목표
- 수십만 ~ 백만 개의 먼지를 렌더링한다.
- 먼지들의 움직임을 물리 기반으로 직접 구현하여 시뮬레이션한다.
- 진공 청소기로 먼지들을 예쁘게 빨아들인다.
주요 개념
Compute Buffer
- 큰 병렬 데이터를 GPU에 전달하거나 쉐이더끼리 공유하기 위해 사용한다.
- Vert/Frag, Compute Shader에서
StructuredBuffer<T>타입 변수로 사용할 수 있다.
Graphics.DrawMeshInstancedIndirect()
- 컴퓨트 버퍼의 메시 데이터를 GPU Instancing을 적용하여 대규모로 렌더링할 수 있다.
Compute Shader
- GPGPU를 통해 병렬적으로 연산을 적용할 수 있다.
1. 10만개의 먼지 만들기
…
GPU 인스턴싱을 통해 십만 단위의 오브젝트를 동시에 렌더링한다.
렌더링될 메시의 버텍스 개수에 따라 성능 차이가 커지므로,
일단 메시는 단순한 큐브 메시를 사용한다.
Dustmanager.cs
- 먼지 생성 및 관리를 담당한다.
Fields
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
private const int TRUE = 1;
private const int FALSE = 0;
private struct Dust
{
public Vector3 position;
public int isAlive;
}
[Header("Dust Options")]
[SerializeField] private Mesh DustMesh; // 먼지 메시
[SerializeField] private Material DustMaterial; // 먼지 마테리얼
[Space]
[SerializeField] private int instanceNumber = 100000; // 생성할 먼지 개수
[SerializeField] private float distributionRange = 100f; // 먼지 분포 범위(정사각형 너비)
[Range(0.01f, 2f)]
[SerializeField] private float DustScale = 1f; // 먼지 크기
private ComputeBuffer dustBuffer; // 먼지 데이터 버퍼(위치, ...)
private ComputeBuffer argsBuffer; // 먼지 렌더링 데이터 버퍼
private Bounds frustumOverlapBounds;
private Dust[] DustArray;
Unity Event Methods
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
private void Start()
{
InitBuffers();
}
private void Update()
{
DustMaterial.SetFloat("_Scale", DustScale);
Graphics.DrawMeshInstancedIndirect(DustMesh, 0, DustMaterial, bounds, argsBuffer);
}
private void OnDestroy()
{
dustBuffer.Release();
argsBuffer.Release();
}
private GUIStyle boxStyle;
private void OnGUI()
{
if (boxStyle == null)
{
boxStyle = new GUIStyle(GUI.skin.box);
boxStyle.fontSize = 48;
}
float scWidth = Screen.width;
float scHeight = Screen.height;
Rect r = new Rect(scWidth * 0.04f, scHeight * 0.04f, scWidth * 0.25f, scHeight * 0.05f);
GUI.Box(r, $"{aliveNumber:#,###,##0} / {instanceNumber:#,###,##0}", boxStyle);
}
Methods
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
/// <summary> 컴퓨트 버퍼들 생성 </summary>
private void InitBuffers()
{
// Args Buffer
// IndirectArguments로 사용되는 컴퓨트 버퍼의 stride는 20byte 이상이어야 한다.
// 따라서 파라미터가 앞의 2개만 필요하지만, 뒤에 의미 없는 파라미터 3개를 더 넣어준다.
uint[] argsData = new uint[] { (uint)DustMesh.GetIndexCount(0), (uint)instanceNumber, 0, 0, 0 };
aliveNumber = instanceNumber;
argsBuffer = new ComputeBuffer(1, 5 * sizeof(uint), ComputeBufferType.IndirectArguments);
argsBuffer.SetData(argsData);
PopulateDusts();
// Dust Buffer
dustBuffer = new ComputeBuffer(instanceNumber, sizeof(float) * 3 + sizeof(int));
dustBuffer.SetData(DustArray);
DustMaterial.SetBuffer("_DustBuffer", dustBuffer);
// 카메라 프러스텀이 이 영역과 겹치지 않으면 렌더링되지 않는다.
frustumOverlapBounds = new Bounds(Vector3.zero, new Vector3(distributionRange, 1f, distributionRange));
}
/// <summary> 먼지들을 영역 내의 무작위 위치에 생성한다. </summary>
private void PopulateDusts()
{
DustArray = new Dust[instanceNumber];
float min = -0.5f * distributionRange;
float max = -min;
for (int i = 0; i < instanceNumber; i++)
{
float x = UnityEngine.Random.Range(min, max);
float z = UnityEngine.Random.Range(min, max);
DustArray[i].position = new Vector3(x, 0f, z);
DustArray[i].isAlive = TRUE;
}
}
DustShader.shader
-
먼지 렌더링을 담당한다.
-
먼지의 위치를 컴퓨트 버퍼에 저장하면, CPU가 아니라 쉐이더를 통해 GPU로 위치 변경사항을 적용한다.
…
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
Shader "Rito/Dust"
{
Properties
{
//_MainTex ("Texture", 2D) = "white" {}
_Color("Color", Color) = (0.2, 0.2, 0.2, 1)
}
SubShader
{
Tags { "RenderType"="Opaque" }
Pass
{
CGPROGRAM
#pragma vertex vert
#pragma fragment frag
#include "UnityCG.cginc"
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
struct v2f
{
float4 pos : SV_POSITION;
float3 normal : TEXCOORD0;
int isAlive : TEXCOORD1;
};
struct Dust
{
float3 position;
int isAlive;
};
uniform float _Scale;
StructuredBuffer<Dust> _DustBuffer;
v2f vert (appdata_full v, uint instanceID : SV_InstanceID)
{
v2f o;
// 먼지 생존 여부 받아와서 프래그먼트 쉐이더에 전달
o.isAlive = _DustBuffer[instanceID].isAlive;
// 먼지 크기 결정
v.vertex *= _Scale;
// 먼지 위치 결정
float3 instancePos = _DustBuffer[instanceID].position;
float3 worldPos = v.vertex + instancePos;
o.pos = mul(UNITY_MATRIX_VP, float4(worldPos, 1));
o.normal = v.normal;
return o;
}
fixed4 _Color;
fixed4 frag (v2f i) : SV_Target
{
// 죽은 먼지는 렌더링 X
if(i.isAlive == FALSE)
{
discard;
}
return _Color;
}
ENDCG
}
}
}
실행 결과
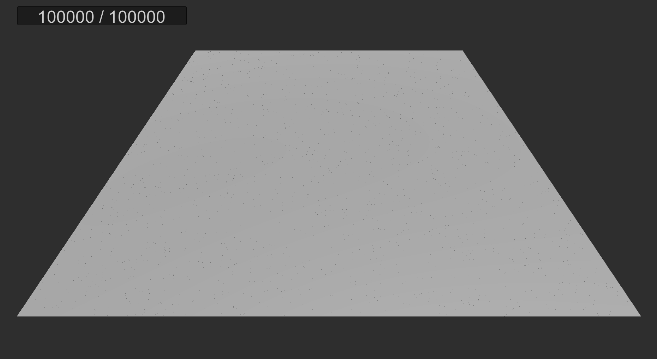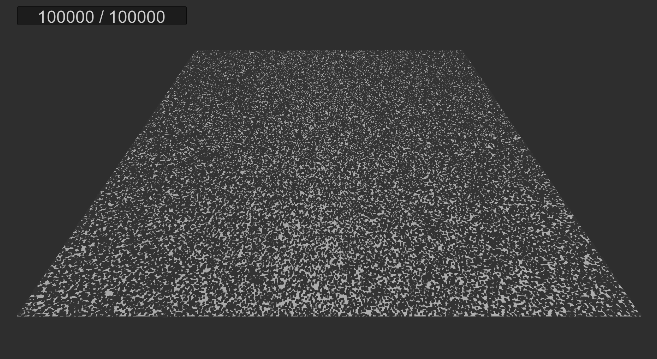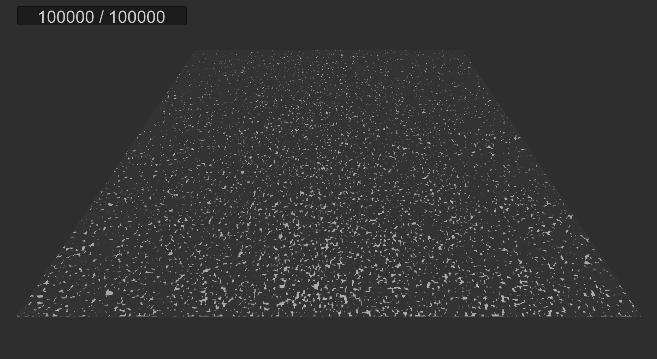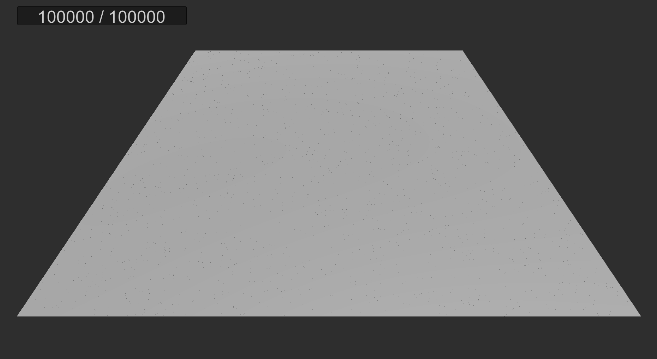
2. 먼지 빨아들이기
…
진공 청소기 입구
- 먼지를 빨아들이는 부분
VacuumCleanerHead.cs
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
[SerializeField] private bool run = true;
[Range(0f, 50f)]
[SerializeField] private float suctionForce = 1f;
[Range(1f, 20f)]
[SerializeField] private float suctionRange = 5f;
[Range(0.01f, 5f)]
[SerializeField] private float deathRange = 0.2f;
public bool Running => run;
public float SqrSuctionRange => suctionRange * suctionRange;
public float SuctionForce => suctionForce;
public float DeathRange => deathRange;
public Vector3 Position => transform.position;
private void OnDrawGizmosSelected()
{
Gizmos.color = Color.cyan;
Gizmos.DrawWireSphere(Position, suctionRange);
Gizmos.color = Color.red;
Gizmos.DrawWireSphere(Position, deathRange);
}
[1] CPU 단일 스레드 계산
- 반복문을 통한 단순 계산을 통해 먼지들의 위치를 업데이트한다.
- 성능이 매우 매우 좋지 않다.
Dustmanager.cs
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
private void Update()
{
UpdateDustPositions();
DustMaterial.SetFloat("_Scale", DustScale);
Graphics.DrawMeshInstancedIndirect(DustMesh, 0, DustMaterial, frustumOverlapBounds, argsBuffer);
}
private void UpdateDustPositions()
{
if (cleanerHead.Running == false) return;
Vector3 headPos = cleanerHead.Position;
float sqrRange = cleanerHead.SqrSuctionRange;
float sqrDeathRange = cleanerHead.DeathRange * cleanerHead.DeathRange;
float force = Time.deltaTime * cleanerHead.SuctionForce;
for (int i = 0; i < instanceNumber; i++)
{
if (DustArray[i].isAlive == FALSE) continue;
// root 연산은 비싸기 때문에 제곱 상태로 거리 비교
float sqrDist = Vector3.SqrMagnitude(DustArray[i].position - headPos);
// 사망 범위
if (sqrDist < sqrDeathRange)
{
DustArray[i].isAlive = FALSE;
aliveNumber--;
}
// 흡입 범위
else if (sqrDist < sqrRange)
{
DustArray[i].position = Vector3.Lerp(DustArray[i].position, headPos, force);
}
}
dustBuffer.SetData(DustArray);
}

[2] CPU 병렬 계산
-
Parallel을 통한 멀티스레딩으로 CPU 연산을 적용한다. -
그리고 먼지가 단순히
Vector3.Lerp()를 통해 이동하는 대신, 거리가 가까울수록 빠르게 이동하도록 계산 방식을 변경한다.
Dustmanager.cs
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
private void UpdateDustPositions()
{
if (cleanerHead.Running == false) return;
Vector3 headPos = cleanerHead.Position;
float sqrRange = cleanerHead.SqrSuctionRange;
float sqrDeathRange = cleanerHead.DeathRange * cleanerHead.DeathRange;
float sqrForce = Time.deltaTime * cleanerHead.SuctionForce * cleanerHead.SuctionForce;
// 병렬 처리(동기)
Parallel.For(0, instanceNumber, i =>
{
if (DustArray[i].isAlive == FALSE) return;
float sqrDist = Vector3.SqrMagnitude(headPos - DustArray[i].position);
// 사망 범위
if (sqrDist < sqrDeathRange)
{
DustArray[i].isAlive = FALSE;
Interlocked.Decrement(ref aliveNumber);
}
// 흡입 범위
else if (sqrDist < sqrRange)
{
Vector3 dir = (headPos - DustArray[i].position).normalized;
float weightedForce = sqrForce / sqrDist;
DustArray[i].position += dir * weightedForce;
}
});
dustBuffer.SetData(DustArray);
}

[3] 컴퓨트 쉐이더 병렬 연산
- 먼지 이동 연산을 컴퓨트 쉐이더로 넘겨서 처리한다.
- 컴퓨트 쉐이더의 연산 결과를 다시 CPU로 가져오는 작업이 없고, 대신 컴퓨트 버퍼를 Vert/Frag 쉐이더에서 바로 참조하여 적용하므로 매우 빠르다.
DustCompute.compute
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
#pragma kernel CSMain
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
struct Dust
{
float3 position;
int isAlive;
};
RWStructuredBuffer<Dust> dustBuffer;
RWStructuredBuffer<uint> aliveNumberBuffer; // 생존한 먼지 개수
float3 headPos;
float sqrRange;
float sqrDeathRange;
float sqrForce;
[numthreads(64,1,1)]
void CSMain (uint3 id : SV_DispatchThreadID)
{
uint i = id.x;
if(DustBuffer[i].isAlive == FALSE) return;
// 제곱 상태로 연산
float3 offs = (headPos - dustBuffer[i].position);
float sqrDist = (offs.x * offs.x) + (offs.y * offs.y) + (offs.z * offs.z);
// 사망 범위
if (sqrDist < sqrDeathRange)
{
dustBuffer[i].isAlive = FALSE;
InterlockedAdd(aliveNumberBuffer[0], -1);
}
// 흡입 범위
else if (sqrDist < sqrRange)
{
float3 dir = normalize(headPos - dustBuffer[i].position);
float weightedForce = sqrForce / sqrDist;
dustBuffer[i].position += dir * weightedForce;
}
}
Dustmanager.cs
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
/* 기타 필드 생략 */
[SerializeField] private ComputeShader DustCompute;
private ComputeBuffer dustBuffer; // 먼지 데이터 버퍼(위치, ...)
private ComputeBuffer argsBuffer; // 먼지 렌더링 데이터 버퍼
private ComputeBuffer aliveNumberBuffer; // 생존 먼지 개수 RW
private Bounds frustumOverlapBounds;
private Dust[] DustArray;
private uint[] aliveNumberArray;
private int aliveNumber;
int kernelGroupSizeX;
private void Start()
{
InitBuffers();
InitComputeShader();
}
private void Update()
{
UpdateDustPositionsGPU();
DustMaterial.SetFloat("_Scale", DustScale);
Graphics.DrawMeshInstancedIndirect(DustMesh, 0, DustMaterial, frustumOverlapBounds, argsBuffer);
}
private void OnDestroy()
{
dustBuffer.Release();
argsBuffer.Release();
aliveNumberBuffer.Release();
}
/// <summary> 컴퓨트 버퍼들 생성 </summary>
private void InitBuffers()
{
// Args Buffer
// IndirectArguments로 사용되는 컴퓨트 버퍼의 stride는 20byte 이상이어야 한다.
// 따라서 파라미터가 앞의 2개만 필요하지만, 뒤에 의미 없는 파라미터 3개를 더 넣어준다.
uint[] argsData = new uint[] { (uint)DustMesh.GetIndexCount(0), (uint)instanceNumber, 0, 0, 0 };
aliveNumber = instanceNumber;
argsBuffer = new ComputeBuffer(1, 5 * sizeof(uint), ComputeBufferType.IndirectArguments);
argsBuffer.SetData(argsData);
PopulateDusts();
// Dust Buffer
dustBuffer = new ComputeBuffer(instanceNumber, sizeof(float) * 3 + sizeof(int));
dustBuffer.SetData(DustArray);
DustMaterial.SetBuffer("_DustBuffer", dustBuffer);
// Alive Number Buffer
// 단순 입력용이 아니라 RW이므로 컴퓨트 버퍼를 사용한다.
aliveNumberBuffer = new ComputeBuffer(1, sizeof(uint));
aliveNumberArray = new uint[] { (uint)instanceNumber };
aliveNumberBuffer.SetData(aliveNumberArray);
// 카메라 프러스텀이 이 영역과 겹치지 않으면 렌더링되지 않는다.
frustumOverlapBounds = new Bounds(Vector3.zero, new Vector3(distributionRange, 1f, distributionRange));
}
/// <summary> 컴퓨트 쉐이더 초기화 </summary>
private void InitComputeShader()
{
DustCompute.SetBuffer(0, "DustBuffer", dustBuffer);
DustCompute.SetBuffer(0, "aliveNumberBuffer", aliveNumberBuffer);
DustCompute.GetKernelThreadGroupSizes(0, out uint tx, out _, out _);
kernelGroupSizeX = Mathf.CeilToInt((float)instanceNumber / tx);
}
private void UpdateDustPositionsGPU()
{
if (cleanerHead.Running == false) return;
Vector3 headPos = cleanerHead.Position;
float sqrRange = cleanerHead.SqrSuctionRange;
float sqrDeathRange = cleanerHead.DeathRange * cleanerHead.DeathRange;
float sqrForce = Time.deltaTime * cleanerHead.SuctionForce * cleanerHead.SuctionForce;
DustCompute.SetVector("headPos", headPos);
DustCompute.SetFloat("sqrRange", sqrRange);
DustCompute.SetFloat("sqrDeathRange", sqrDeathRange);
DustCompute.SetFloat("sqrForce", sqrForce);
DustCompute.Dispatch(0, kernelGroupSizeX, 1, 1);
aliveNumberBuffer.GetData(aliveNumberArray);
aliveNumber = (int)aliveNumberArray[0];
}

3. 먼지 생성 최적화
…
난수를 발생시켜 먼지를 무작위 위치에 생성하던 부분을 CPU가 아니라 컴퓨트 쉐이더 내에서 연산하도록 한다.
