.direction);
float sNDH = saturate(dot(world.normal, wHalf));
float spec = pow(sNDH, 300.);
return spec * dLight.color * dLight.intensity;
}
// Point Light : Diffuse
vec3 CalculatePointLightDiffuse(PointLight pLight)
{
float dist = distance(world.pos, pLight.position);
// 라이트 범위를 벗어나는 경우 색상 0
if(dist > pLight.range) return vec3(0.);
float distAtten = 1. - saturate(dist / pLight.range);
vec3 lightDir = normalize(pLight.position - world.pos);
float diff = saturate(dot(world.normal, lightDir));
return diff * pLight.color * pLight.intensity * distAtten;
}
// Point Light : Blinn Phong Specular
vec3 CalculatePointLightSpecular(PointLight pLight)
{
float dist = distance(world.pos, pLight.position);
// 라이트 범위를 벗어나는 경우 색상 0
if(dist > pLight.range) return vec3(0.);
float distAtten = 1. - saturate(dist / pLight.range);
vec3 lightDir = normalize(pLight.position - world.pos);
vec3 wHalf = normalize(world.view + lightDir);
float sNDH = saturate(dot(world.normal, wHalf));
float spec = pow(sNDH, 300.);
return spec * pLight.color * pLight.intensity * distAtten;
}
2. Mesh 클래스 작성
- 버텍스와 인덱스 배열, VAO, VBO, EBO 관련 데이터 및 기능을 하나의 클래스에 작성한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
// mesh.hpp
#pragma once
class Mesh
{
private:
Vertex* vertices;
GLuint* indices;
unsigned int numOfVertices;
unsigned int numOfIndices;
GLuint vao;
GLuint vbo;
GLuint ebo;
Transform transform;
void InitVertexData(
Vertex* vertices,
GLuint* indices)
{
//this->numOfVertices = (sizeof(vertices) / sizeof(Vertex));
//this->numOfIndices = (sizeof(indices) / sizeof(GLuint));
this->vertices = new Vertex[this->numOfVertices];
this->indices = new GLuint[this->numOfIndices];
for (size_t i = 0; i < this->numOfVertices; i++)
{
this->vertices[i] = vertices[i];
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < this->numOfIndices; i++)
{
this->indices[i] = indices[i];
}
}
void InitVAO()
{
glCreateVertexArrays(1, &this->vao);
glBindVertexArray(this->vao);
// VBO : Vertex Buffer Object
// VBO Gen & Bind & Send Data
glGenBuffers(1, &this->vbo);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, this->vbo);
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, this->numOfVertices * sizeof(Vertex), this->vertices, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
// EBO : Element Buffer Object
// EBO Gen & Bind & Send Data
glGenBuffers(1, &this->ebo);
glBindBuffer(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, this->ebo);
glBufferData(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, this->numOfIndices * sizeof(GLuint), this->indices, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
// Set VertexAttribPointers & Enable
// 1. Position
glVertexAttribPointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, sizeof(Vertex), (GLvoid*)offsetof(Vertex, position));
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);
// 2. Color
glVertexAttribPointer(1, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, sizeof(Vertex), (GLvoid*)offsetof(Vertex, color));
glEnableVertexAttribArray(1);
// 3. TexCoord
glVertexAttribPointer(2, 2, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, sizeof(Vertex), (GLvoid*)offsetof(Vertex, texcoord));
glEnableVertexAttribArray(2);
// 4. Normal
glVertexAttribPointer(3, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, sizeof(Vertex), (GLvoid*)offsetof(Vertex, normal));
glEnableVertexAttribArray(3);
}
public:
Mesh(Vertex* vertices, GLuint* indices, const unsigned& numOfVertices, const unsigned& numOfIndices)
{
this->numOfVertices = numOfVertices;
this->numOfIndices = numOfIndices;
this->InitVertexData(vertices, indices);
this->InitVAO();
}
~Mesh()
{
glDeleteVertexArrays(1, &this->vao);
glDeleteBuffers(1, &this->vbo);
glDeleteBuffers(1, &this->ebo);
delete[] this->vertices;
delete[] this->indices;
}
void BindVAO()
{
glBindVertexArray(this->vao);
}
void Render()
{
glDrawElements(GL_TRIANGLES, this->numOfIndices, GL_UNSIGNED_INT, 0);
}
};
- Quad, Cube 메시 정보를 미리 meshData.hpp 헤더에 정의한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
// meshData.hpp
#pragma once
// 1. 평면
Vertex quadVertices[] =
{
// Position // Color // TexCoord // Normal
glm::vec3(-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f), glm::vec3(1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec2(0.0f, 1.0f), glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f), // LT
glm::vec3(-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f), glm::vec3(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec2(0.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f), // LB
glm::vec3(0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f), glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f), glm::vec2(1.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f), // RB
glm::vec3(0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f), glm::vec3(1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec2(1.0f, 1.0f), glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f), // RT
};
// NOTE : Counter Clockwise
GLuint quadIndices[] =
{
0, 1, 2,
0, 2, 3
};
// 2. 육면체
Vertex cubeVertices[] =
{
// Position // Color // TexCoord // Normal
//glm::vec3(-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f), glm::vec3(1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec2(.0f, .0f), glm::vec3(.0f, .0f, .0f), // 0
//glm::vec3(-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f), glm::vec3(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec2(.0f, .0f), glm::vec3(.0f, .0f, .0f), // 1
//glm::vec3(+0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f), glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f), glm::vec2(.0f, .0f), glm::vec3(.0f, .0f, .0f), // 2
//glm::vec3(+0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f), glm::vec3(1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec2(.0f, .0f), glm::vec3(.0f, .0f, .0f), // 3
//glm::vec3(-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f), glm::vec3(1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec2(.0f, .0f), glm::vec3(.0f, .0f, .0f), // 4
