설치
- 비주얼 스튜디오 -
프로젝트-NuGet 패키지 관리-Benchmark를 검색하여 설치
사용법
[1] 테스트 대상 클래스
…
[1-1] 네임스페이스
.
1
2
using BenchmarkDotNet;
using BenchmarkDotNet.Attributes;
[1-2] 클래스 애트리뷰트
.
[SimpleJob()]- https://benchmarkdotnet.org/articles/guides/choosing-run-strategy.html
- 실행 옵션을 간단히 지정할 수 있다.
launchCount: 벤치마크 전체 반복 횟수(기본값 :1)warmupCount: 실제 벤치마크 수행 전, 가상 벤치마크 횟수(기본값 :10~15내외)targetCount: 벤치마크 내에서 워크로드의 반복 실행 횟수(기본값 :15)invocationCount: 한 번의 워크로드 내에서 메소드 반복 실행 횟수(너무 작을 경우 신뢰도가 떨어지므로, 천만 단위 이상으로 높이는 것을 권장)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
[SimpleJob(
launchCount: 3,
warmupCount: 4,
targetCount: 5,
invocationCount: 6
)]
public class MyBenchmark
{
//...
}
[1-3] 필드, 프로퍼티 애트리뷰트
.
[Params()]- https://benchmarkdotnet.org/articles/features/parameterization.html
- 테스트 진행마다 해당 필드 또는 프로퍼티에 지정된 값을 차례로 넣어 테스트한다.
- 대상 필드 또는 프로퍼티는
public이어야 한다.
1
2
3
4
5
[Params(10)]
public int a;
[Params(100, 200)]
public int B { get; set;}
[1-4] 메소드 애트리뷰트
.
[Benchmark]- https://benchmarkdotnet.org/articles/features/baselines.html
- 테스트를 진행할 메소드를 지정한다.
[Benchmark(Baseline = true)]로 지정할 경우, 모든 테스트 메소드의 소요 시간 비율을 계산하며, 이 메소드는 기준 값인1.00을 갖는다.
[BenchmarkCategory("~~")]- https://benchmarkdotnet.org/articles/features/baselines.html#sample-introcategorybaseline
- 카테고리를 통해 테스트 메소드를 구분하여 실행할 수 있다.
- 클래스에
[GroupBenchmarksBy(BenchmarkLogicalGroupRule.ByCategory)]를 지정해야 한다. - 클래스에
[CategoriesColumn]를 지정하면 벤치마크 결과 컬럼에 카테고리가 표시된다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
[GroupBenchmarksBy(BenchmarkLogicalGroupRule.ByCategory)]
[CategoriesColumn]
public class IntroCategoryBaseline
{
[BenchmarkCategory("Fast"), Benchmark(Baseline = true)]
public void Time50() => Thread.Sleep(50);
[BenchmarkCategory("Fast"), Benchmark]
public void Time100() => Thread.Sleep(100);
[BenchmarkCategory("Slow"), Benchmark(Baseline = true)]
public void Time550() => Thread.Sleep(550);
[BenchmarkCategory("Slow"), Benchmark]
public void Time600() => Thread.Sleep(600);
}
[Arguments()]- https://benchmarkdotnet.org/articles/features/parameterization.html
- 매개변수가 존재하는 메소드일 경우, 매개변수에 맞추어 값을 넣어줄 수 있다.
- 테스트 진행마다 차례로 인자를 넣어 테스트한다.
1
2
3
[Arguments(1, 2)]
[Arguments(10, 20)]
public int AddTest(int a, int b) => (a + b);
[ArgumentSource(nameof(...))]- https://benchmarkdotnet.org/articles/features/parameterization.html#sample-introargumentssource
IEnumerable<object>를 리턴하는 메소드를 통해 인자 목록을 작성할 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
// 1. 매개변수 1개인 경우
[Benchmark]
[ArgumentsSource(nameof(TimeSpans))]
public void SingleArgument(TimeSpan time) => Thread.Sleep(time);
public IEnumerable<object> TimeSpans()
{
yield return TimeSpan.FromMilliseconds(10);
yield return TimeSpan.FromMilliseconds(100);
}
// 2. 매개변수가 2개인 경우
[Benchmark]
[ArgumentsSource(nameof(Numbers))]
public double ManyArguments(double x, double y) => Math.Pow(x, y);
public IEnumerable<object[]> Numbers()
{
yield return new object[] { 1.0, 1.0 };
yield return new object[] { 2.0, 2.0 };
yield return new object[] { 4.0, 4.0 };
yield return new object[] { 10.0, 10.0 };
}
-
https://benchmarkdotnet.org/articles/features/setup-and-cleanup.html
[GlobalSetup]- 각
Launch시작 전에 한 번씩 실행된다.
