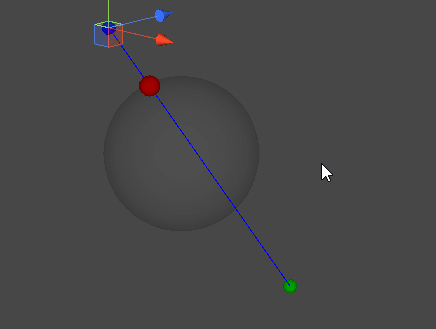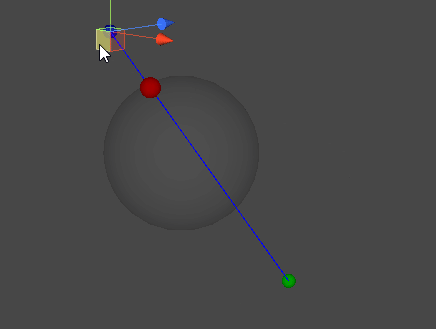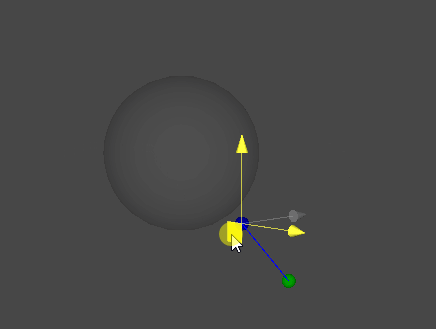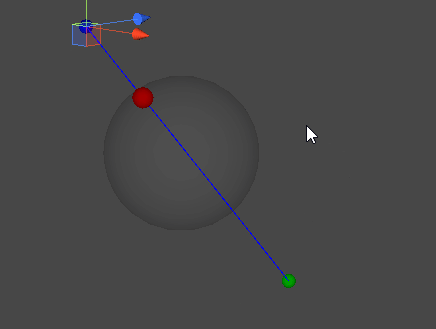
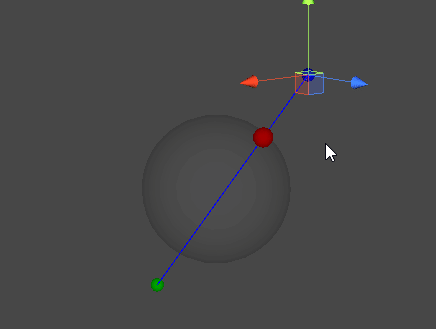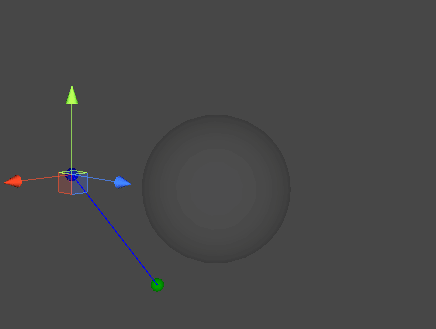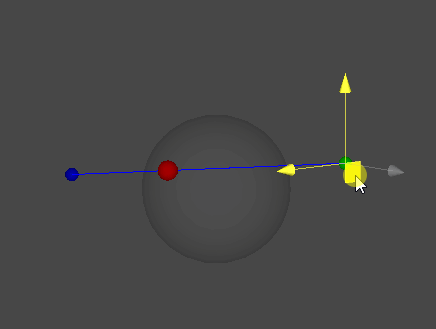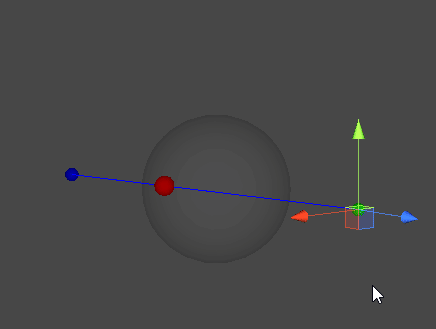
레이캐스트(Raycast)
- 공간 상의 한 점에서부터 목표 지점까지 가상의 광선을 발사하여, 광선에 닿는 물체의 표면을 검출한다.