그리고 평면이 아닌, 공간에서 큐브 형태로 분포할 수 있도록 변경한다.
[1] 컴퓨트 쉐이더
- 기존 커널의 이름을
Update로 변경하고, 새로운 커널 함수Populate를 작성한다.
DustCompute.compute
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
#pragma kernel Populate
#pragma kernel Update
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
struct Dust
{
float3 position;
int isAlive;
};
/*************************************************
/* Methods
/*************************************************/
float Random(float2 seed)
{
return frac(sin(dot(seed, float2(73.867, 25.241))) * 39482.17593);
}
float RandomRange(float2 seed, float min, float max)
{
return lerp(min, max, Random(seed));
}
float3 RandomRange3(float2 seed, float3 min, float3 max)
{
float3 vec;
vec.x = RandomRange(seed, min.x, max.x);
vec.y = RandomRange(seed + 7.219, min.y, max.y);
vec.z = RandomRange(seed + 79.714, min.z, max.z);
return vec;
}
/*************************************************
/* Variables
/*************************************************/
RWStructuredBuffer<Dust> dustBuffer;
RWStructuredBuffer<uint> aliveNumberBuffer; // 생존한 먼지 개수
float3 boundsMin; // 먼지 생성 영역 - 최소 지점
float3 boundsMax; // 먼지 생성 영역 - 최대 지점
float3 headPos;
float sqrRange;
float sqrDeathRange;
float sqrForce;
/*************************************************
/* Kernels
/*************************************************/
// 0 - 초기 생성
[numthreads(64,1,1)]
void Populate (uint3 id : SV_DispatchThreadID)
{
uint i = id.x;
float width = boundsMax.x - boundsMin.x;
float f = float(i);
float2 uv = float2(f % width, f / width) / width;
dustBuffer[i].position = RandomRange3(uv, boundsMin, boundsMax);
dustBuffer[i].isAlive = TRUE;
}
// 1 - 실시간 업데이트
[numthreads(64,1,1)]
void Update (uint3 id : SV_DispatchThreadID)
{
uint i = id.x;
if(DustBuffer[i].isAlive == FALSE) return;
float3 offs = (headPos - dustBuffer[i].position);
float sqrDist = (offs.x * offs.x) + (offs.y * offs.y) + (offs.z * offs.z);
if (sqrDist < sqrDeathRange)
{
dustBuffer[i].isAlive = FALSE;
InterlockedAdd(aliveNumberBuffer[0], -1);
}
else if (sqrDist < sqrRange)
{
float3 dir = normalize(headPos - dustBuffer[i].position);
float weightedForce = sqrForce / sqrDist;
dustBuffer[i].position += dir * weightedForce;
}
}
[2] 먼지 관리 컴포넌트
- 커널 함수들의 인덱스를 필드로 저장한다.
- 먼지들에 대한 CPU 작업은 더이상 필요하지 않으므로,
DustArray필드는 제거하고 모두DustBuffer를 통해 GPU에서 작업한다.
DustManager.cs
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
[SerializeField] private float distributionHeight = 5f; // 먼지 분포 높이
private int kernelPopulateID;
private int kernelUpdateID;
private int kernelGroupSizeX;
private void Start()
{
InitBuffers();
InitComputeShader();
PopulateDusts();
}
private void Update()
{
UpdateDustPositionsGPU();
DustMaterial.SetFloat("_Scale", DustScale);
Graphics.DrawMeshInstancedIndirect(DustMesh, 0, DustMaterial, frustumOverlapBounds, argsBuffer);
}
/// <summary> 컴퓨트 버퍼들 생성 </summary>
private void InitBuffers()
{
uint[] argsData = new uint[] { (uint)DustMesh.GetIndexCount(0), (uint)instanceNumber, 0, 0, 0 };
aliveNumber = instanceNumber;
argsBuffer = new ComputeBuffer(1, 5 * sizeof(uint), ComputeBufferType.IndirectArguments);
argsBuffer.SetData(argsData);
// Dust Buffer => DustArray는 완전히 제거
dustBuffer = new ComputeBuffer(instanceNumber, sizeof(float) * 3 + sizeof(int));
DustMaterial.SetBuffer("_DustBuffer", dustBuffer);
aliveNumberBuffer = new ComputeBuffer(1, sizeof(uint));
aliveNumberArray = new uint[] { (uint)instanceNumber };
aliveNumberBuffer.SetData(aliveNumberArray);
frustumOverlapBounds = new Bounds(Vector3.zero, new Vector3(distributionRange, 1f, distributionRange));
}
/// <summary> 컴퓨트 쉐이더 초기화 </summary>
private void InitComputeShader()
{
// 커널 인덱스 찾아 가져오기
kernelPopulateID = DustCompute.FindKernel("Populate");
kernelUpdateID = DustCompute.FindKernel("Update");
// 버퍼는 커널마다 각각 할당해주어야 한다.
DustCompute.SetBuffer(kernelPopulateID, "DustBuffer", dustBuffer);
DustCompute.SetBuffer(kernelUpdateID, "DustBuffer", dustBuffer);
DustCompute.SetBuffer(kernelUpdateID, "aliveNumberBuffer", aliveNumberBuffer);
DustCompute.GetKernelThreadGroupSizes(kernelUpdateID, out uint tx, out _, out _);
kernelGroupSizeX = Mathf.CeilToInt((float)instanceNumber / tx);
}
/// <summary> 먼지들을 영역 내의 무작위 위치에 생성한다. </summary>
private void PopulateDusts()
{
Vector3 boundsMin, boundsMax;
boundsMin.x = boundsMin.z = -0.5f * distributionRange;
boundsMax.x = boundsMax.z = -boundsMin.x;
boundsMin.y = 0f;
boundsMax.y = distributionHeight;
DustCompute.SetVector("boundsMin", boundsMin);
DustCompute.SetVector("boundsMax", boundsMax);
DustCompute.GetKernelThreadGroupSizes(kernelPopulateID, out uint tx, out _, out _);
int groupSizeX = Mathf.CeilToInt((float)instanceNumber / tx);
DustCompute.Dispatch(kernelPopulateID, groupSizeX, 1, 1);
}
private void UpdateDustPositionsGPU()
{
// 생략
// Dispatch(0, ...) => Dispatch(kernelUpdateID, ...) 변경
DustCompute.Dispatch(kernelUpdateID, kernelGroupSizeX, 1, 1);
}
[3] 진공 청소기 컴포넌트
- 임시 이동을 구현한다.
VacuumCleanerHead.cs
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
[Range(0.01f, 100f)]
[SerializeField] private float moveSpeed = 50f;
private void Update()
{
// On/Off
if (Input.GetKeyDown(KeyCode.Space))
run ^= true;
// Move
float x = Input.GetAxisRaw("Horizontal");
float z = Input.GetAxisRaw("Vertical");
float y = 0f;
if (Input.GetKey(KeyCode.E)) y += 1f;
else if (Input.GetKey(KeyCode.Q)) y -= 1f;
Vector3 moveVec = new Vector3(x, y, z).normalized * moveSpeed;
if (Input.GetKey(KeyCode.LeftShift))
moveVec *= 2f;
transform.Translate(moveVec * Time.deltaTime, Space.World);
}
[4] 실행 결과
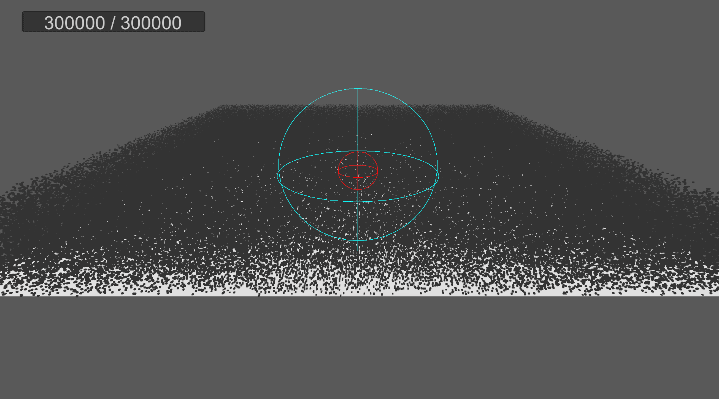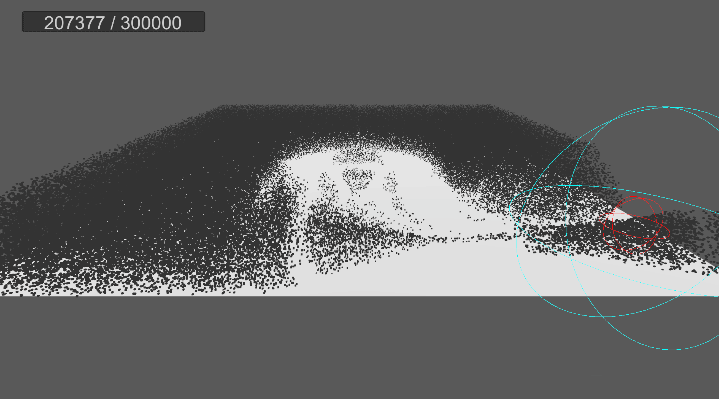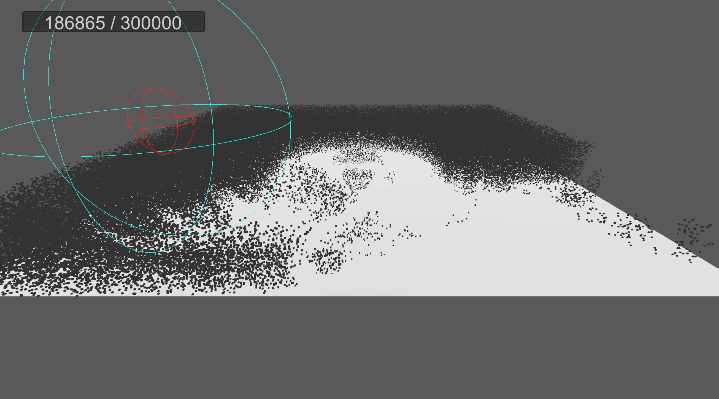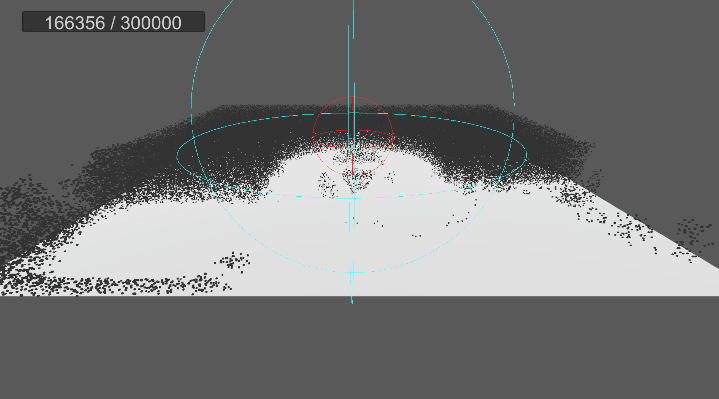
4. 원뿔 영역 흡수 구현
…
구형 범위에서 흡수하는 것은 블랙홀이나 마찬가지이므로,
방향을 지정하여 해당 방향에서 원뿔 범위로 흡수할 수 있게 변경한다.
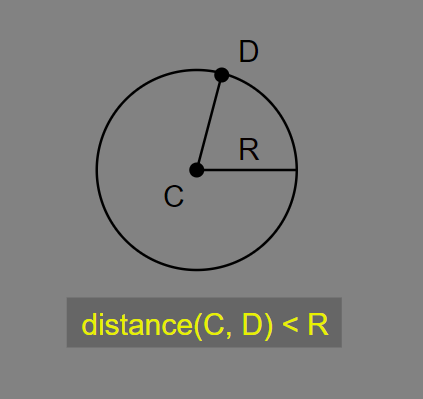
1차로 단순히 거리 계산을 통해 구형 범위로 검사하는 것은 동일하다.
R : 구형 범위
C : 청소기 입구 위치
D : 각 먼지의 위치
2차로 내적을 이용해 원뿔(밑면이 평면이 아닌 구의 일부) 범위로 검사할 수 있다.
C : 청소기 입구 위치
D : 각 먼지의 위치
E : 원뿔 밑단 외곽의 한 점
F : 원뿔 밑단 중심점
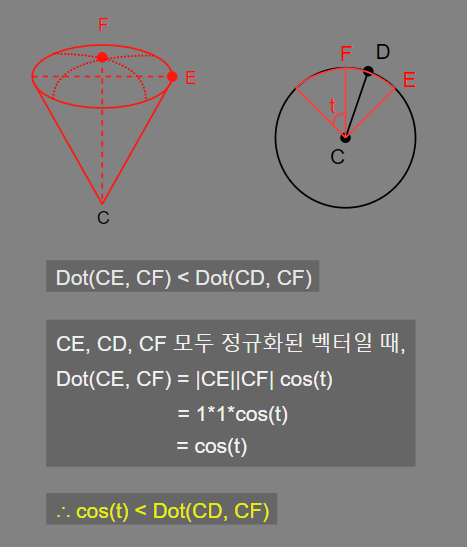
[1] 컴퓨트 쉐이더
- 내적을 이용하여 원뿔 범위 흡수를 구현한다.
DustCompute.compute
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
/* 관련 없는 코드는 생략 */
/*************************************************
/* Variables
/*************************************************/
RWStructuredBuffer<Dust> dustBuffer;
float3 headPos; // 진공 청소기 입구 위치
float sqrRange; // 먼지 흡입 범위(반지름)
float sqrDeathRange; // 먼지 소멸 범위(반지름)
float sqrForce;
float3 forward; // 진공 청소기 전방 벡터
float dotThreshold; // 진공 청소기 원뿔 영역 내적 범위
/*************************************************
/* Methods
/*************************************************/
float SqrMagnitude(float3 vec)
{
return (vec.x * vec.x) + (vec.y * vec.y) + (vec.z * vec.z);
}
// 먼지 파괴
void DestroyDust(uint i)
{
dustBuffer[i].isAlive = FALSE;
InterlockedAdd(aliveNumberBuffer[0], -1);
}
/*************************************************
/* Kernels
/*************************************************/
// 1 - 실시간 업데이트
[numthreads(64,1,1)]
void Update (uint3 id : SV_DispatchThreadID)
{
uint i = id.x;
if(DustBuffer[i].isAlive == FALSE) return;
float3 pos = dustBuffer[i].position;
float3 offs = (headPos - pos);
float sqrDist = SqrMagnitude(offs);
// 입구 주변 - 먼지 소멸
if (sqrDist < sqrDeathRange)
{
DestroyDust(i);
return;
}
// 먼지 이동
if (sqrDist < sqrRange)
{
float3 dir = normalize(offs); // 먼지 -> 청소기 입구 방향
float dotValue = dot(forward, -dir);
// 원뿔 범위 내에 있을 경우 빨아들이기
if(dotValue > dotThreshold)
{
float weightedForce = sqrForce / sqrDist;
dustBuffer[i].position += dir * weightedForce * dotValue;
// 청소기 뒤편으로 넘어가면 먼지 소멸
if(dot(headPos - dustBuffer[i].position, dir) < 0)
DestroyDust(i);
}
}
}
[2] 먼지 관리 컴포넌트
- 미리 내적 기준값을 계산하여 컴퓨트 쉐이더에 전달한다.
DustManager.cs
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
private void UpdateDustPositionsGPU()
{
// ...
ref var head = ref cleanerHead;
// 청소기 전방 벡터(+Z)
DustCompute.SetVector("forward", head.Forward);
// Dot(A, B) = |A||B|cos(t) 일 때, A와 B가 정규 벡터이면
// Dot(A, B) = cos(t) 이므로
// 원뿔 각도 t를 이용해 미리 계산한 cos(t)를 컴퓨트 쉐이더에 전달한다.
DustCompute.SetFloat("dotThreshold", Mathf.Cos(head.SuctionAngleRad));
// ...
}
[3] 진공 청소기 컴포넌트
- 숄더뷰 이동/회전을 구현한다.
- 이동과 좌우 회전은 부모 오브젝트가 담당하고, 상하 회전은 이 컴포넌트가 있는 게임오브젝트가 담당한다.
- 마우스 우클릭에 따라 마우스를 숨기고 드러낼 수 있도록 구현한다.
- 원뿔 기즈모를 그린다.