//glm::vec3(-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f), glm::vec3(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec2(.0f, .0f), glm::vec3(.0f, .0f, .0f), // 5
//glm::vec3(+0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f), glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f), glm::vec2(.0f, .0f), glm::vec3(.0f, .0f, .0f), // 6
//glm::vec3(+0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f), glm::vec3(1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec2(.0f, .0f), glm::vec3(.0f, .0f, .0f), // 7
glm::vec3(-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f), glm::vec3(1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec2(0.0f, 1.0f), glm::vec3(-1.0f, .0f, .0f), // 0 // 0
glm::vec3(-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f), glm::vec3(1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec2(0.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec3(-1.0f, .0f, .0f), // 4 // 1
glm::vec3(-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f), glm::vec3(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec2(1.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec3(-1.0f, .0f, .0f), // 5 // 2
glm::vec3(-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f), glm::vec3(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec2(1.0f, 1.0f), glm::vec3(-1.0f, .0f, .0f), // 1 // 3
//
glm::vec3(-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f), glm::vec3(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec2(0.0f, 1.0f), glm::vec3(.0f, .0f, +1.0f), // 1 // 4
glm::vec3(-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f), glm::vec3(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec2(0.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec3(.0f, .0f, +1.0f), // 5 // 5
glm::vec3(+0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f), glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f), glm::vec2(1.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec3(.0f, .0f, +1.0f), // 6 // 6
glm::vec3(+0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f), glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f), glm::vec2(1.0f, 1.0f), glm::vec3(.0f, .0f, +1.0f), // 2 // 7
//
glm::vec3(+0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f), glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f), glm::vec2(0.0f, 1.0f), glm::vec3(+1.0f, .0f, .0f), // 2 // 8
glm::vec3(+0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f), glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f), glm::vec2(0.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec3(+1.0f, .0f, .0f), // 6 // 9
glm::vec3(+0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f), glm::vec3(1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec2(1.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec3(+1.0f, .0f, .0f), // 7 // 10
glm::vec3(+0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f), glm::vec3(1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec2(1.0f, 1.0f), glm::vec3(+1.0f, .0f, .0f), // 3 // 11
//
glm::vec3(+0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f), glm::vec3(1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec2(0.0f, 1.0f), glm::vec3(.0f, .0f, -1.0f), // 3 // 12
glm::vec3(+0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f), glm::vec3(1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec2(0.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec3(.0f, .0f, -1.0f), // 7 // 13
glm::vec3(-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f), glm::vec3(1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec2(1.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec3(.0f, .0f, -1.0f), // 4 // 14
glm::vec3(-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f), glm::vec3(1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec2(1.0f, 1.0f), glm::vec3(.0f, .0f, -1.0f), // 0 // 15
//
glm::vec3(-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f), glm::vec3(1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec2(0.0f, 1.0f), glm::vec3(.0f, +1.0f, .0f), // 0 // 16
glm::vec3(-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f), glm::vec3(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec2(0.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec3(.0f, +1.0f, .0f), // 1 // 17
glm::vec3(+0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f), glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f), glm::vec2(1.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec3(.0f, +1.0f, .0f), // 2 // 18
glm::vec3(+0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f), glm::vec3(1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec2(1.0f, 1.0f), glm::vec3(.0f, +1.0f, .0f), // 3 // 19
//
glm::vec3(-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f), glm::vec3(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec2(0.0f, 1.0f), glm::vec3(.0f, -1.0f, .0f), // 5 // 20
glm::vec3(-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f), glm::vec3(1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec2(0.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec3(.0f, -1.0f, .0f), // 4 // 21
glm::vec3(+0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f), glm::vec3(1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec2(1.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec3(.0f, -1.0f, .0f), // 7 // 22
glm::vec3(+0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f), glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f), glm::vec2(1.0f, 1.0f), glm::vec3(.0f, -1.0f, .0f), // 6 // 23
};
// NOTE : Counter Clockwise
GLuint cubeIndices[] =
{
0, 1, 2, 0, 2, 3,
4, 5, 6, 4, 6, 7,
8, 9, 10, 8, 10, 11,
12, 13, 14, 12, 14, 15,
16, 17, 18, 16, 18, 19,
20, 21, 22, 20, 22, 23,
};
- 메인 함수 내용을 수정한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
// Meshes
Mesh Quad(quadVertices, quadIndices, sizeof(quadVertices) / sizeof(Vertex), sizeof(quadIndices) / sizeof(GLuint));
Mesh Cube(cubeVertices, cubeIndices, sizeof(cubeVertices) / sizeof(Vertex), sizeof(cubeIndices) / sizeof(GLuint));
/* Game Loop */
Cube.BindVAO();
// ...