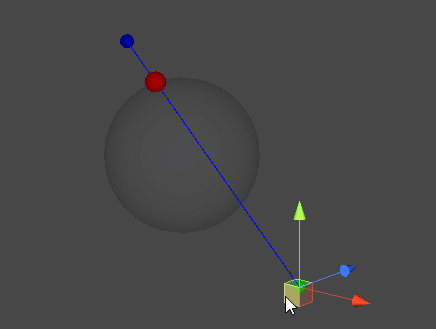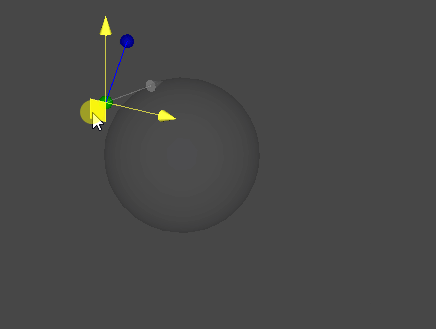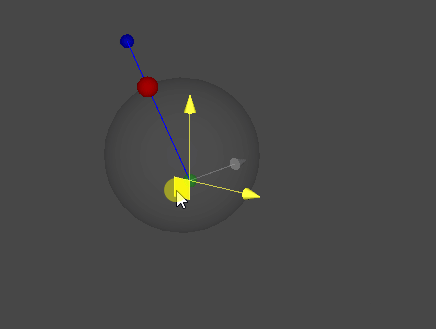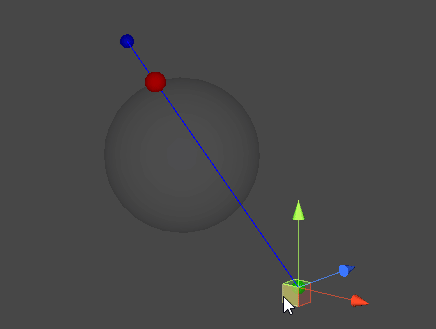
직선과 구체 표면의 접점 찾기
- 시작 지점에서부터 목표 지점으로 광선을 발사하여, 두 점이 이루는 직선과 교차하는 구체의 표면 지점을 찾아낸다.
- 3차원에서 수행하면 구체, 2차원에서 수행하면 원(Circle)의 표면을 검출할 수 있다.
- 직선과 구체가 생성하는 접점은 두 개가 존재할 수 있지만, 레이캐스트의 특성 상 시작 지점에 더 가까운 접점을 찾아내는 것이 목표이다.
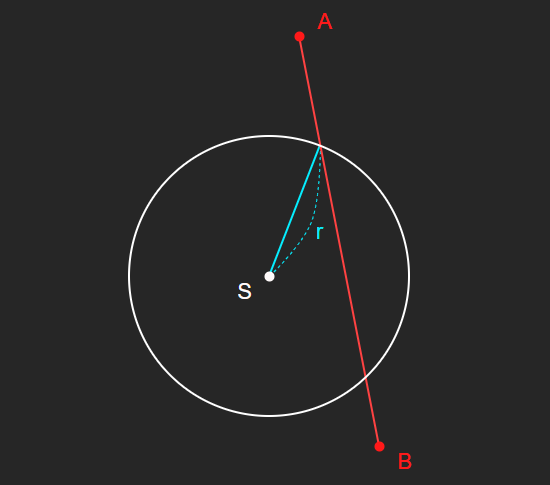
먼저, 주어진 조건은 다음과 같다.
- A : 레이캐스트 시작 위치
- B : 레이캐스트 종료 위치
- S : 구체 중심 위치
- r : 구체 반지름 길이
다음과 같은 공간상의 지점 C, D를 가정할 수 있다.
- C : 점 S에서 직선 AB에 내린 수선의 발
- D : 직선 AB와 구체가 맞닿는 점들 중 A에 가까운 지점(최종 목표)
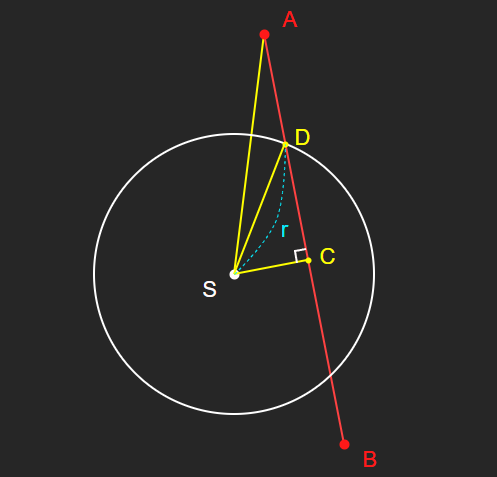
내적을 이용해 선분 AC의 길이를 구할 수 있다.