VacuumCleanerHead.cs
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
[SerializeField] private bool run = true;
[Range(0f, 100f), Tooltip("빨아들이는 힘")]
[SerializeField] private float suctionForce = 1f;
[Range(1f, 50f), Tooltip("빨아들이는 범위(거리)")]
[SerializeField] private float suctionRange = 5f;
[Range(0.01f, 90f), Tooltip("빨아들이는 원뿔 각도")]
[SerializeField] private float suctionAngle = 45f;
[Range(0.01f, 5f), Tooltip("먼지가 사망하는 영역 반지름")]
[SerializeField] private float deathRange = 0.2f;
[Range(0.01f, 100f)]
[SerializeField] private float moveSpeed = 50f;
private Transform parent;
private float deltaTime;
private bool mouseLocked = false;
public bool Running => run;
public float SqrSuctionRange => suctionRange * suctionRange;
public float SuctionForce => suctionForce;
public float DeathRange => deathRange;
public float SuctionAngleRad => suctionAngle * Mathf.Deg2Rad;
public Vector3 Position => transform.position;
public Vector3 Forward => transform.forward;
private void Awake()
{
parent = transform.parent;
}
private void OnDrawGizmos()
{
Gizmos.color = Color.blue;
DrawConeGizmo(Position, suctionRange, suctionAngle);
//Gizmos.color = Color.red;
//Gizmos.DrawWireSphere(Position, deathRange);
}
private void Update()
{
deltaTime = Time.deltaTime;
MouseControl();
if (mouseLocked)
{
Move();
Rotate();
}
}
private void MouseControl()
{
// On/Off
run = Input.GetMouseButton(0);
// 마우스 보이기/숨기기
if (Input.GetMouseButtonDown(1))
{
mouseLocked ^= true;
Cursor.lockState = mouseLocked ? CursorLockMode.Locked : CursorLockMode.None;
Cursor.visible = !mouseLocked;
}
}
private void Move()
{
float x = Input.GetAxisRaw("Horizontal");
float z = Input.GetAxisRaw("Vertical");
float y = 0f;
if (Input.GetKey(KeyCode.Space)) y += .5f;
else if (Input.GetKey(KeyCode.LeftControl)) y -= .5f;
Vector3 moveVec = new Vector3(x, y, z).normalized * moveSpeed;
if (Input.GetKey(KeyCode.LeftShift))
moveVec *= 2f;
parent.Translate(moveVec * deltaTime, Space.Self);
}
private void Rotate()
{
float v = Input.GetAxisRaw("Mouse X") * deltaTime * 100f;
float h = Input.GetAxisRaw("Mouse Y") * deltaTime * 100f;
// 부모 : 좌우 회전
parent.localRotation *= Quaternion.Euler(0, v, 0);
// 상하 회전
Vector3 eRot = transform.localEulerAngles;
float nextX = eRot.x - h;
if (0f < nextX && nextX < 90f)
{
eRot.x = nextX;
}
transform.localEulerAngles = eRot;
}
// origin : 원뿔 꼭대기
// height : 원뿔 높이
// angle : 원뿔 각도
private void DrawConeGizmo(Vector3 origin, float height, float angle, int sample = 24)
{
float deltaRad = Mathf.PI * 2f / sample;
float circleRadius = Mathf.Tan(angle * Mathf.Deg2Rad) * height;
Vector3 forward = Vector3.forward * height;
Vector3 prevPoint = default;
for (int i = 0; i <= sample; i++)
{
float delta = deltaRad * i;
Vector3 circlePoint = new Vector3(Mathf.Cos(delta), Mathf.Sin(delta), 0f) * circleRadius;
circlePoint += forward;
circlePoint = circlePoint.normalized * height;
circlePoint = transform.TransformPoint(circlePoint);
Gizmos.DrawLine(circlePoint, origin);
if (i > 0)
Gizmos.DrawLine(circlePoint, prevPoint);
prevPoint = circlePoint;
}
}
[4] 실행 결과
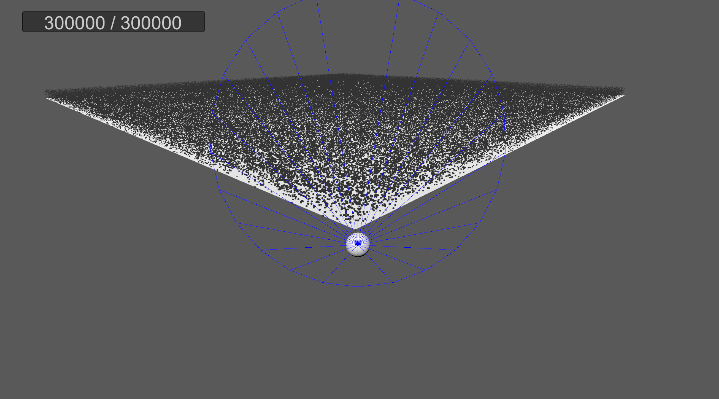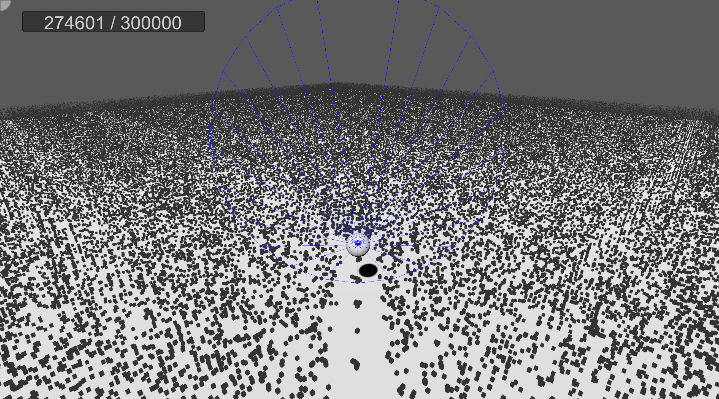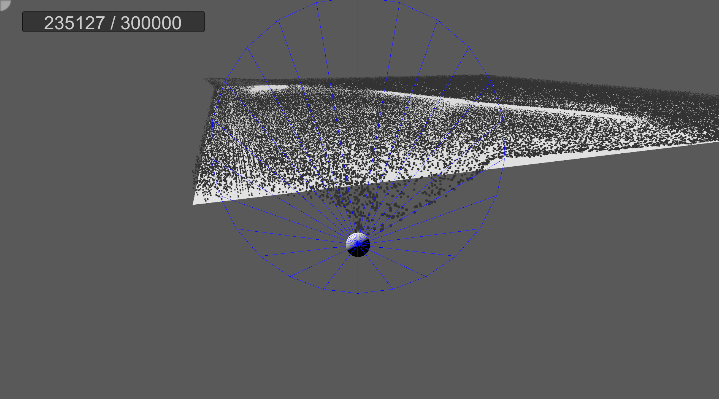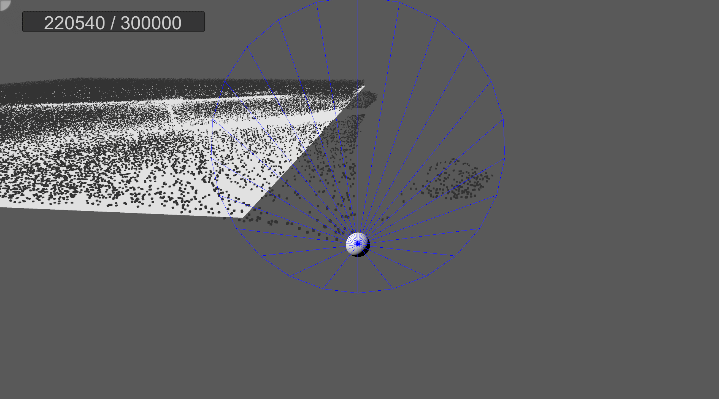
5. 물리 계산
…
먼지의 속도를 새로운 컴퓨트 버퍼에 저장한다.
기존의 Dust 구조체에 속도를 포함시키지 않고 새로운 버퍼를 만들어 저장하는 이유는
컴퓨트 쉐이더 내에서만 기록하는 용도로 사용되며, 다른 쉐이더(Vert/Frag)에서는 참조할 필요가 없기 때문이다.
기존의 계산을 속도, 가속도, 힘 기반으로 변경하고, 중력과 공기저항력을 계산한다.
그리고 현재 위치와 다음 위치 벡터를 이용해 기본적인 충돌(Plane)을 구현한다.
[1] 컴퓨트 쉐이더
velocityBuffer변수 선언- 물리 계산에 필요한 변수들 선언
- 청소기 흡수 계산을 단순 위치 변동 대신 힘 계산으로 변경
- 힘, 가속도, 속도 계산 적용
- 원뿔 영역 교차, Plane 충돌 구현
DustCompute.compute
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
RWStructuredBuffer<Dust> dustBuffer; // 먼지 위치, 생존 여부
RWStructuredBuffer<float3> velocityBuffer; // 먼지 속도
RWStructuredBuffer<uint> aliveNumberBuffer; // 생존한 먼지 개수
int isRunning; // 청소기 가동 여부
float deltaTime;
float3 boundsMin; // 먼지 생성 영역 - 최소 지점
float3 boundsMax; // 먼지 생성 영역 - 최대 지점
float3 headPos; // 진공 청소기 입구 위치
float sqrRange; // 먼지 흡입 범위(반지름) - 제곱
float sqrDeathRange; // 먼지 소멸 범위(반지름) - 제곱
float sqrForce; // 빨아들이는 힘 - 제곱
float3 headForwardDir; // 진공 청소기 전방 벡터
float dotThreshold; // 진공 청소기 원뿔 영역 내적 범위
float mass; // 질량
float gravityForce; // -Y 방향 중력 강도
float airResistance; // 공기 저항력
[numthreads(64,1,1)]
void Update (uint3 id : SV_DispatchThreadID)
{
uint i = id.x;
if(dustBuffer[i].isAlive == FALSE) return;
bool sucking = false;
float3 F = 0; // 힘 합 벡터
float3 A = 0; // 가속도 합 벡터
// ===================================================
// 청소기로 먼지 흡수
// ===================================================
float3 currPos = dustBuffer[i].position; // 현재 프레임 먼지 위치
float3 currToHead = (headPos - currPos); // 청소기 입구 -> 먼지
float sqrDist = SqrMagnitude(currToHead); // 청소기 입구 <-> 먼지 사이 거리 제곱
// 먼지 이동
if (isRunning == TRUE && sqrDist < sqrRange)
{
float3 dustToHeadDir = normalize(currToHead); // 먼지 -> 청소기 입구 방향
float dotValue = dot(headForwardDir, -dustToHeadDir);
// 원뿔 범위 내에 있을 경우 빨아들이기
if(dotValue > dotThreshold)
{
float suctionForce = sqrForce / sqrDist;
// 빨아들이는 힘
F += dustToHeadDir * suctionForce * dotValue;
sucking = true;
}
}
// F = m * a
// v = a * t
// ===================================================
// 가속도 계산
// ===================================================
// [1] 외력
A += F / mass;
// [2] 중력
A += float3(0, -gravityForce, 0);
// [3] 공기 저항
A -= velocityBuffer[i] * airResistance;
// 속도 적용 : V = A * t
velocityBuffer[i] += A * deltaTime;
// ===================================================
// 이동 시뮬레이션, 충돌 검사
// ===================================================
// 다음 프레임 위치 계산 : S = S0 + V * t
float3 nextPos = currPos + velocityBuffer[i] * deltaTime;
// 교차 지점에서 충돌 검사
// [1] Plane (Y = 0)
nextPos.y = max(0, nextPos.y);
// [2] 입구로 완전히 빨아들인 경우, 먼지 파괴
if(sucking)
{
float3 headToNext = nextPos - headPos;
float3 headToCurrDir = normalize(-currToHead);
float3 headToNextDir = normalize(headToNext);
// 현재 프레임에 먼지가 원뿔 범위 내에 있었다면
if(dot(headForwardDir, headToCurrDir) > dotThreshold)
{
// 다음 프레임에 원뿔 밖으로 나가거나 입구에 근접하면 파괴
if(dot(headForwardDir, headToNextDir) < dotThreshold ||
SqrMagnitude(headToNext) < sqrDeathRange)
{
DestroyDust(i);
}
}
}
// 다음 위치 적용
dustBuffer[i].position = nextPos;
}
[2] 먼지 관리 컴포넌트
- 먼지의 속도를 저장하기 위한 새로운 컴퓨트 버퍼
dustVelocityBuffer를 만들고 컴퓨트 쉐이더에 할당한다. - 물리 시뮬레이션에 필요한 변수들을 추가하고 컴퓨트 쉐이더에 전달한다.
- 메소드 구조를 더 깔끔하게 변경한다.
DustManager.cs
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
[Header("Physics Options")]
[Range(0f, 20f)]
[SerializeField] private float mass = 1f; // 먼지 질량
[Range(0f, 20f)]
[SerializeField] private float gravityForce = 9.8f; // 중력 강도
[Range(0f, 100f)]
[SerializeField] private float airResistance = 1f; // 공기 저항력
private ComputeBuffer dustVelocityBuffer; // 먼지 현재 속도 버퍼
private void InitBuffers()
{
// ...
// Dust Velocity Buffer
dustVelocityBuffer = new ComputeBuffer(instanceNumber, sizeof(float) * 3);
// ...
}
/// <summary> 컴퓨트 쉐이더 초기화 </summary>
private void InitComputeShader()
{
// ...
dustCompute.SetBuffer(kernelUpdateID, "velocityBuffer", dustVelocityBuffer);
// ...
}
private void OnDestroy()
{
// ...
dustVelocityBuffer.Release();
}
private void UpdateDustPositionsGPU()
{
ref var head = ref cleanerHead;
Vector3 headPos = head.Position;
float sqrRange = head.SqrSuctionRange;
//float sqrDeathRange = head.DeathRange * head.DeathRange;
float sqrForce = head.SuctionForce * head.SuctionForce;
dustCompute.SetInt("isRunning", head.Running ? TRUE : FALSE);
dustCompute.SetFloat("deltaTime", deltaTime);
dustCompute.SetVector("headPos", headPos);
dustCompute.SetFloat("sqrRange", sqrRange);
//dustCompute.SetFloat("sqrDeathRange", sqrDeathRange);
dustCompute.SetFloat("sqrForce", sqrForce);
// 원뿔
dustCompute.SetVector("headForwardDir", head.Forward);
dustCompute.SetFloat("dotThreshold", Mathf.Cos(head.SuctionAngleRad));
// 물리
dustCompute.SetFloat("mass", mass);
dustCompute.SetFloat("gravityForce", gravityForce);
dustCompute.SetFloat("airResistance", airResistance);
dustCompute.Dispatch(kernelUpdateID, kernelGroupSizeX, 1, 1);
aliveNumberBuffer.GetData(aliveNumberArray);
aliveNumber = (int)aliveNumberArray[0];
}
DustManager.cs - 메소드 구조 변경
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
private void Start()
{
Init();
InitBuffers();
SetBuffersToShaders();
PopulateDusts();
}
private void Init()
{
aliveNumber = instanceNumber;
kernelPopulateID = dustCompute.FindKernel("Populate");
kernelUpdateID = dustCompute.FindKernel("Update");
dustCompute.GetKernelThreadGroupSizes(kernelUpdateID, out uint tx, out _, out _);
kernelGroupSizeX = Mathf.CeilToInt((float)instanceNumber / tx);
}
/// <summary> 컴퓨트 버퍼들 생성 </summary>
private void InitBuffers()
{
/* [Note]
*
* argsBuffer
* - IndirectArguments로 사용되는 컴퓨트 버퍼의 stride는 20byte 이상이어야 한다.
* - 따라서 파라미터가 앞의 2개만 필요하지만, 뒤에 의미 없는 파라미터 3개를 더 넣어준다.
*/
// Args Buffer
uint[] argsData = new uint[] { dustMesh.GetIndexCount(0), (uint)instanceNumber, 0, 0, 0 };
argsBuffer = new ComputeBuffer(1, 5 * sizeof(uint), ComputeBufferType.IndirectArguments);
argsBuffer.SetData(argsData);
// Dust Buffer
dustBuffer = new ComputeBuffer(instanceNumber, sizeof(float) * 3 + sizeof(int));
// Dust Velocity Buffer
dustVelocityBuffer = new ComputeBuffer(instanceNumber, sizeof(float) * 3);
// Alive Number Buffer
aliveNumberBuffer = new ComputeBuffer(1, sizeof(uint));
aliveNumberArray = new uint[] { (uint)instanceNumber };
aliveNumberBuffer.SetData(aliveNumberArray);
// 카메라 프러스텀이 이 영역과 겹치지 않으면 렌더링되지 않는다.
frustumOverlapBounds = new Bounds(
Vector3.zero,
new Vector3(distributionRange, distributionHeight, distributionRange));
}
/// <summary> 컴퓨트 버퍼들을 쉐이더에 할당 </summary>
private void SetBuffersToShaders()
{
dustMaterial.SetBuffer("_DustBuffer", dustBuffer);
dustCompute.SetBuffer(kernelPopulateID, "dustBuffer", dustBuffer);
dustCompute.SetBuffer(kernelUpdateID, "dustBuffer", dustBuffer);
dustCompute.SetBuffer(kernelUpdateID, "aliveNumberBuffer", aliveNumberBuffer);
dustCompute.SetBuffer(kernelUpdateID, "velocityBuffer", dustVelocityBuffer);
}
[3] 실행 결과
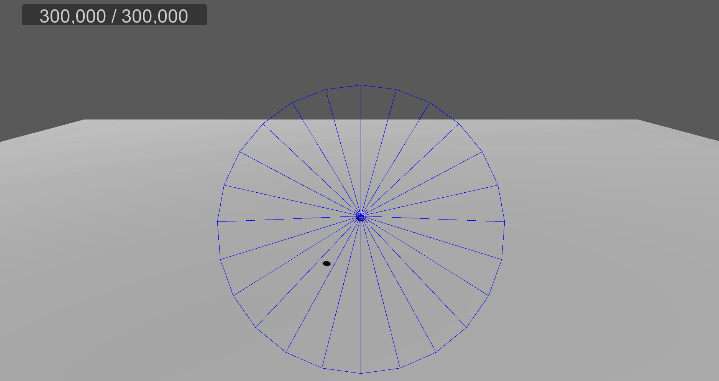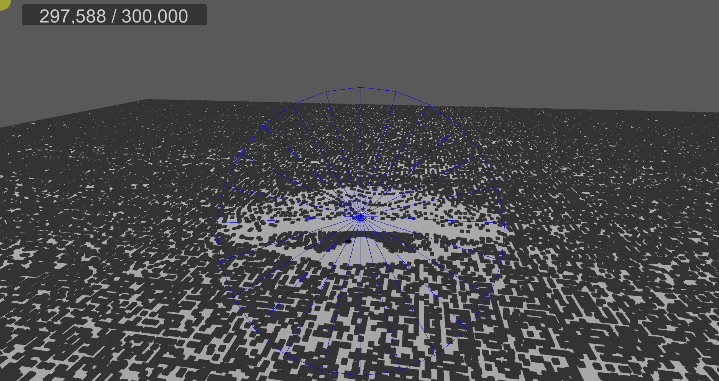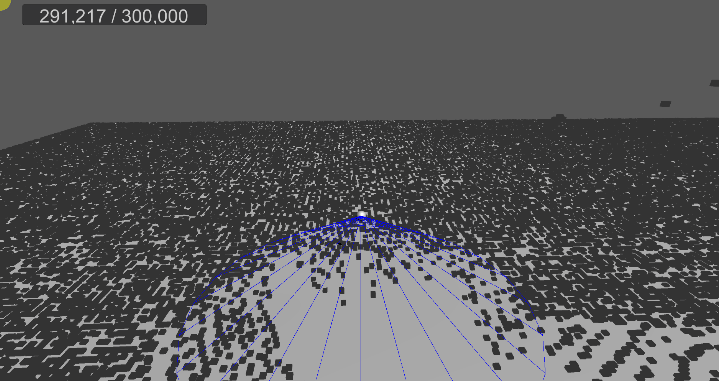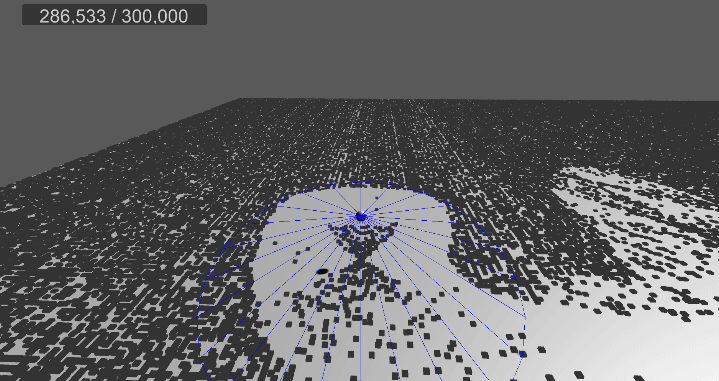
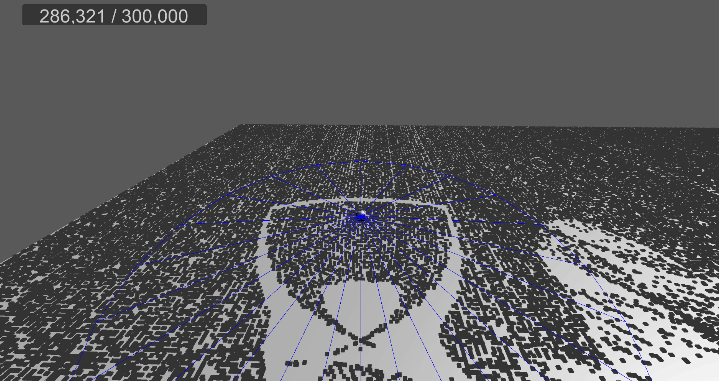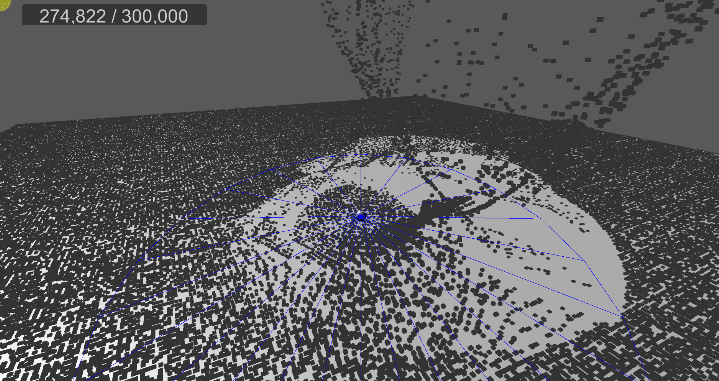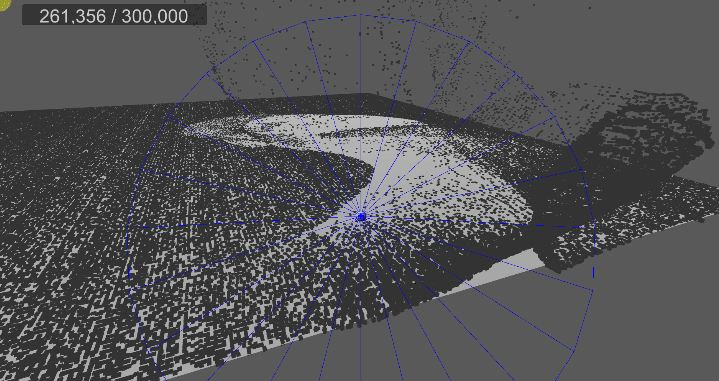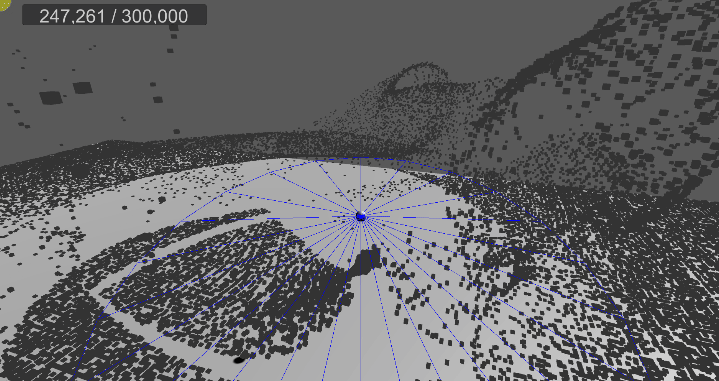
6. 메시 변경, 쉐이더 수정
…
Cube 메시 대신 Quad 메시를 사용한다.