Cube.Render();
3. GameObject 클래스 작성
유니티엔진의 GameObject처럼 기능하기 위한 최소한의 조건은 다음과 같다.
- 고유한 Transform 객체를 갖는다.
- 고유한 Mesh를 갖거나 동일한 Mesh를 참조할 수 있다.
- 고유한 Shader를 갖거나 동일한 Shader를 참조할 수 있다.
따라서 다음과 같이 작성한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
// gameObject.hpp
#pragma once
class GameObject
{
private:
Mesh* mesh;
Shader* shader;
Transform transform;
public:
GameObject(Mesh* mesh, Shader* shader)
{
this->mesh = mesh;
this->shader = shader;
this->transform = Transform();
}
GameObject(Mesh* mesh, Shader* shader, Transform transform)
{
this->mesh = mesh;
this->shader = shader;
this->transform = transform;
}
Transform& GetTransform()
{
return this->transform;
}
Shader& GetShader()
{
return *this->shader;
}
void AttachMesh(Mesh* mesh)
{
this->mesh = mesh;
}
void AttachShader(Shader* shader)
{
this->shader = shader;
}
void Render()
{
this->mesh->BindVAO();
this->shader->Use();
this->mesh->Render();
}
};
4. 여러 개의 게임오브젝트 렌더링하기
이제 N개의 쉐이더와 게임오브젝트를 만들어서 렌더링해주면 된다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
// main.cpp
Shader shaders[] =
{
Shader("vertex_core.glsl", "fragment_core.glsl"),
Shader("vertex_core.glsl", "fragment_core.glsl"),
Shader("vertex_core.glsl", "fragment_core.glsl"),
Shader("vertex_core.glsl", "fragment_core.glsl"),
Shader("vertex_core.glsl", "fragment_core.glsl"),
Shader("vertex_core.glsl", "fragment_core.glsl"),
Shader("vertex_core.glsl", "fragment_core.glsl"),
Shader("vertex_core.glsl", "fragment_core.glsl"),
};
unsigned int shaderCount = sizeof(shaders) / sizeof(Shader);
for (int i = 0; i < shaderCount; i++)
{
if (!shaders[i].IsValid())
{
glfwTerminate();
}
}
GameObject gameObjects[] =
{
GameObject(&Cube, &shaders[0]),
GameObject(&Cube, &shaders[1]),
GameObject(&Cube, &shaders[2]),
GameObject(&Cube, &shaders[3]),
GameObject(&Cube, &shaders[4]),
GameObject(&Cube, &shaders[5]),
GameObject(&Quad, &shaders[6]),
GameObject(&Quad, &shaders[7]),
};
// Cubes
gameObjects[0].GetTransform().Init(glm::vec3( 0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f), glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f));