선분 AS, AC의 길이를 모두 알고 있으므로,
피타고라스의 정리를 이용하여 선분 CS의 길이의 제곱 값을 구할 수 있다.
선분 DS의 길이는 반지름 r이며, 이와 위에서 구한 |CS|를 이용해 선분 CD의 길이를 구할 수 있다.
그리고 이제 선분 AD의 길이는 아주 간단히 구할 수 있다.
마지막으로, 지금까지 알아낸 조건들을 이용해 점 D의 위치를 계산할 수 있다.
구현 예시(Unity)
Raycast Method
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
private Vector3? RaycastToSphere(Vector3 origin, Vector3 end, Vector3 sphereCenter, float sphereRadius)
{
ref Vector3 A = ref origin;
ref Vector3 B = ref end;
ref Vector3 S = ref sphereCenter;
Vector3 AS = S - A;
ref float r = ref sphereRadius;
float r2 = r * r;
float as2 = AS.sqrMagnitude;
// A가 구체 내부에 위치한 경우
if (as2 < r2) return null;
float ab = (B - A).magnitude;
float as_ = Mathf.Sqrt(as2);
// 레이가 구체 표면까지의 최단거리보다도 짧은 경우
if (ab < as_ - r) return null;
Vector3 nAB = (B - A).normalized;
float ac = Vector3.Dot(AS, nAB);
// 레이의 진행 방향이 구체의 위치와 반대인 경우
if (ac < 0) return null;
float ac2 = ac * ac;
float sc2 = as2 - ac2;
// 교차점이 없는 경우
if (sc2 > r2) return null;
float cd = Mathf.Sqrt(r2 - sc2);
float ad = ac - cd;
// 레이의 도착점이 구체 표면보다 레이 시작점에 가까울 경우
if (ab < ad) return null;
Vector3 D = A + nAB * ad;
return D;
}
Simplified Method
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
private Vector3 RaycastToSphere_Simple(Vector3 origin, Vector3 end, Vector3 sphereCenter, float sphereRadius)
{
ref Vector3 A = ref origin;
ref Vector3 B = ref end;
ref Vector3 S = ref sphereCenter;
ref float r = ref sphereRadius;
Vector3 AS = S - A;
Vector3 nAB = (B - A).normalized;
float r2 = r * r;
float as2 = AS.sqrMagnitude;
float ac = Vector3.Dot(AS, nAB);
float ac2 = ac * ac;
float sc2 = as2 - ac2;
float cd = Mathf.Sqrt(r2 - sc2);
float ad = ac - cd;
Vector3 D = A + nAB * ad;
return D;
}
Gizmo Example
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
// MonoBehaviour Script
public Transform rayBegin;
public Transform rayEnd;
public Transform sphereCenter;
public float sphereRadius = 3f;
[Space]
public Mesh sphereMesh;
private void OnDrawGizmos()
{
if (!rayBegin || !rayEnd || !sphereCenter || !sphereMesh) return;
Gizmos.color = Color.blue;
Gizmos.DrawSphere(rayBegin.position, 0.2f);
Gizmos.color = Color.green;
Gizmos.DrawSphere(rayEnd.position, 0.2f);
Gizmos.color = Color.white * 0.5f;
Gizmos.DrawMesh(sphereMesh, 0, sphereCenter.position, Quaternion.identity, Vector3.one * sphereRadius * 2);
Gizmos.color = Color.blue;
Gizmos.DrawLine(rayBegin.position, rayEnd.position);
Vector3? interPoint = RaycastToSphere(rayBegin.position, rayEnd.position, sphereCenter.position, sphereRadius);
if (interPoint != null)
{
Gizmos.color = Color.red;
Gizmos.DrawSphere(interPoint.Value, 0.3f);
}
}