렌더 타입을 Transparent로 바꾸고, 먼지 텍스쳐를 적용한다.
그리고 Billboard 효과를 적용한다.
GPU 인스턴싱을 이용해 그리며, 하나의 트랜스폼을 기반으로 하므로 보통의 빌보드 쉐이더와는 다른 연산을 적용해야 한다.
[1] 먼지 쉐이더
DustShader.shader
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
Properties
{
_MainTex ("Texture", 2D) = "white" {}
_Color("Color", Color) = (0.2, 0.2, 0.2, 1)
}
SubShader
{
Tags { "Queue"="Geometry" "RenderType"="Transparent" "IgnoreProjector"="True" }
ZWrite Off
Lighting Off
Fog { Mode Off }
Blend SrcAlpha OneMinusSrcAlpha
Pass
{
CGPROGRAM
#pragma vertex vert
#pragma fragment frag
#include "UnityCG.cginc"
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
struct v2f
{
float4 pos : SV_POSITION;
float3 uv : TEXCOORD0;
int isAlive : TEXCOORD1;
};
struct Dust
{
float3 position;
int isAlive;
};
// ========================================================================================
// Vertex Shader
// ========================================================================================
uniform float _Scale;
StructuredBuffer<Dust> _DustBuffer;
float4 CalculateVertex(float4 vertex, float3 worldPos)
{
float3 camUpVec = normalize( UNITY_MATRIX_V._m10_m11_m12 );
float3 camForwardVec = -normalize( UNITY_MATRIX_V._m20_m21_m22 );
float3 camRightVec = normalize( UNITY_MATRIX_V._m00_m01_m02 );
float4x4 camRotMat = float4x4( camRightVec, 0, camUpVec, 0, camForwardVec, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1 );
vertex = mul(vertex, camRotMat); // Billboard
vertex.xyz *= _Scale; // Scale
vertex.xyz += worldPos; // Instance Position
// World => VP => Clip
return mul(UNITY_MATRIX_VP, vertex);
}
v2f vert (appdata_full v, uint instanceID : SV_InstanceID)
{
v2f o;
o.isAlive = _DustBuffer[instanceID].isAlive;
o.pos = CalculateVertex(v.vertex, _DustBuffer[instanceID].position);
o.uv = v.texcoord;
return o;
}
// ========================================================================================
// Fragment Shader
// ========================================================================================
sampler2D _MainTex;
fixed4 _Color;
fixed4 frag (v2f i) : SV_Target
{
// 죽은 먼지는 렌더링 X
if(i.isAlive == FALSE)
{
discard;
}
fixed4 col = tex2D(_MainTex, i.uv);
col.rgb = _Color.rgb * col.a;
return col;
}
ENDCG
}
}
[2] 실행 결과
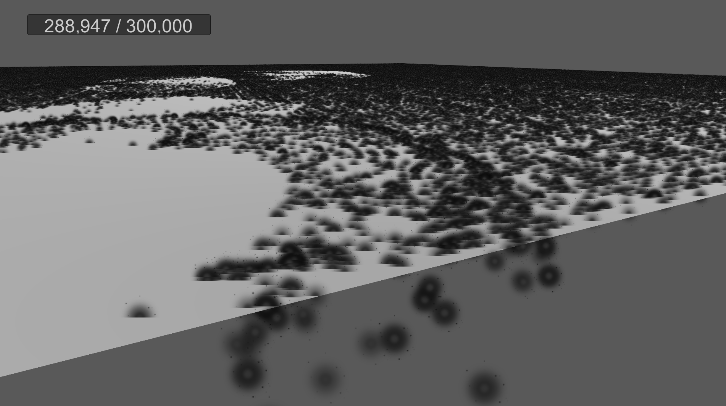
빌보드 효과는 성공적으로 적용되었으나
각 먼지의 충돌 반경이 고려되지 않았으므로,
다른 오브젝트와 겹치면 위와 같이 잘려 보일 수밖에 없다.
7. 충돌 반경 적용
…
충돌 시 먼지의 반지름을 고려하여, 다른 오브젝트에 겹치지 않도록 한다.
앞으로 각 먼지들은 점이 아닌, 반경을 가진 구체(Sphere)로 취급되어야 한다.
[1] 컴퓨트 쉐이더
DustCompute.compute
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
float radius; // 먼지 반지름
[numthreads(64,1,1)]
void Update (uint3 id : SV_DispatchThreadID)
{
// ...
// 교차 지점에서 충돌 검사
// [1] Plane (Y = 0)
nextPos.y = max(radius, nextPos.y); // 반지름 고려
// ...
}
[2] 먼지 관리 컴포넌트
DustManager.cs
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
private void UpdateDustPositionsGPU()
{
// ...
dustCompute.SetFloat("radius", dustScale);
// ...
}
[3] 실행 결과
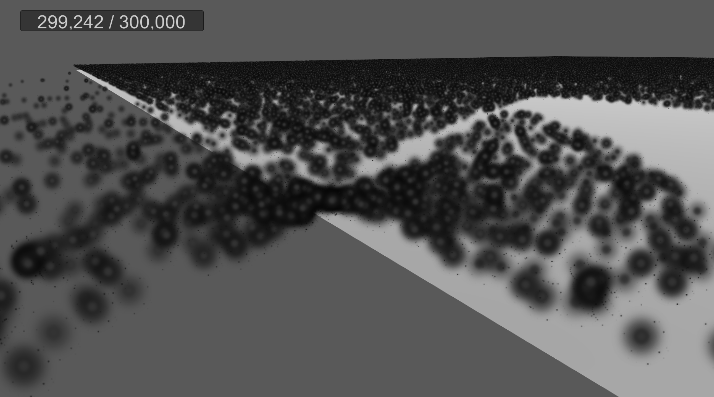
추가 : 원뿔 영역 메시 구현
…
기즈모는 다른 물체보다 항상 위에 보이므로 영역을 정확히 확인하기가 어렵다.
따라서 영역을 정확히 파악할 수 있도록 메시를 만들어 렌더링한다.
진공 청소기 컴포넌트
VacuumCleanerHead.cs
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
private Transform childConeTr;
[Space]
[SerializeField] private Material coneMaterial;
private void Awake()
{
parent = transform.parent;
CreateChildCone();
}
private void Update()
{
deltaTime = Time.deltaTime;
ChangeConeScale();
MouseControl();
if (mouseLocked)
{
Move();
Rotate();
}
}
/// <summary> 자식 게임오브젝트 생성하여 메시 렌더러, 필터 추가 </summary>
private void CreateChildCone()
{
GameObject go = new GameObject("Cone Mesh");
childConeTr = go.transform;
childConeTr.SetParent(transform, false);
MeshRenderer mr = go.AddComponent<MeshRenderer>();
mr.material = coneMaterial;
mr.shadowCastingMode = UnityEngine.Rendering.ShadowCastingMode.Off;
mr.receiveShadows = false;
MeshFilter mf = go.AddComponent<MeshFilter>();
mf.sharedMesh = CreateConeMesh();
}
/// <summary> 원뿔 모양 메시 생성 </summary>
private Mesh CreateConeMesh(int sample = 24)
{
Mesh mesh = new Mesh();
Vector3[] verts = new Vector3[sample + 1];
int[] tris = new int[sample * 3];
verts[0] = Vector3.zero; // 꼭짓점
float deltaRad = Mathf.PI * 2f / sample;
for (int i = 1; i <= sample; i++)
{
float r = i * deltaRad;
verts[i] = new Vector3(Mathf.Cos(r), Mathf.Sin(r), 1f);
}
int t = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < sample; i++)
{
tris[t] = 0;
tris[t + 1] = i + 1;
tris[t + 2] = i;
t += 3;
}
tris[t] = 0;
tris[t + 1] = 1;
tris[t + 2] = sample;
mesh.vertices = verts;
mesh.triangles = tris;
mesh.RecalculateNormals();
mesh.RecalculateBounds();
return mesh;
}
/// <summary> 옵션 변경에 따라 자식 스케일 변경 </summary>
private void ChangeConeScale()
{
float r = Mathf.Tan(suctionAngle * Mathf.Deg2Rad) * suctionRange * 0.5f;
float z = suctionRange * 0.5f;
childConeTr.localScale = new Vector3(r, r, z);
}
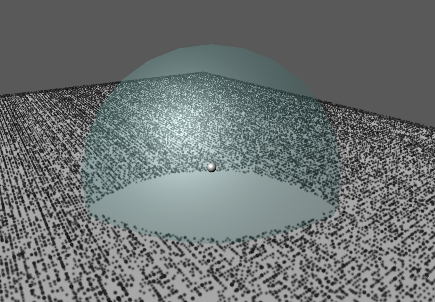
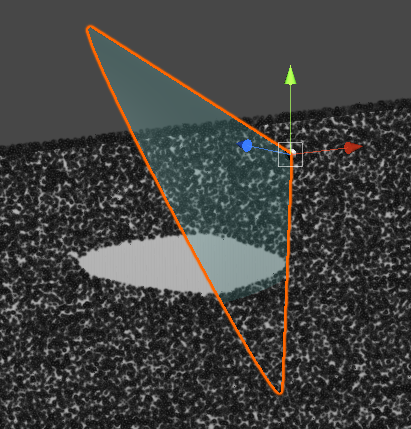
기본 PBR 쉐이더를 Transparent로 설정하고 적용하면 위와 같이 다른 오브젝트와 겹치는 부분이 명확하게 보이지 않는다.
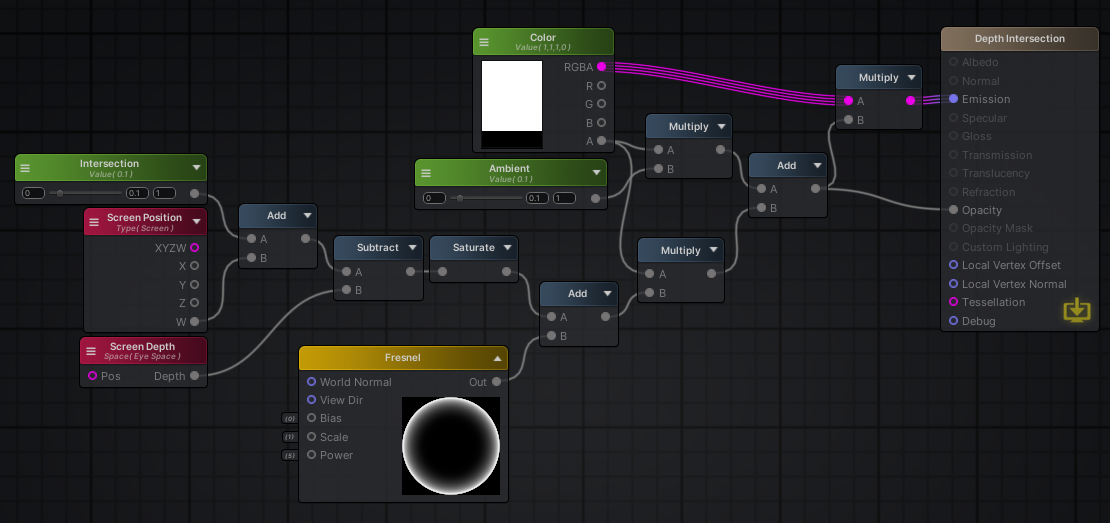
따라서 다음과 같은 쉐이더를 작성하여 적용한다.
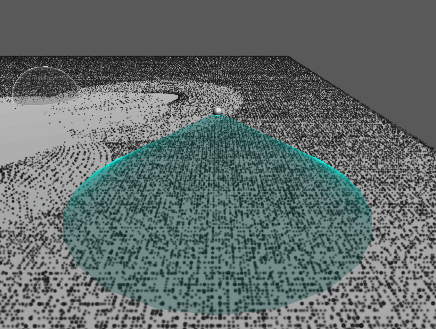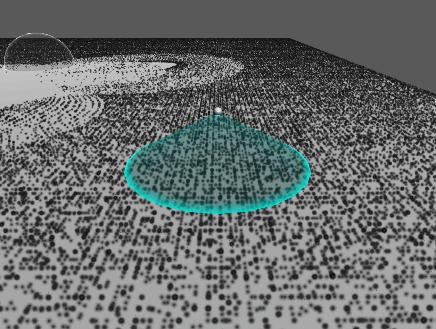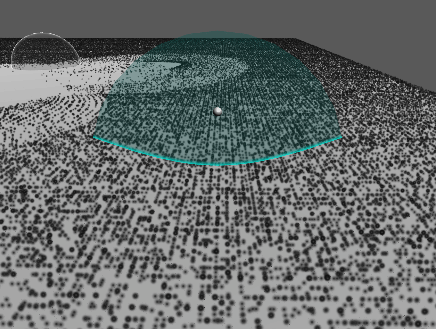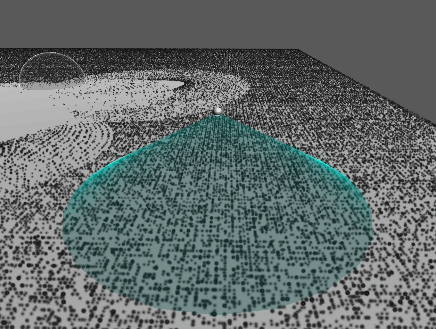
이제 다른 오브젝트와 맞닿는 부분이 더 또렷하게 보이는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
추가 : 다양한 난수 생성 함수들
…
기존에는 단순히 2D 시드값을 통해 float 값, float3 값의 난수를 생성하는 함수들만 있었지만,
앞으로 여러 차원의 입력 및 출력에 대응할 수 있도록 다양한 함수들을 작성한다.