gameObjects[1].GetTransform().Init(glm::vec3(-3.0f, 1.0f, -2.0f), glm::vec3(45.0f, 0.0f, 45.0f), glm::vec3(1.0f));
gameObjects[2].GetTransform().Init(glm::vec3( 2.0f, 1.5f, -2.0f), glm::vec3(30.0f, 30.0f, 10.0f), glm::vec3(1.0f));
gameObjects[3].GetTransform().Init(glm::vec3(-1.5f, -1.5f, -1.5f), glm::vec3(25.0f, 15.0f, 20.0f), glm::vec3(1.5f));
gameObjects[4].GetTransform().Init(glm::vec3( 1.0f, -1.5f, -2.5f), glm::vec3(45.0f, 15.0f, 30.0f), glm::vec3(1.5f));
gameObjects[5].GetTransform().Init(glm::vec3(-1.0f, 1.5f, -2.5f), glm::vec3(75.0f, 45.0f, 40.0f), glm::vec3(1.0f));
// Quads
gameObjects[6].GetTransform().Init(glm::vec3(-3.0f, 1.5f, -4.0f), glm::vec3(15.0f, 00.0f, 10.0f), glm::vec3(3.0f));
gameObjects[7].GetTransform().Init(glm::vec3( 4.0f, -2.5f, -3.0f), glm::vec3(-15.0f, -15.0f, -10.0f), glm::vec3(3.0f));
unsigned int goCount = sizeof(gameObjects) / sizeof(GameObject);
이렇게 배열로 선언해주고,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
for (int i = 0; i < goCount; i++)
{
Shader& currentShader = gameObjects[i].GetShader();
// 1. Materials, Textures
material.SendToShader(currentShader);
currentShader.SetTexture("wallTex", texture1);
// 2. Matrices
currentShader.SetMat4fv("ViewMatrix", viewMatrix);
currentShader.SetMat4fv("ProjectionMatrix", projectionMatrix);
// 3. Lights
mainLight.SendToShader(currentShader, "mainLight");
for (int j = 0; j < pointLightCount; j++)
{
pointLights[j].SendToShader(currentShader, "pointLights[" + std::to_string(j) + "]");
}
currentShader.SetInt("pointLightCount", pointLightCount);
// 4. Cam Pos
currentShader.SetVec3f("cameraPos", camPos);
}
각각의 게임오브젝트를 순회하며 필요한 쉐이더 유니폼 변수들을 전달한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
// main.cpp
while (!glfwWindowShouldClose(window))
{
// =========================== Init ============================ //
GLCheck(
// Update Input
glfwPollEvents();
UpdateInputs(window);
// Clear
glClearColor(0.f, 0.f, 0.f, 1.f);
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT | GL_STENCIL_BUFFER_BIT);
// Variables
double time = glfwGetTime();
);
// ========================= Track Frame Size Change ============ //
GLCheck(
glfwGetFramebufferSize(window, &framebufferWidth, &framebufferHeight);