- 각
[GlobalCleanup]- 각
Launch종료 후에 한 번씩 실행된다.
- 각
[IterationSetup]- 각
Benchmark시작 전에 한 번씩 실행된다.
- 각
[IterationCleanup]- 각
Benchmark종료 후에 한 번씩 실행된다.
- 각
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
public class IntroSetupCleanupIteration
{
private int setupCounter;
private int cleanupCounter;
[IterationSetup]
public void IterationSetup()
=> Console.WriteLine($"// IterationSetup ({++setupCounter})");
[IterationCleanup]
public void IterationCleanup()
=> Console.WriteLine($"// IterationCleanup ({++cleanupCounter})");
[GlobalSetup]
public void GlobalSetup()
=> Console.WriteLine("// " + "GlobalSetup");
[GlobalCleanup]
public void GlobalCleanup()
=> Console.WriteLine("// " + "GlobalCleanup");
[Benchmark]
public void Benchmark()
=> Console.WriteLine("// " + "Benchmark");
}
[2] 테스트 대상 메소드
…
-
테스트 메소드는 public이어야 한다.
-
테스트 메소드는 동적(Non-static)이어야 한다.
-
테스트 메소드에 매개변수가 존재하는 경우, 반드시
[Arguments()]애트리뷰트를 추가하고 매개변수 개수에 맞춰 인자를 넣어줘야 한다. -
테스트 메소드는 리턴이 존재해도 된다.
-
테스트 메소드에
[Benchmark]애트리뷰트를 추가한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
[Benchmark]
public void TestMethod1()
{
// ...
}
[Benchmark]
[Arguments(10, 12.34f)]
public void TestMethod2(int a, float b)
{
// ...
}
[3] 메인 메소드
…
네임스페이스
1
using BenchmarkDotNet.Running;
소스코드
1
2
3
4
static void Main()
{
BenchmarkRunner.Run<테스트클래스타입>();
}
주의사항
…
-
Debug가 아닌Release모드에서 진행해야 한다. -
테스트 대상 클래스도
public이어야 한다.
사용 예시
[1] 테스트 코드
…
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
using System;
using BenchmarkDotNet;
using BenchmarkDotNet.Attributes;
[SimpleJob(
launchCount: 3,
warmupCount: 4,
targetCount: 5,
invocationCount:6
)]
public class ByteSerializationBenchmark
{
public byte[] array;
[Params(0, 100, 666)]
public int offset;
public ushort data;
[GlobalSetup]
public void GlobalSetup()
{
array = new byte[1024];
data = 1234;
}
[Benchmark(Baseline = true)]
public void BitConverter_GetBytes()
{
byte[] result = BitConverter.GetBytes(data);
Array.Copy(result, 0, array, offset, result.Length);
}
[Benchmark]
public void BitConverter_TryWriteBytes()
{
BitConverter.TryWriteBytes(new Span<byte>(array, offset, sizeof(ushort)), data);
}
}
[2] 메인 메소드
…
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
using System;
using BenchmarkDotNet.Running;
class CoreMainClass
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
BenchmarkRunner.Run<ByteSerializationBenchmark>();
}
}
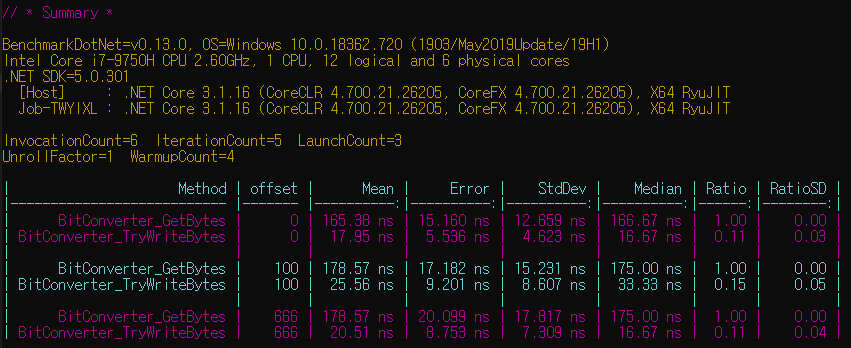
[3] 실행 결과