Random functions
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
#define RM 39482.17593
#define RD1 7.8671
#define RD2 3.3419
#define RD3 5.8912
#define RP1 2.1759
#define RP2 4.7921
float Random11(float seed)
{
return frac(sin(dot(float2(RD1, seed), float2(seed, RD2))) * RM);
}
float2 Random12(float seed)
{
return float2(
frac(sin(dot(float2(RD1, seed), float2(seed, RD2))) * RM),
frac(sin(dot(float2(seed, RD2), float2(RD3, seed))) * RM)
);
}
float3 Random13(float seed)
{
return float3(
frac(sin(dot(float2(seed, RD1), float2(RD2, seed))) * RM),
frac(sin(dot(float2(seed, RD2), float2(RD3, seed))) * RM),
frac(sin(dot(float2(seed, RD3), float2(RD1, seed))) * RM)
);
}
float RandomRange11(float seed, float min, float max)
{
return lerp(min, max, Random11(seed));
}
float2 RandomRange12(float seed, float2 min, float2 max)
{
float2 vec;
vec.x = RandomRange11(seed, min.x, max.x);
vec.y = RandomRange11(seed + RP1, min.y, max.y);
return vec;
}
float3 RandomRange13(float seed, float3 min, float3 max)
{
float3 vec;
vec.x = RandomRange11(seed, min.x, max.x);
vec.y = RandomRange11(seed + RP1, min.y, max.y);
vec.z = RandomRange11(seed + RP2, min.z, max.z);
return vec;
}
float Random21(float2 seed)
{
return frac(sin(dot(seed, float2(RD1, RD2))) * RM);
}
float2 Random22(float2 seed)
{
return float2(
frac(sin(dot(seed, float2(RD1, RD2))) * RM),
frac(sin(dot(seed + float2(RP1, RP2), float2(RD2, RD3))) * RM)
);
}
float3 Random23(float2 seed)
{
return float3(
frac(sin(dot(seed, float2(RD1, RD2))) * RM),
frac(sin(dot(seed + float2(RP1, RP2), float2(RD2, RD3))) * RM),
frac(sin(dot(seed + float2(RP2, RP1), float2(RD3, RD1))) * RM)
);
}
float RandomRange21(float2 seed, float min, float max)
{
return lerp(min, max, Random21(seed));
}
float2 RandomRange22(float2 seed, float2 min, float2 max)
{
float2 vec;
vec.x = RandomRange21(seed, min.x, max.x);
vec.y = RandomRange21(seed + float2(RP1, RP2), min.y, max.y);
return vec;
}
float3 RandomRange23(float2 seed, float3 min, float3 max)
{
float3 vec;
vec.x = RandomRange21(seed, min.x, max.x);
vec.y = RandomRange21(seed + float2(RP1, RP2), min.y, max.y);
vec.z = RandomRange21(seed + float2(RP2, RP1), min.z, max.z);
return vec;
}
8. 방출 기능 구현
…
진공 청소기로 흡수했던 먼지들을 한 번에 뿜어내어 발사하는 기능을 구현한다.
suctionAngle 각도를 발사 각도로 사용하고,
suctionForce 값을 발사 강도로 사용한다.
그리고 각 먼지마다 0 ~ 1 범위의 난수를 생성하여, 발사 확률을 결정한다.
발사 확률은 발사되는 먼지 개수를 간접적으로 결정하게 된다.
[1] 이론 : 발사 방향 설정
[1-1] 무작위 원형 범위 생성(XY 2D)
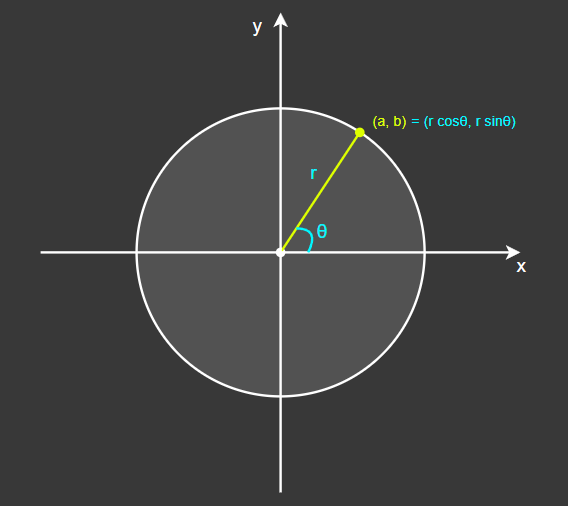
xy 평면에서 원형 범위를 생성한다.
θ(각도) 값을 -360 ~ 360도 범위로,
r(반지름) 값을 0 ~ 1 범위로 난수를 생성한다.
그러면 위에서 보이는 원 내부의 모든 영역이 xy평면의 발사 방향으로 설정되며,
이는 발사 방향을 결정하는 원뿔의 밑면이 된다.
[1-2] 원뿔 영역 생성(XY-Z 2D)
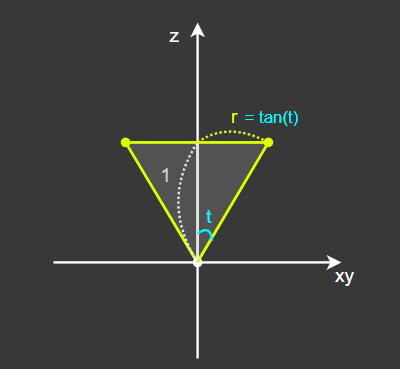
원뿔의 높이인 Z 값을 상수 1로 고정한다.
그리고 여기서 원뿔의 각도, 즉 발사 각도 t를 조정하면 3D 공간의 원뿔 영역을 형성할 수 있는데,
원뿔의 밑면 반지름 r은 tan(t)와 같으므로
tan(t)를 계산하여 [1-1]의 r 값에 곱해주면
최종적인 원뿔 영역을 완성할 수 있다.
이 때 t는 청소기 객체의 suctionAngle 필드이다.
[1-3] 공간 변환
원뿔의 꼭짓점이 원점(0, 0, 0), 밑면의 중심 위치가 (0, 1, 0)인 원뿔 영역을 완성했다.
그리고 이 영역 내의 모든 점은 각각이 발사 방향 벡터이므로,
이제 진공 청소기 트랜스폼의 Local to World 행렬을 여기에 곱하여 공간 변환을 해주면 최종적인 발사 방향 설정이 완료된다.
그리고 여기에 힘을 곱해주기만 하면 발사 벡터가 완성되며,
이 때 힘 값은 청소기 객체의 suctionForce이다.
[2] 컴퓨트 쉐이더
DustCompute.compute
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
#define TAU 6.28318530
uint maxNumber; // 먼지 개수
float time; // Time.time
float blowForce; // 발사 강도(suctionForce 필드값)
float blowAngleRad; // 발사 각도(suctionAngle 필드값)
float4x4 headMatrix; // CleanerHead : localToWorld
// 2 - 죽었던 먼지들 살려서 발사
[numthreads(64,1,1)]
void Blow (uint3 id : SV_DispatchThreadID)
{
uint i = id.x;
if(dustBuffer[i].isAlive == TRUE) return;
if(i >= maxNumber) return;
// 발사 확률 계산
float seed = (i + time) / 79238.288;
float r = Random11(seed);
if(r > 0.01) return;
// Note : localDir의 z를 1로 고정하고, xy를 tan(blowAngleRad)로 지정함으로써
// 발사되는 먼지들이 형성하는 원뿔의 각도를 suctionAngle로 설정하는 효과를 얻는다.
// r2.x : 각 먼지의 각도 (-360 ~ 360), r2.y : 원의 반지름(원뿔의 각도 결정)
float seed2 = i / 82801.277;
float2 r2 = RandomRange12(seed2, float2(-TAU, 0), float2(TAU, 1));
float2 randomCircle = float2(cos(r2.x), sin(r2.x)) * r2.y * tan(blowAngleRad);
// 발사 방향 벡터 공간 변환
float3 localDir = float3(randomCircle.x, randomCircle.y, 1);
float3 worldDir = mul(headMatrix, float4(localDir, 0)).xyz;
dustBuffer[i].position = headPos; // 청소기 입구로 위치 이동
velocityBuffer[i] = (worldDir) * blowForce; // 발사 속도 벡터 설정(방향 * 크기)
// 먼지 되살리기
dustBuffer[i].isAlive = TRUE;
InterlockedAdd(aliveNumberBuffer[0], 1);
}
[3] 먼지 관리 컴포넌트
DustManager.cs
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
private int kernelBlowID;
private void Update()
{
// ...
// 마우스 중앙 버튼 누르면 먼지 발사
if (Input.GetMouseButton(2))
BlowDusts();
}
private void Init()
{
// ...
kernelBlowID = dustCompute.FindKernel("Blow");
// ...
}
private void SetBuffersToShaders()
{
// ...
dustCompute.SetBuffer(kernelBlowID, "dustBuffer", dustBuffer);
dustCompute.SetBuffer(kernelBlowID, "aliveNumberBuffer", aliveNumberBuffer);
dustCompute.SetBuffer(kernelBlowID, "velocityBuffer", dustVelocityBuffer);
}
private void BlowDusts()
{
dustCompute.SetFloat("time", Time.time);
dustCompute.SetFloat("blowForce", cleanerHead.SuctionForce);
dustCompute.SetFloat("blowAngleRad", cleanerHead.SuctionAngleRad);
dustCompute.SetMatrix("headMatrix", cleanerHead.transform.localToWorldMatrix);
dustCompute.Dispatch(kernelBlowID, kernelGroupSizeX, 1, 1);
}
[3] 실행 결과
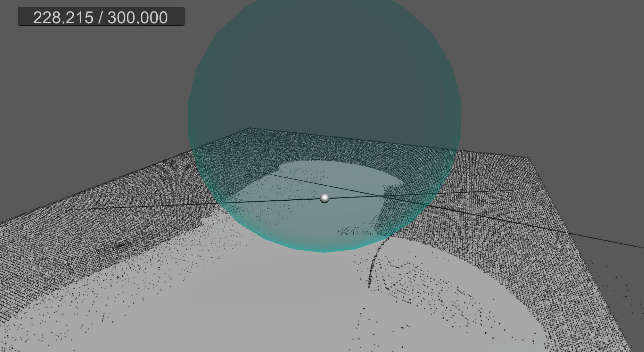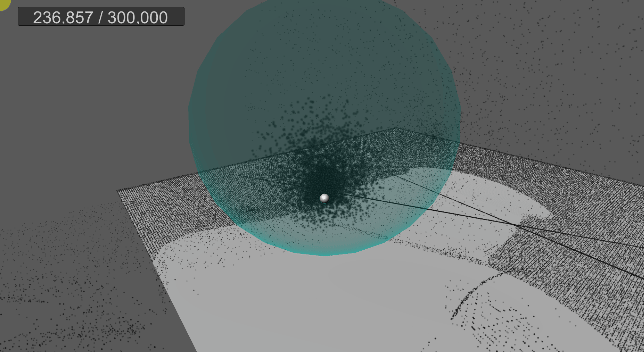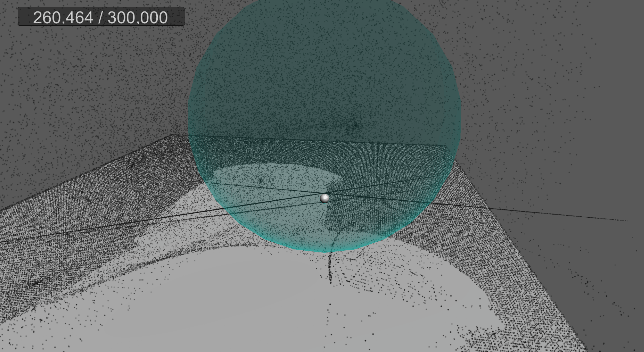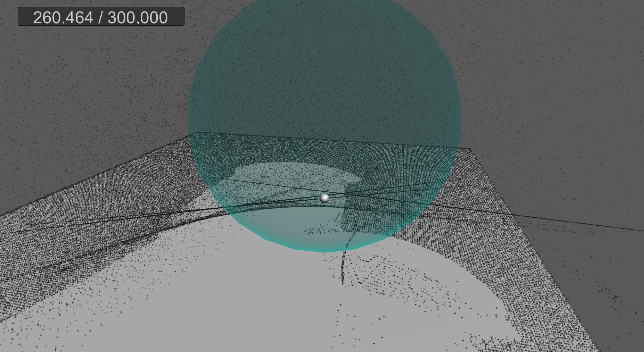
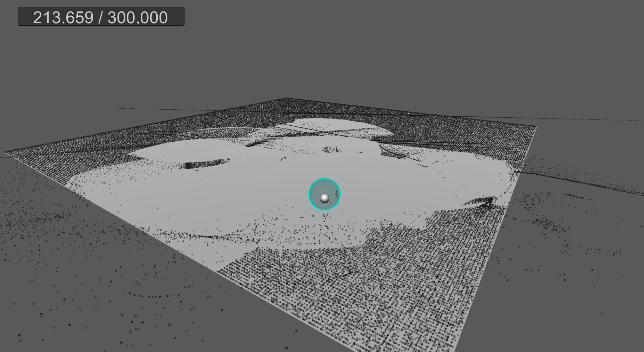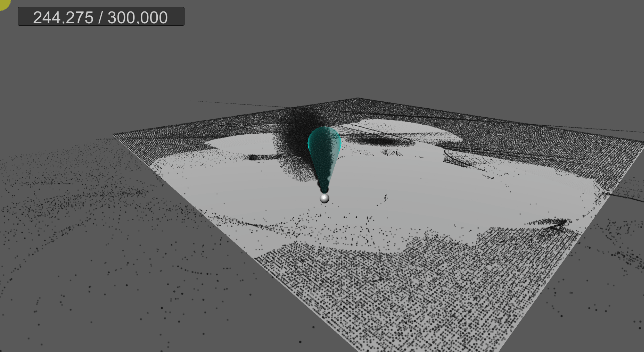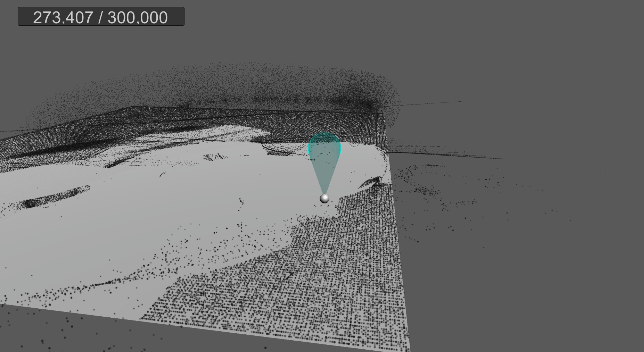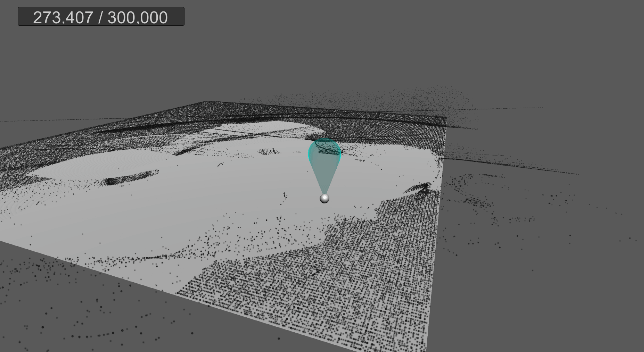
9. 바닥 평면 충돌 및 탄성 구현
…
먼지가 바닥에 부딪힐 경우, 현재는 바로 굴러간다.
탄성 계수를 추가하고, 바닥에 떨어졌을 때 반사 벡터를 구하여 적당히 튕기도록 구현한다.
[1] 반사 벡터 계산 최적화
reflect(inDir, normal) 함수를 통한 연산은
1
inDir - 2 * dot(inDir, normal) * normal
내부적으로 위와 같은 연산을 통해 반사 벡터를 계산한다.
그림으로 나타내면 다음과 같다.

그런데 y = 0, x = 1, z = 2와 같이
법선 벡터가 월드 축과 일치하는 평면의 반사 벡터 계산은
아주 훨씬 저렴하게 이루어질 수 있다.
예를 들어 월드의 바닥 평면인 y = 0의 경우,
입사 벡터의 y 성분의 부호만 뒤집어주면 된다.
예를 들어 입사 벡터가 (a, b, c)일 때 반사 벡터는 (a, -b, c) 이다.
[2] 다음 프레임 위치 계산하기
평면의 충돌 감지는 사실 아주 간단하다.
법선 벡터가 (0, 1, 0)인 평면을 예시로,
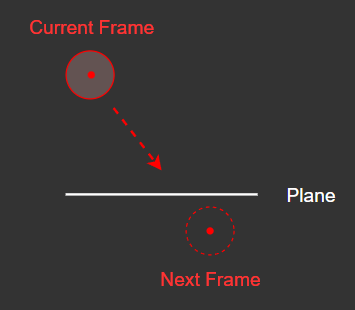
현재 프레임에는 아직 평면에 닿지 않았으나 다음 프레임에는 평면에 접촉, 혹은 평면을 지나가게 된다면 충돌 판정을 해주면 된다.
그리고 이 때의 속도가 (a, b, c)라고 한다면, (a, -b, c)로 바꿔주면 된다.
하지만 위와 같이 속도를 변경해주기만 한다면
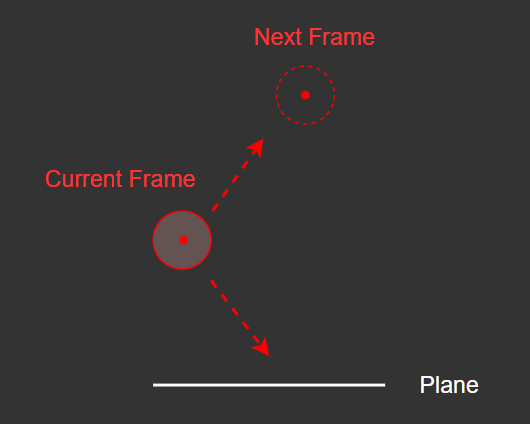
이렇게 된다.
충돌 했다고 가정하고, 그대로 현재 위치에서 반사 벡터를 따라 튕겨져 나간다.
따라서 정확한 충돌을 구현하기 위해서는 충돌 지점을 계산하고,
해당 지점을 기점으로 벡터의 방향을 꺾으며 벡터의 여분 길이를 계산하여
다음 프레임 위치를 결정하는 방식으로 계산을 해주어야 한다.

- 참고 : 직선 - 평면 접점 구하기 : Link
[3] 탄성 계수 고려하기
물체가 다른 물체에 부딪혀 튕겨 나갈 때 운동량을 일정량 상실한다.
따라서 이를 결정하는 값을 임의로 탄성 계수라고 정의하며,
값이 1이면 운동량 보존, 값이 0이면 모든 운동량을 상실한다고 가정한다.
예를 들어 탄성 계수가 0.6이면 40%의 운동량을 상실하여
충돌 이후 속도가 40% 감소한다.
[4] 구현 : 컴퓨트 쉐이더
DustCompute.compute
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
float elasticity; // 탄성 계수 : CPU에서 값 제공(범위 : 0 ~ 1)
// 점 A에서 점 B로 레이캐스트하여 평면과 접점 찾기
float3 RaycastToPlane(float3 A, float3 B, float3 P, float3 N)
{
//A = Ray Origin;
//B = Ray End;
//P = Plane Point;
//N = Plane Normal;
float3 AB = (B - A);
float3 nAB = normalize(AB);
float d = dot(N, P - A) / dot(N, nAB);
float3 C = A + nAB * d;
return C;
}
float3 ReverseY(float3 vec)
{
return float3(vec.x, -vec.y, vec.z);
}
// 1 - 실시간 업데이트
[numthreads(64,1,1)]
void Update (uint3 id : SV_DispatchThreadID)
{
uint i = id.x;
if(dustBuffer[i].isAlive == FALSE) return;
// ...
float3 currPos = dustBuffer[i].position; // 현재 프레임 먼지 위치
// ...