projectionMatrix = glm::perspective
(
glm::radians(fov),
static_cast<float>(framebufferWidth) / framebufferHeight,
nearPlane,
farPlane
);
)
// ========================= Update Transform =================== //
GLCheck(
UpdateTransformByInputs(window, gameObjects[0].GetTransform(), 0.04f, 5.0f, 0.04f);
for (int i = 0; i < goCount; i++)
{
GameObject& currentGO = gameObjects[i];
Shader& currentShader = currentGO.GetShader();
currentShader.SetMat4fv("ProjectionMatrix", projectionMatrix);
currentShader.SetMat4fv("ModelMatrix", gameObjects[i].GetTransform().GetModelMatrix());
// 회전만 적용되는 노멀 변환용 행렬
glm::mat4 modelMatrixForNormal(1.0f);
glm::vec3 rotation = currentGO.GetTransform().GetRotation();
modelMatrixForNormal = glm::rotate(modelMatrixForNormal, glm::radians(rotation.x), glm::vec3(1.f, 0.f, 0.f));
modelMatrixForNormal = glm::rotate(modelMatrixForNormal, glm::radians(rotation.y), glm::vec3(0.f, 1.f, 0.f));
modelMatrixForNormal = glm::rotate(modelMatrixForNormal, glm::radians(rotation.z), glm::vec3(0.f, 0.f, 1.f));
currentShader.SetMat4fv("ModelMatrixForNormal", modelMatrixForNormal);
}
);
// ========================= Update Uniforms ==================== //
// ========================== Draw ============================== //
GLCheck(
// Activate, Bind Textures
texture0.Bind();
texture1.Bind();
for (int i = 0; i < goCount; i++)
{
gameObjects[i].Render();
}
);
// ========================== End ============================== //
// End Draw
GLCheck(glfwSwapBuffers(window););
GLCheck(glFlush(););
// Reset bindings
GLCheck(glBindVertexArray(0););
GLCheck(glUseProgram(0););
GLCheck(glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0););
//GLCheck(glActiveTexture(0);) // error
}
그리고 이렇게 루프에서도 반복문으로 순회하며 렌더링을 해주면
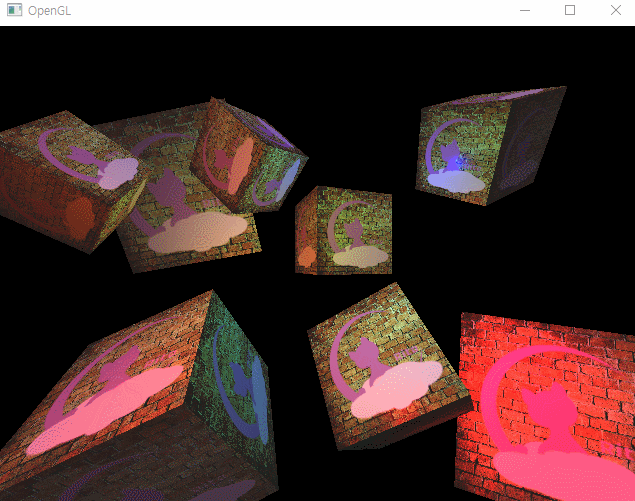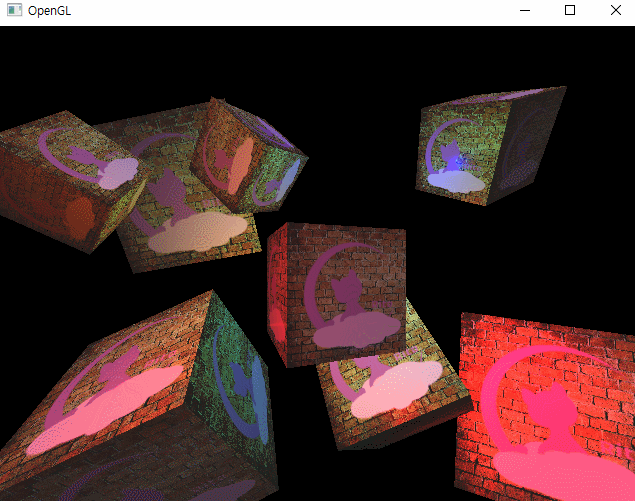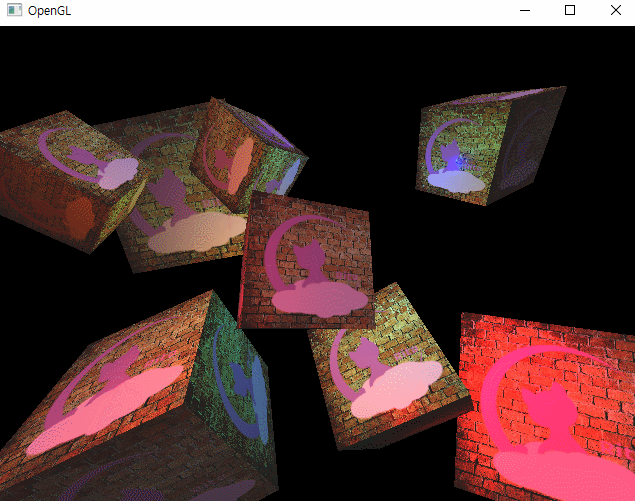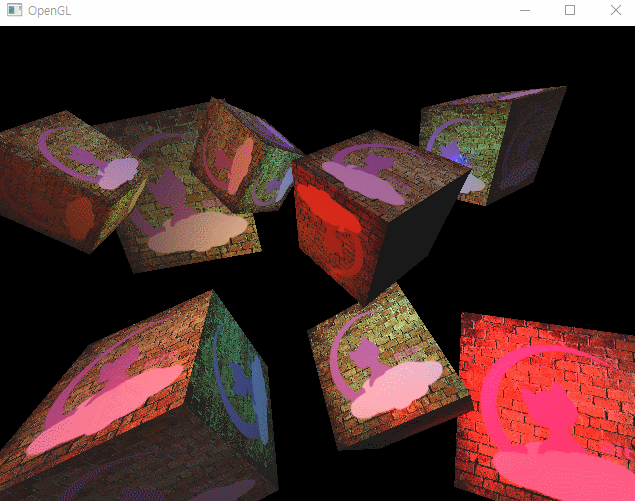
이런 모습을 확인할 수 있다.
아쉬운 점은 동일한 쉐이더를 지저분하게 여러 번 선언하고 있다는 것.
그리고 쉐이더 객체는 메시처럼 공통 참조하는 것이 아니라 각각의 게임오브젝트가 하나의 쉐이더를 소유하고 있어야 한다.
각각 쉐이더마다 서로 다른 변환 매트릭스를 받아서, 그걸 기반으로 렌더링하기 때문이다.
그래서 다음에는 쉐이더 복사본을 만들어서 각각 게임오브젝트에서 유니크하게 갖도록 할 예정.