// ===================================================
// 이동 시뮬레이션, 충돌 검사
// ===================================================
// 다음 프레임 위치 계산 : S = S0 + V * t
float3 nextPos = currPos + velocityBuffer[i] * deltaTime;
// [1] Plane 충돌 (Y = 0)
if(nextPos.y < radius) // 먼지 반지름 고려
{
if(currPos.y > radius)
{
float3 currToNext = nextPos - currPos;
// 평면과의 충돌 지점
float3 contact = RaycastToPlane(currPos, nextPos, float3(0, radius, 0), float3(0, 1, 0));
float rayLen = length(currToNext);
float inLen = length(currPos - contact); // 입사 벡터 길이
float outLen = (rayLen - inLen) * elasticity; // 반사 벡터 길이(운동량 감소)
float3 outVec = ReverseY(currToNext) * (outLen / rayLen);
nextPos = contact + outVec;
velocityBuffer[i] = ReverseY(velocityBuffer[i]) * elasticity;
}
else
{
nextPos.y = max(radius, nextPos.y);
}
}
// [2] 입구로 완전히 빨아들인 경우, 먼지 파괴
// ...
// 다음 위치 적용
dustBuffer[i].position = nextPos;
}
[5] 실행 결과
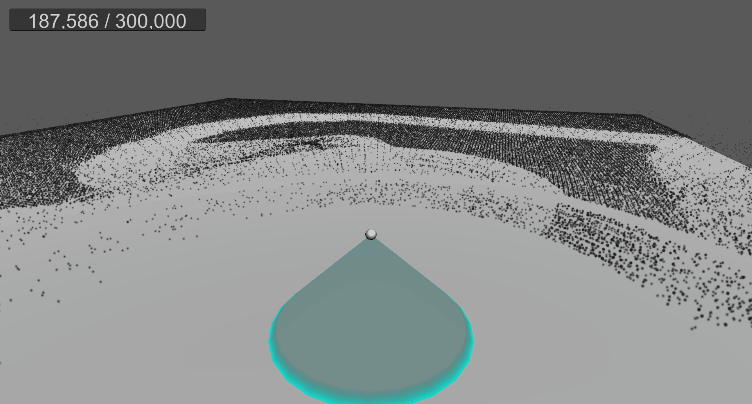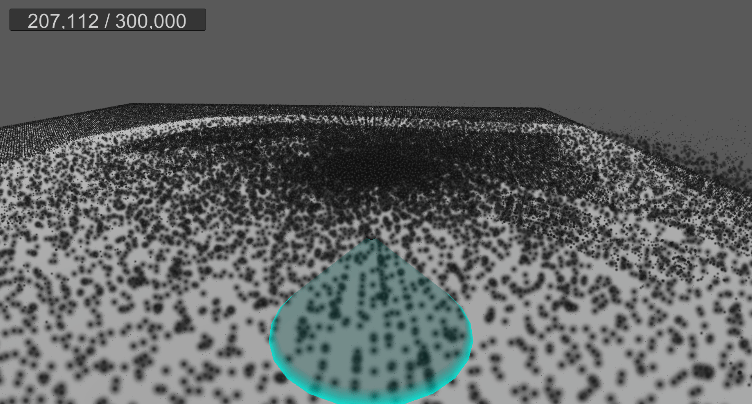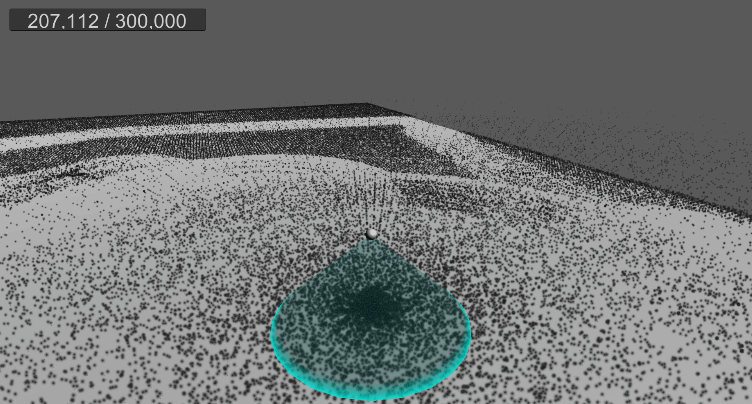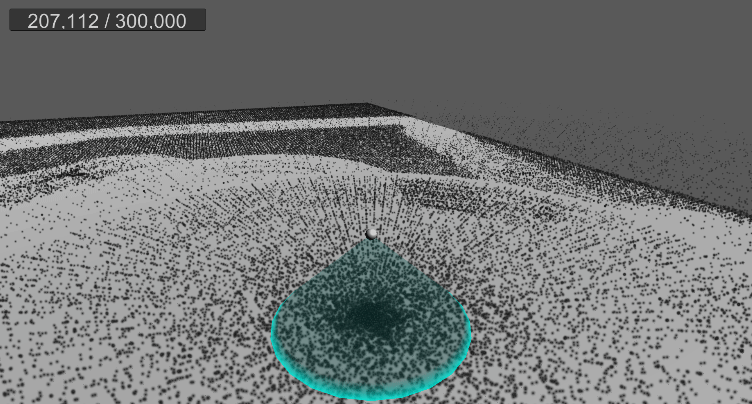
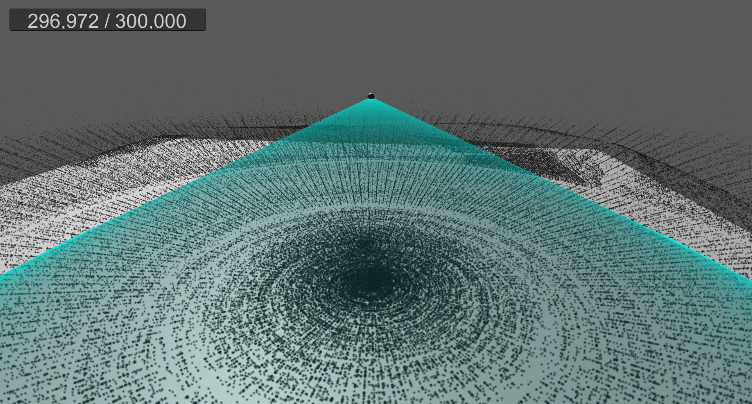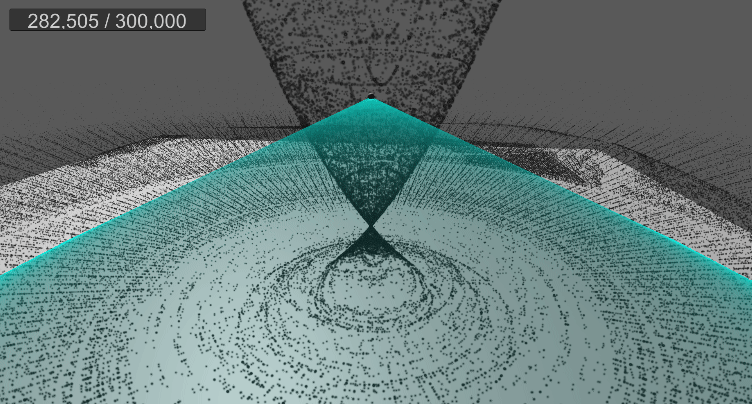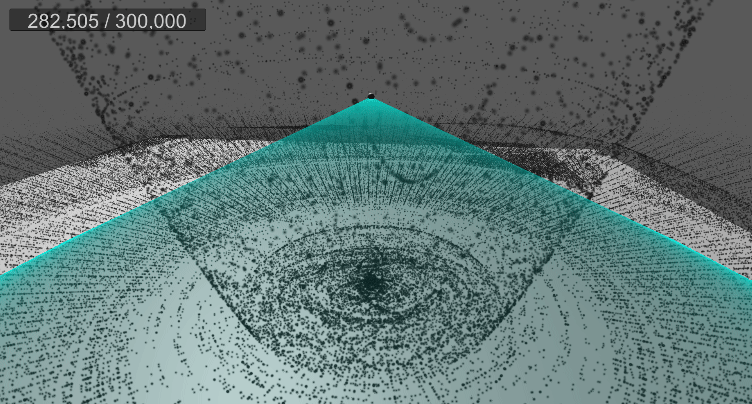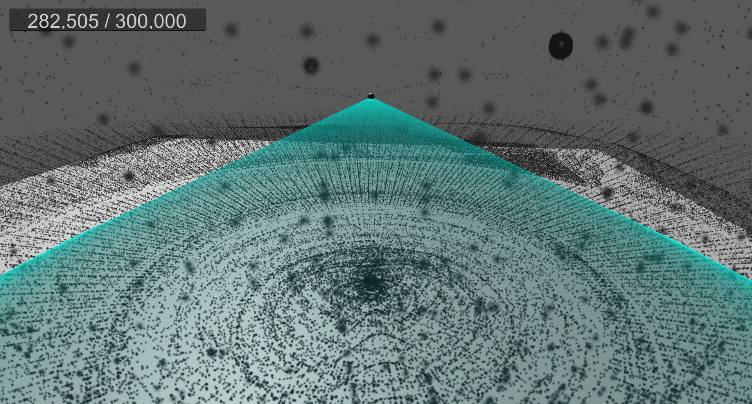
10. 월드 영역 제한(큐브)
…
지금까지는 바닥만 제한 영역을 설정했으나,
월드 전체를 여섯 면이 이루는 큐브 형태로 영역을 제한한다.
따라서 월드의 제한 영역을 이루는 각 면에 부딪힐 경우 튕겨 나가도록 구현한다.
[1] 컴퓨트 쉐이더
Type Definitions
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
// 육면체 영역
struct Bounds
{
float3 min;
float3 max;
};
// 평면
struct Plane
{
float3 position; // 평면 위의 한 점
float3 normal; // 평면의 법선
};
Physics Functions
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
// 점 A에서 점 B로 레이캐스트하여 평면과 접점 찾기
float3 RaycastToPlane(float3 A, float3 B, Plane plane)
{
//A = Ray Origin;
//B = Ray End;
//P = Plane Point;
//N = Plane Normal;
float3 AB = (B - A);
float3 nAB = normalize(AB);
float d = dot(plane.normal, plane.position - A) / dot(plane.normal, nAB);
float3 C = A + nAB * d;
return C;
}
#define IN_BOUNDS 0
#define OUT_OF_PX 1 // +x
#define OUT_OF_MX 2 // -x
#define OUT_OF_PY 3 // +y
#define OUT_OF_MY 4 // -y
#define OUT_OF_PZ 5 // +z
#define OUT_OF_MZ 6 // -z
// 육면체 범위 내로 위치 제한 및 충돌 검사
// - cur : 현재 프레임에서의 위치
// - next : 다음 프레임에서의 위치
// - velocity : 현재 이동 속도
// - threshold : 입자의 크기
// - elasticity : 탄성력 계수(0 ~ 1)
// - bounds : 큐브 영역
void ConfineWithinCubeBounds(float3 cur, inout float3 next, inout float3 velocity, float threshold, float elasticity, Bounds bounds)
{
// 1. 큐브 영역 밖에 있는지, 안에 있는지 검사
int status = IN_BOUNDS;
if(next.x > bounds.max.x - threshold) status = OUT_OF_PX;
else if(next.x < bounds.min.x + threshold) status = OUT_OF_MX;
else if(next.y > bounds.max.y - threshold) status = OUT_OF_PY;
else if(next.y < bounds.min.y + threshold) status = OUT_OF_MY;
else if(next.z > bounds.max.z - threshold) status = OUT_OF_PZ;
else if(next.z < bounds.min.z + threshold) status = OUT_OF_MZ;
else return; // 영역 내부에 있는 경우, 종료
Plane plane;
float limit;
float3 reversedCurToNext;
float3 reversedVelocity;
switch(status)
{
case OUT_OF_PX:
limit = bounds.max.x - threshold;
if(cur.x > limit) // 외부에서 외부로 이동하는 경우, 단순히 위치만 변경하기
{
next.x = min(limit, next.x);
return;
}
// 내부에서 외부로 이동하는 경우, 반사 벡터 계산을 위한 변수들 초기화
plane.normal = float3(1, 0, 0);
plane.position = float3(limit, 0, 0);
reversedCurToNext = ReverseX(next - cur);
reversedVelocity = ReverseX(velocity);
break;
case OUT_OF_MX:
limit = bounds.min.x + threshold;
if(cur.x < limit)
{
next.x = max(limit, next.x);
return;
}
plane.normal = float3(-1, 0, 0);
plane.position = float3(limit, 0, 0);
reversedCurToNext = ReverseX(next - cur);
reversedVelocity = ReverseX(velocity);
break;
case OUT_OF_PY:
limit = bounds.max.y - threshold;
if(cur.y > limit)
{
next.y = min(limit, next.y);
return;
}
plane.normal = float3(0, 1, 0);
plane.position = float3(0, limit, 0);
reversedCurToNext = ReverseY(next - cur);
reversedVelocity = ReverseY(velocity);
break;
case OUT_OF_MY:
limit = bounds.min.y + threshold;
if(cur.y < limit)
{
next.y = max(limit, next.y);
return;
}
plane.normal = float3(0, -1, 0);
plane.position = float3(0, limit, 0);
reversedCurToNext = ReverseY(next - cur);
reversedVelocity = ReverseY(velocity);
break;
case OUT_OF_PZ:
limit = bounds.max.z - threshold;
if(cur.z > limit)
{
next.z = min(limit, next.z);
return;
}
plane.normal = float3(0, 0, 1);
plane.position = float3(0, 0, limit);
reversedCurToNext = ReverseZ(next - cur);
reversedVelocity = ReverseZ(velocity);
break;
case OUT_OF_MZ:
limit = bounds.min.z + threshold;
if(cur.z < limit)
{
next.z = max(limit, next.z);
return;
}
plane.normal = float3(0, 0, -1);
plane.position = float3(0, 0, limit);
reversedCurToNext = ReverseZ(next - cur);
reversedVelocity = ReverseZ(velocity);
break;
}
// 직선과 평면의 충돌 계산
float3 currToNext = next - cur;
float3 contact = RaycastToPlane(cur, next, plane); // 이동 벡터와 평면의 접점
float rayLen = length(currToNext); // 이동 벡터의 길이
float inLen = length(cur - contact); // 입사 벡터 길이
float outLen = (rayLen - inLen) * elasticity; // 반사 벡터 길이(운동량 감소)
float3 outVec = reversedCurToNext * (outLen / rayLen);
// Outputs
next = contact + outVec; // 다음 프레임 위치 변경
velocity = reversedVelocity * elasticity; // 속도 변경
}
DustCompute.compute
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
[numthreads(64,1,1)]
void Update (uint3 id : SV_DispatchThreadID)
{
// ...
// ===================================================
// 이동 시뮬레이션, 충돌 검사
// ===================================================
// 다음 프레임 위치 계산 : S = S0 + V * t
float3 nextPos = currPos + velocityBuffer[i] * deltaTime;
// [1] Cube 영역 제한
Bounds bounds;
bounds.min = boundsMin;
bounds.max = boundsMax;
ConfineWithinCubeBounds(currPos, nextPos, velocityBuffer[i], radius, elasticity, bounds);
// ...
}
[2] 실행 결과


구조 개편
…
원래는 진공 청소기 기능만 구현하려 했으나, 다양한 기능들을 구현하게 되었으므로
진공 청소기/방출기/컨트롤러를 분리한다.
[1] 컴퓨트 쉐이더
- 구조체 정의, 함수 구현을 별도의
.cginc파일로 분리하고#include로 가져온다. - 진공 청소기 흡수 기능을
Update에서 분리하여 새로운 커널에 구현한다. Update커널은 물리 업데이트만 담당한다.Blow는Emit으로 이름을 변경한다.- 변수들도 알맞게 네이밍을 변경한다.
DustCompute.compute
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
#pragma kernel Populate
#pragma kernel Update
#pragma kernel VacuumUp
#pragma kernel Emit
#include "Type Definitions.cginc"
#include "Math Functions.cginc"
#include "Random Functions.cginc"
#include "Physics Functions.cginc"
/*******************************************************************
* Naming Conventions
/*******************************************************************
- AToB : B - A
- ~Dir : 방향 벡터(크기 1)
- ~Dist : 두 위치 벡터 사이의 거리(스칼라)
- ~Len : 한 벡터의 길이
/*******************************************************************/
/*******************************************************************
/* Definitions
/*******************************************************************/
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
#define TAU 6.28318530
/*******************************************************************
/* Variables
/*******************************************************************/
RWStructuredBuffer<Dust> dustBuffer; // 먼지 위치, 생존 여부
RWStructuredBuffer<float3> velocityBuffer; // 먼지 속도
RWStructuredBuffer<uint> aliveNumberBuffer; // 생존한 먼지 개수
/* Common */
float3 spawnBoundsMin; // 먼지 생성 영역 - 최소 지점
float3 spawnBoundsMax; // 먼지 생성 영역 - 최대 지점
float3 worldBoundsMin; // 월드 제한 영역 - 최소 지점
float3 worldBoundsMax; // 월드 제한 영역 - 최대 지점
float deltaTime;
/* Controller */
float3 controllerPos; // 월드 위치
float3 controllerForward; // 전방 벡터
/* Vacuum Cleaner */
float cleanerSqrDist; // 먼지 흡입 범위(반지름) - 제곱
float cleanerSqrDeathRange; // 먼지 소멸 범위(반지름) - 제곱
float cleanerSqrForce; // 빨아들이는 힘 - 제곱
float cleanerDotThreshold; // 진공 청소기 원뿔 영역 내적 범위
/* Emitter */
uint dustCount; // 먼지 개수
float time; // Time.time
float emitterForce; // 방출 강도
float emitterDist; // 방출 거리
float emitterAngleRad; // 방출 각도
float4x4 controllerMatrix; // localToWorld
/* Physics(Update) */
float3 gravity; // 중력 가속도
float radius; // 먼지 반지름
float mass; // 질량
float airResistance; // 공기 저항력
float elasticity; // 탄성력
/*******************************************************************
/* Functions
/*******************************************************************/
// 먼지 파괴
void DestroyDust(uint i)
{
dustBuffer[i].isAlive = FALSE;
InterlockedAdd(aliveNumberBuffer[0], -1);
}
Kernel : Update
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
[numthreads(64,1,1)]
void Update (uint3 id : SV_DispatchThreadID)
{
uint i = id.x;
if(dustBuffer[i].isAlive == FALSE) return;
if(i >= dustCount) return;
float3 A = 0; // 가속도 합 벡터
// F = m * a
// v = a * t
// ===================================================
// 속도 계산
// ===================================================
//A += F / mass;
// [1] 중력
A += gravity;
// [2] 공기 저항
A -= velocityBuffer[i] * airResistance;
// 속도 적용 : V = A * t
velocityBuffer[i] += A * deltaTime;
// ===================================================
// 이동 시뮬레이션, 충돌 검사
// ===================================================
// 다음 프레임 위치 계산 : S = S0 + V * t
float3 currPos = dustBuffer[i].position;
float3 nextPos = currPos + velocityBuffer[i] * deltaTime;
// [1] 월드 영역 제한(Cube)
Bounds bounds;
bounds.min = worldBoundsMin;
bounds.max = worldBoundsMax;
ConfineWithinCubeBounds(currPos, nextPos, velocityBuffer[i], radius, elasticity, bounds);
// 다음 위치 적용
dustBuffer[i].position = nextPos;
}
Kernel : VacuumUp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
[numthreads(64,1,1)]
void VacuumUp (uint3 id : SV_DispatchThreadID)
{
uint i = id.x;
if(dustBuffer[i].isAlive == FALSE) return;
if(i >= dustCount) return;
float3 F = 0; // 힘 합 벡터
bool flag = false;
float3 currPos = dustBuffer[i].position; // 현재 프레임 먼지 위치
float3 currToHead = (controllerPos - currPos); // 청소기 입구 -> 먼지
float sqrDist = SqrMagnitude(currToHead); // 청소기 입구 <-> 먼지 사이 거리 제곱
// 원뿔 범위 및 힘 계산
if (sqrDist < cleanerSqrDist)
{
float3 dustToHeadDir = normalize(currToHead); // 먼지 -> 청소기 입구 방향
float dotValue = dot(controllerForward, -dustToHeadDir);
// 원뿔 범위 내에 있을 경우 빨아들이기
if(dotValue > cleanerDotThreshold)
{
float force = cleanerSqrForce / sqrDist;
// 빨아들이는 힘
F += dustToHeadDir * force * dotValue;
flag = true;
}
}
// 속도 계산
if(flag)
{
// 가속도
float3 A = F / mass;
// 속도
velocityBuffer[i] += A * deltaTime;
// 다음 프레임 위치 예측 : S = S0 + V * t
float3 nextPos = currPos + velocityBuffer[i] * deltaTime;
float3 headToNext = nextPos - controllerPos;
float3 headToCurrDir = normalize(-currToHead);
float3 headToNextDir = normalize(headToNext);
// 현재 프레임에 먼지가 원뿔 범위 내에 있었다면
if(dot(controllerForward, headToCurrDir) > cleanerDotThreshold)
{
// 다음 프레임에 원뿔 밖으로 나가거나 입구에 근접하면 파괴
if(dot(controllerForward, headToNextDir) < cleanerDotThreshold ||
SqrMagnitude(headToNext) < cleanerSqrDeathRange)
{
DestroyDust(i);
}
}
}
}
Kernel : Emit
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
[numthreads(64,1,1)]
void Emit (uint3 id : SV_DispatchThreadID)
{
uint i = id.x;
if(dustBuffer[i].isAlive == TRUE) return;
if(i >= dustCount) return;
// 발사 확률 계산
float seed = (i + time) / 79238.288;
float r = Random11(seed);
if(r > 0.01) return;
// Note : localDir의 z를 1로 고정하고, xy를 tan(emitterAngleRad)로 지정함으로써
// 발사되는 먼지들이 형성하는 원뿔의 각도를 suctionAngle로 설정하는 효과를 얻는다.
// r2.x : 각 먼지의 각도 (-360 ~ 360), r2.y : 원의 반지름(원뿔의 각도 결정)
float seed2 = i / 82801.277;
float2 r2 = RandomRange12(seed2, float2(-TAU, 0), float2(TAU, 1));
float2 randomCircle = float2(cos(r2.x), sin(r2.x)) * r2.y * tan(emitterAngleRad);
// 발사 방향 벡터 공간 변환
float3 localDir = float3(randomCircle.x, randomCircle.y, 1);
float3 worldDir = mul(controllerMatrix, float4(localDir, 0)).xyz;
float3 F = worldDir * emitterForce * emitterDist;
float3 A = F / mass;
float3 V = A * deltaTime;
dustBuffer[i].position = controllerPos; // 청소기 입구로 위치 이동
velocityBuffer[i] = V;
// 먼지 되살리기
dustBuffer[i].isAlive = TRUE;
InterlockedAdd(aliveNumberBuffer[0], 1);
}
[2] C# 스크립트
- 이름 변경 :
VacuumCleanerHead->VacuumCleaner - 이동 및 회전 기능 분리하여 새로운 클래스 작성 :
PlayerController - 원뿔 공통 클래스 작성 :
Cone - 방출 기능 담당 클래스 작성 :
DustEmitter
DustManager
- 키보드 버튼 1, 2, … : 도구 선택
- 마우스 좌클릭 : 현재 선택된 도구 작동
-
마우스 우클릭 : 마우스 보이기/숨기기
- 각 도구가 실행될 때만, 해당되는 컴퓨트 쉐이더 커널 실행
- 지정한 World Bounds에 따라 기즈모 표시, 게임 시작 시 메시 생성
11. Blow 기능 구현
…
원뿔 범위에서 바람이 불듯 밀쳐내는 기능을 구현한다.
새로운 커널 BlowWind를 작성하며,
다른 커널과 마찬가지로 사용자의 입력에 따라 독립적으로 실행시킨다.
VacuumUp과 유사하게 구현하며, 먼지의 진행 방향만 반대로 바꾸면 된다.
[1] 컴퓨트 쉐이더
DustCompute.compute
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
void BlowWind (uint3 id : SV_DispatchThreadID)
{
uint i = id.x;
if(dustBuffer[i].isAlive == FALSE) return;
if(i >= dustCount) return;
float3 dustPos = dustBuffer[i].position; // 현재 프레임 먼지 위치
float3 headToDust = (dustPos - controllerPos); // 입구 -> 먼지
float sqrDist = SqrMagnitude(headToDust); // 입구<-> 먼지 사이 거리 제곱
// 구형 범위 내에 포함되는 경우
if (sqrDist < blowerSqrDist)
{
float3 headToDustDir = normalize(headToDust); // 입구 -> 먼지 방향
float dotValue = dot(controllerForward, headToDustDir);
// 원뿔 범위 내에 포함되는 경우, 밀쳐내기
if(dotValue > blowerDotThreshold)
{
float force = blowerSqrForce / sqrt(sqrDist);
float3 F = headToDustDir * force * dotValue;
float3 A = F / mass;
velocityBuffer[i] += A * deltaTime;
}
}
}
[2] 먼지 관리 컴포넌트
DustManager.cs
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
private int kernelBlowID;
private void Init()
{
// ...
kernelBlowID = dustCompute.FindKernel("BlowWind");
// ...
}
private void SetBuffersToShaders()
{
// ...
dustCompute.SetBuffer(kernelBlowID, "dustBuffer", dustBuffer);
dustCompute.SetBuffer(kernelBlowID, "velocityBuffer", dustVelocityBuffer);
}
private void UpdateBlower()
{
if (!blower.IsRunning) return;
dustCompute.SetFloat("blowerSqrForce", blower.SqrForce);
dustCompute.SetFloat("blowerSqrDist", blower.SqrDistance);
dustCompute.SetFloat("blowerDotThreshold", Mathf.Cos(blower.AngleRad));
dustCompute.Dispatch(kernelBlowID, kernelGroupSizeX, 1, 1);
}
[3] 실행 결과
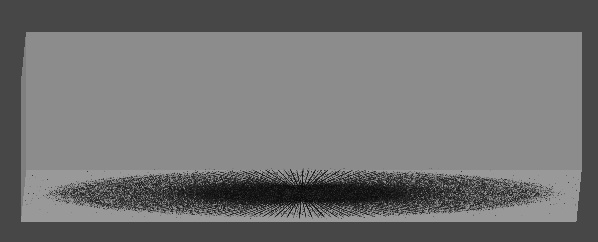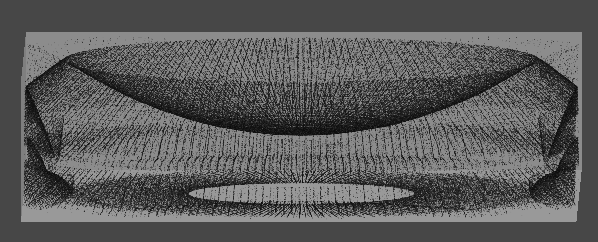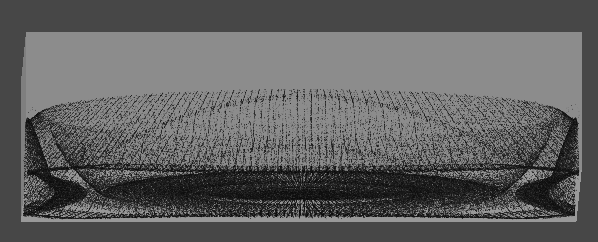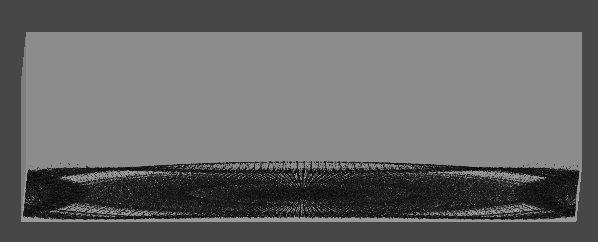
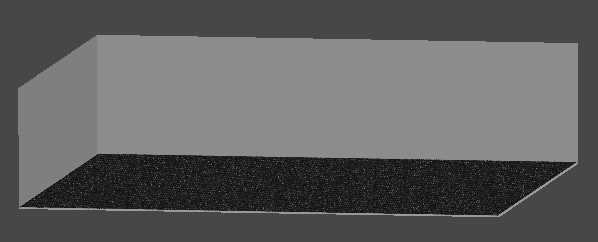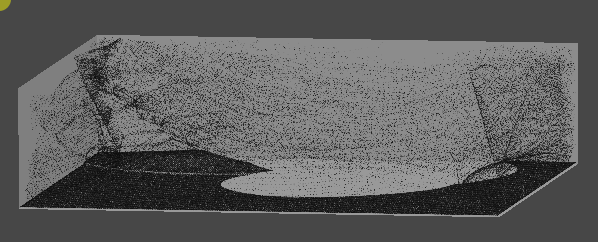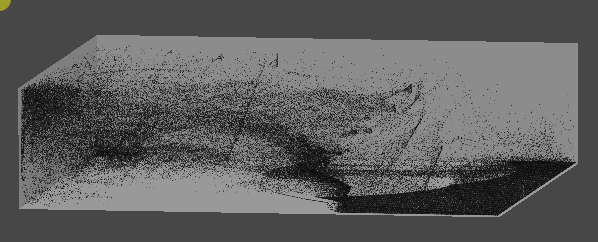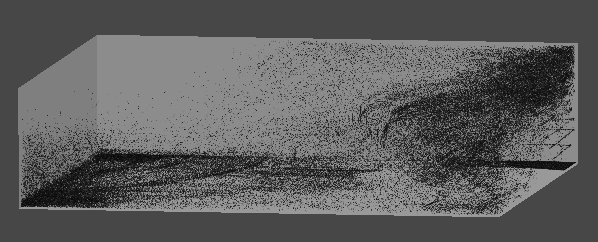
12. 무작위 색상 설정
…
두 개의 색상을 지정하여,
각 먼지가 두 색상 사이에서 랜덤한 색상으로 설정되도록 구현한다.
[1] 컴퓨트 쉐이더
DustCompute.compute
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
RWStructuredBuffer<half3> dustColorBuffer; // 먼지 색상 RGB
half3 dustColorA; // 무작위 색상 A
half3 dustColorB; // 무작위 색상 B
void Populate (uint3 id : SV_DispatchThreadID)
{
uint i = id.x;
// [1] 위치
float width = spawnBoundsMax.x - spawnBoundsMin.x;
float seed = i / (width * width);
dustBuffer[i].position = RandomRange13(seed, spawnBoundsMin, spawnBoundsMax);
dustBuffer[i].isAlive = TRUE;
// [2] 색상
float2 seed2d = float2(i % width, i / width);
float t = Random21(seed2d);
dustColorBuffer[i] = lerp(dustColorA, dustColorB, t);
}
[2] 먼지 쉐이더
Dust.shader
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
StructuredBuffer<half3> _DustColorBuffer;
struct v2f
{
// ...
half3 dustColor : COLOR0;
};
v2f vert (appdata_full v, uint instanceID : SV_InstanceID)
{
v2f o;
// ...
o.dustColor = _DustColorBuffer[instanceID];
return o;
}
fixed4 frag (v2f i) : SV_Target
{
// ...
fixed4 col = tex2D(_MainTex, i.uv);
col.rgb = i.dustColor * col.a;
return col;
}
[3] 먼지 관리 컴포넌트
DustManager.cs
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
[SerializeField] private Color dustColorA = Color.black;
[SerializeField] private Color dustColorB = Color.gray;
private ComputeBuffer dustColorBuffer;
private void InitBuffers()
{
// ...
// Color Buffer
dustColorBuffer = new ComputeBuffer(dustCount, sizeof(float) * 3);
// ...
}
private void SetBuffersToShaders()
{
dustMaterial.SetBuffer("_DustBuffer", dustBuffer);
dustMaterial.SetBuffer("_DustColorBuffer", dustColorBuffer);
dustCompute.SetBuffer(kernelPopulateID, "dustBuffer", dustBuffer);
dustCompute.SetBuffer(kernelPopulateID, "dustColorBuffer", dustColorBuffer);
// ...
}
private void OnDestroy()
{
// ...
if (dustColorBuffer != null) dustColorBuffer.Release();
}
[4] 실행 결과
- 지정 색상 : Red, Blue
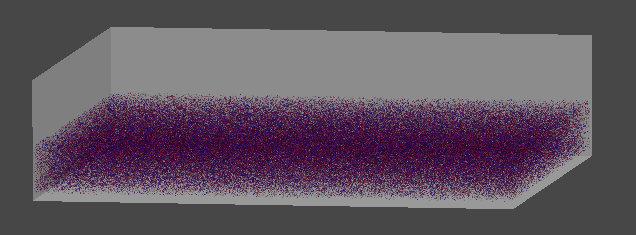
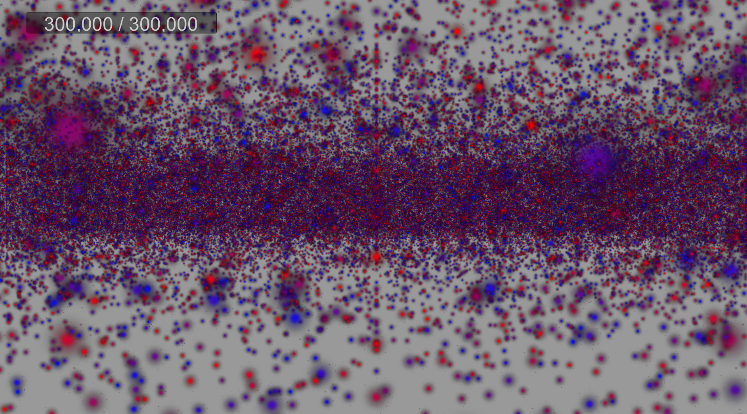
13. Sphere Collision 구현
…
고정된 위치에 존재하는 Sphere Collider와 먼지의 충돌을 구현한다.
먼지 역시 반지름이 있는 Sphere이므로,
먼지와 Sphere Collider의 충돌은 Sphere to Sphere 충돌로 계산되어야 한다.
[1] 충돌 감지
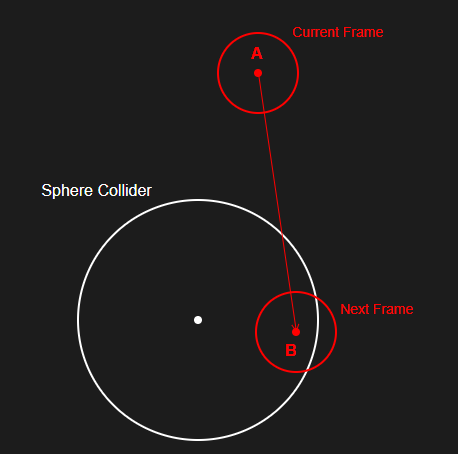
충돌 감지 자체는 어렵지 않다.
다음 프레임의 먼지 위치를 검사했을 때, 먼지(빨간 구체)와 충돌체(하얀 구체)의 반지름 합이 두 구체 중심 위치 사이의 거리보다 같거나 크다면 충돌로 간주하면 된다.
[2] Sphere Cast to Sphere
- Post : Sphere Cast to Sphere
- 구체를 전진시켜 다른 구체와의 충돌 지점을 찾아낸다.
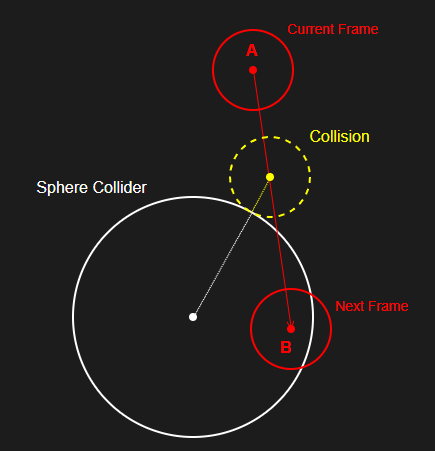
현재 프레임의 먼지 위치에서부터 다음 프레임의 먼지 위치까지 Sphere Cast를 통해 충돌 지점을 찾는다.
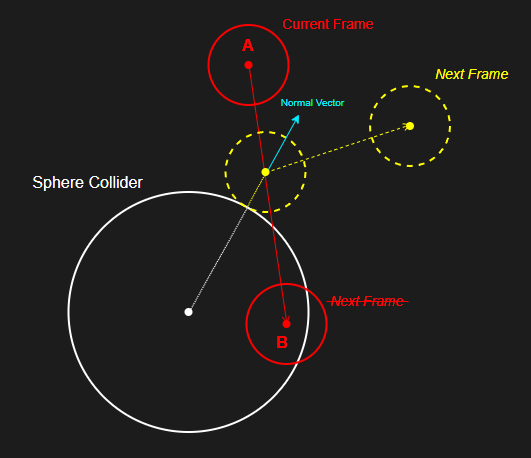
충돌 지점에서부터 충돌체 중심 위치와 반대 방향을 향하는 법선 벡터를 구하고,
입사 벡터를 반사시켜 충돌 이후 실제로 먼지가 이동할 다음 프레임의 위치를 계산한다.
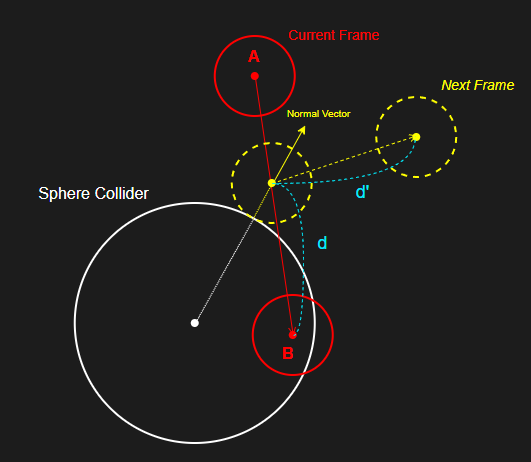
이 때 d와 d'의 길이는 같으며,
충돌 시 손실되는 운동량을 계산하여 d'에 곱해주면 된다.
[3] 컴퓨트 쉐이더 - 계산 함수
functions
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
// 구체끼리의 충돌 여부 검사
// xyz : Position
// w : Radius
bool CheckSphereIntersection(float4 sphereA, float4 sphereB)
{
return SqrMagnitude(sphereA.rgb - sphereB.rgb) < Square(sphereA.w + sphereB.w);
}
// A -> B 위치로 Sphere Cast
// S : Target Sphere Position
// r1 : Radius of Casted Sphere
// r2 : Radius of Target Sphere
float3 SphereCastToSphere(float3 A, float3 B, float3 S, float r1, float r2)
{
float3 nAB = normalize(B - A);
float3 AS = (S - A);
float as2 = SqrMagnitude(AS);
float ad = dot(AS, nAB);
float ad2 = ad * ad;
float ds2 = as2 - ad2;
float cs = r1 + r2;
float cs2 = cs * cs;
float cd = sqrt(cs2 - ds2);
float ac = ad - cd;
float3 C = A + nAB * ac; // 충돌 시 구체 중심 좌표
//float3 E = C + (S - C) * r1 / cs; // 충돌 지점 좌표
return C;
}
// Sphere Collider에 충돌 검사하여 먼지 위치 및 속도 변경
// - cur : 현재 프레임에서의 위치
// - next : 다음 프레임에서의 위치 [INOUT]
// - velocity : 현재 이동 속도 [INOUT]
// - sphere : 구체 중심 위치(xyz), 구체 반지름(w)
// - dustRadius : 먼지 반지름
// - elasticity : 탄성력 계수(0 ~ 1) : 충돌 시 보존되는 운동량 비율
void CalculateSphereCollision(float3 cur, inout float3 next, inout float3 velocity, float4 sphere,
float dustRadius, float elasticity)
{
// 충돌 시 먼지 위치
float3 contactPos = SphereCastToSphere(cur, next, sphere.xyz, dustRadius, sphere.w);
// 충돌 지점의 노멀 벡터
float3 contactNormal = (contactPos - sphere.xyz) / (dustRadius + sphere.w);
// 충돌 지점에서 원래 다음 위치를 향한 벡터 : 잉여 벡터
float3 extraVec = next - contactPos;
// 반사 벡터
float3 outVec = reflect(extraVec, contactNormal) * elasticity;
// 다음 프레임 위치 변경
next = contactPos + outVec;
// 속도 변경
velocity = reflect(velocity, contactNormal) * elasticity;
}
[4] 컴퓨트 쉐이더 - Update 커널
DustCompute.compute
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
void Update (uint3 id : SV_DispatchThreadID)
{
uint i = id.x;
if(dustBuffer[i].isAlive == FALSE) return;
if(i >= dustCount) return;
// ...
// ===================================================
// 속도 계산
// ===================================================
// ...
// ===================================================
// 이동 시뮬레이션, 충돌 검사
// ===================================================
// 다음 프레임 위치 계산 : S = S0 + V * t
float3 currPos = dustBuffer[i].position;
float3 nextPos = currPos + velocityBuffer[i] * deltaTime;
// [1] 월드 영역 제한(Cube)
// ...
// [2] Sphere Collider
float4 sphere = float4(0, 2.5, 0, 5);
bool sphereCollided = CheckSphereIntersection(float4(nextPos, radius), sphere);
if(sphereCollided)
{
CalculateSphereCollision(currPos, nextPos, velocityBuffer[i], sphere, radius, elasticity);
}
// 다음 위치 적용
dustBuffer[i].position = nextPos;
}
[5] 실행 결과


14. 여러 개의 Sphere Collider 구현
…
게임 내에서 직접 여러 개의 Sphere Collider를 배치하고 위치와 반지름을 수정할 수 있도록 구현한다.
Sphere Collider 데이터들은 하나의 Compute Buffer에 담아 전달하며,
변동사항이 생길 때마다 Compute Buffer의 데이터 역시 변경해주어야 한다.
[1] 컴퓨트 쉐이더
DustCompute.compute
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
/* Colliders */
RWStructuredBuffer<float4> sphereColliderBuffer;
uint sphereColliderCount;
void Update (uint3 id : SV_DispatchThreadID)
{
// ...
float3 currPos = dustBuffer[i].position;
float3 nextPos = currPos + velocityBuffer[i] * deltaTime;
// [1] 월드 영역 제한(Cube)
// ...
// [2] Sphere Colliders
for(uint scIndex = 0; scIndex < sphereColliderCount; scIndex++)
{
float4 sphere = sphereColliderBuffer[scIndex];
bool sphereCollided = CheckSphereIntersection(float4(nextPos, radius), sphere);
if(sphereCollided)
{
CalculateSphereCollision(currPos, nextPos, velocityBuffer[i], sphere, radius, elasticity);
}
}
// 다음 위치 적용
dustBuffer[i].position = nextPos;
}
[2] 구형 충돌체 컴포넌트
DustSphereCollider.cs
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
/* public class DustSphereCollider : MonoBehaviour */
[SerializeField] private Vector3 position = Vector3.zero;
[SerializeField] private float radius = 1f;
private DustManager dustManager;
public Vector4 SphereData => new Vector4(
position.x, position.y, position.z, radius
);
private void OnValidate()
{
ValidateData();
}
private void OnEnable()
{
if (dustManager == null)
dustManager = FindObjectOfType<DustManager>();
ValidateData();
dustManager.AddSphereCollider(this);
}
private void OnDisable()
{
dustManager.RemoveSphereCollider(this);
}
private void ValidateData()
{
if (radius < 0.1f)
radius = 0.1f;
transform.position = position;
transform.localScale = Vector3.one * 2f * radius;
}
[3] 먼지 관리 컴포넌트
DustManager.cs - SphereColliderSet
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
private class SphereColliderSet
{
/* Collider */
private ComputeBuffer colliderBuffer;
private List<DustSphereCollider> colliders;
/* Data */
private Vector4[] dataArray;
private int dataCount;
/* Compute Shader, Compute Buffer */
private ComputeShader computeShader;
private int shaderKernel;
private string bufferName;
private string countVariableName;
public SphereColliderSet(ComputeShader computeShader, int shaderKernel, string bufferName, string countVariableName)
{
this.colliders = new List<DustSphereCollider>(4);
this.dataArray = new Vector4[4];
this.computeShader = computeShader;
this.shaderKernel = shaderKernel;
this.bufferName = bufferName;
this.countVariableName = countVariableName;
this.dataCount = 0;
colliderBuffer = new ComputeBuffer(1, 4); // 기본 값
computeShader.SetBuffer(shaderKernel, bufferName, colliderBuffer);
computeShader.SetInt(countVariableName, 0);
}
~SphereColliderSet()
{
ReleaseBuffer();
}
private void ReleaseBuffer()
{
if (colliderBuffer != null)
colliderBuffer.Release();
}
private void ExpandDataArray()
{
Vector4[] newArray = new Vector4[this.dataArray.Length * 2];
Array.Copy(this.dataArray, newArray, dataCount);
this.dataArray = newArray;
}
/// <summary> Collider 리스트로부터 Vector4 배열에 데이터 전달 </summary>
private void UpdateDataArray()
{
if (dataArray.Length < dataCount)
ExpandDataArray();
for (int i = 0; i < dataCount; i++)
{
dataArray[i] = colliders[i].SphereData;
}
}
/// <summary> 컴퓨트 버퍼의 데이터를 새롭게 갱신하고 컴퓨트 쉐이더에 전달 </summary>
public void UpdateBuffer()
{
ReleaseBuffer();
if (dataCount == 0) return;
UpdateDataArray();
colliderBuffer = new ComputeBuffer(dataCount, sizeof(float) * 4);
colliderBuffer.SetData(dataArray, 0, 0, dataCount);
computeShader.SetBuffer(shaderKernel, bufferName, colliderBuffer);
computeShader.SetInt(countVariableName, dataCount);
}
public void AddCollider(DustSphereCollider collider)
{
if (colliders.Contains(collider)) return;
dataCount++;
colliders.Add(collider);
UpdateBuffer();
}
public void RemoveCollider(DustSphereCollider collider)
{
if (!colliders.Contains(collider)) return;
dataCount--;
colliders.Remove(collider);
UpdateBuffer();
}
}
private SphereColliderSet sphereColliderSet;
public void AddSphereCollider(DustSphereCollider collider)
{
if (sphereColliderSet == null)
{
afterInitJobQueue.Enqueue(() => sphereColliderSet.AddCollider(collider));
}
else
{
sphereColliderSet.AddCollider(collider);
}
}
public void RemoveSphereCollider(DustSphereCollider collider)
{
if (sphereColliderSet == null) return;
sphereColliderSet.RemoveCollider(collider);
}
DustManager.cs
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
// 게임 시작 시 초기화 작업 완료 후 처리
private Queue<Action> afterInitJobQueue = new Queue<Action>();
private void Start()
{
// ...
InitColliders();
ProcessInitialJobs();
}
private void InitColliders()
{
sphereColliderSet = new SphereColliderSet(this.dustCompute, kernelUpdateID, "sphereColliderBuffer", "sphereColliderCount");
}
[4] 실행 결과
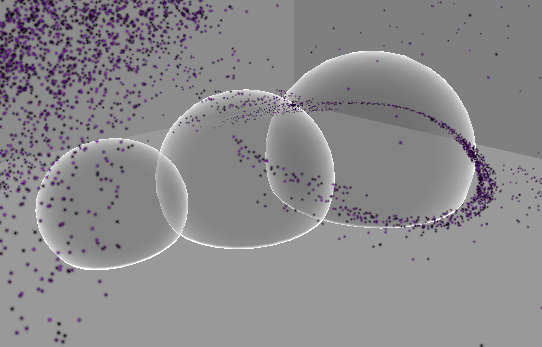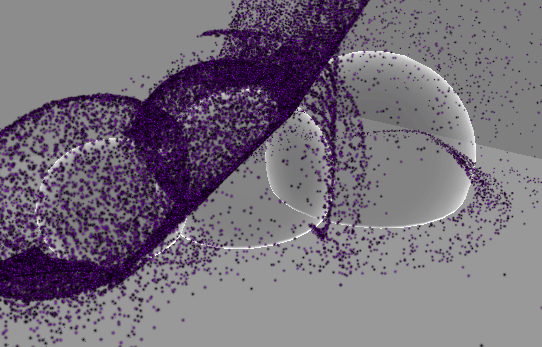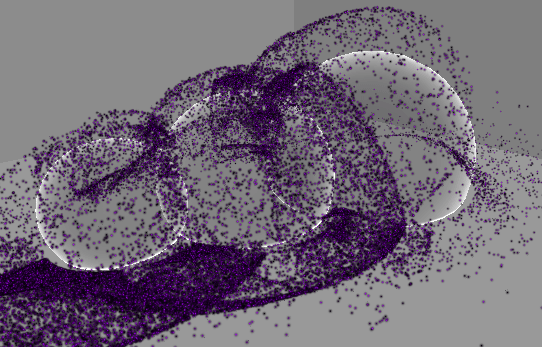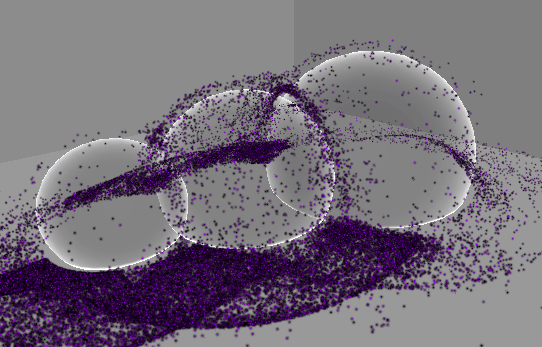
15. 투사체 발사 및 폭발 효과 구현
…
투사체를 발사하여 충돌체에 닿으면 폭발하는 기능을 구현한다.
[1] 충돌체 동기화 방식
컴퓨트 쉐이더 내에서 World Bounds, Sphere Collider가 구현되어 있다.
이는 유니티엔진 내에서 사용할 수 있는 물리 엔진의 Collider와는 별개이므로, 두 가지 선택지가 있다.
- 투사체의 움직임, 충돌 감지를 모두 컴퓨트 쉐이더 내에서 구현한다.
- 컴퓨트 쉐이더 내의 충돌체들을 유니티 엔진 내에서 컴포넌트로 동일하게 생성한다.
1번의 방식대로 구현하려면, 일단 현재 사용 중인 DustCompute 컴퓨트 쉐이더 내에서는 할 수 없다.
DustCompute에서 실제로 동작하는 각각의 스레드는, 각자 하나의 먼지를 담당하여 동작한다.
그러니 이 컴퓨트 쉐이더의 수십만 스레드 전부가 투사체의 움직임을 중복해서 계산할 수는 없는 노릇이고,
그렇다고 투사체의 개수만큼의 스레드를 지정해서 계산토록 하는 것은 병렬처리의 불균형을 초래하므로 바람직하지 않다.
그래서 또다른 컴퓨트 쉐이더를 구현하자니, 고작 몇 개의 투사체 연산 때문에 컴퓨트 쉐이더를 사용하는건 오히려 낭비이므로 차라리 CPU에서 연산하는 것이 낫다.
따라서 2번을 선택하여, 컴퓨트 쉐이더 내의 충돌체를 CPU, 즉 유니티 월드 내에도 동기화하여 유니티의 물리엔진을 활용하는 것이 낫다.
어차피 컴퓨트 쉐이더에서 충돌체들을 선언하여 사용하는 것이 아니라, 애초에 CPU에서 충돌체 정보를 정의하여 컴퓨트 쉐이더에 전달해주는 방식이었으므로
이 충돌체 정보들을 토대로 Collider 컴포넌트들을 추가해주고 투사체의 움직임은 Rigidbody를 기반으로 구현하면 된다.
다시 말해, CPU에서 정의한 충돌체를 컴퓨트 쉐이더와 유니티 물리엔진이 동기화하여 사용하는 것이다.
[2] 유니티 엔진에서 충돌체 추가
방법은 아주 간단하다.
월드 영역을 제한하는 World Bounds는 큐브 형태지만,
일반적인 큐브 콜라이더와는 달리 충돌 영역이 외부가 아니라 내부를 향한다.
월드 영역 메시도 폴리곤이 내부를 향하도록 구현되어 있으므로,
그냥 Mesh Collider 컴포넌트만 추가해주면 된다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
/* DustManager.cs */
private void InitWorldBounds()
{
// ...
if (!worldGO.TryGetComponent(out MeshCollider _))
worldGO.AddComponent<MeshCollider>();
// ...
}
마찬가지로 DustSphereCollider 클래스에서도 SphereCollider 컴포넌트를 추가해준다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
/* DustSphereCollider.cs */
private void OnEnable()
{
// ...
if (!TryGetComponent(out SphereCollider _))
gameObject.AddComponent<SphereCollider>();
}
모든 충돌체 게임오브젝트는 DustCollider 컴포넌트를 가지며, "DustCollider" 태그로 설정한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
public class DustCollider : MonoBehaviour
{
public const string ColliderTag = "DustCollider";
protected void Awake()
{
tag = ColliderTag;
}
}
[3] 투사체 구현
발사되는 투사체를 구현한다.
Rigidbody를 통해 물리엔진 기반으로 이동하며,
Sphere Collider를 통해 OnTriggerEnter() 메소드에서 충돌을 감지한다.
"DustCollider" 태그를 갖는 충돌체를 감지할 경우, 스스로를 파괴하며 DustManager의 Explode() 메소드를 실행한다.
Rigidbody, Sphere Collider 컴포넌트와 함께 하나의 게임오브젝트에 담아서 미리 프리팹화한다.
CannonBall.cs
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
public class CannonBall : MonoBehaviour
{
[SerializeField] private Rigidbody rBody;
private float explosionSqrRange;
private float explosionForce;
private void Init()
{
if (rBody == null)
rBody = GetComponent<Rigidbody>();
if (rBody == null)
rBody = gameObject.AddComponent<Rigidbody>();
TryGetComponent(out Collider col);
col.isTrigger = true;
}
public void Shoot(in Vector3 movement, in float explosionRange, in float explosionForce, in float lifespan = 5f)
{
Init();
Destroy(gameObject, lifespan);
rBody.AddForce(movement, ForceMode.Impulse);
this.explosionSqrRange = explosionRange * explosionRange;
this.explosionForce = explosionForce;
}
private void OnTriggerEnter(Collider other)
{
if (other.CompareTag(DustCollider.ColliderTag) == false) return;
DustManager.Instance.Explode(transform.position, explosionSqrRange, explosionForce);
Destroy(gameObject);
}
}
[4] 발사대 구현
Cone 클래스를 상속받는 Cannon 클래스를 정의한다.
발사 쿨타임을 설정하며, 쿨타임이 돌아왔을 때 isRunning 필드가 true 값을 갖게될 경우 포탄 프리팹을 복제하여 발사한다.
Cannon.cs
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
public class Cannon : Cone
{
[Header("Cannon Options")]
[SerializeField] private GameObject cannonBallPrefab;
[Range(1, 200f)]
[SerializeField] private float explosionRange = 25f;
[Range(100f, 10000f)]
[SerializeField] private float explosionForce = 3000f;
[Range(0.1f, 2f)]
[SerializeField] private float shootingInterval = 1f;
private float currentCooldown = 0f;
private void Update()
{
if (currentCooldown > 0f)
currentCooldown -= Time.deltaTime;
// 발사
if (isRunning && currentCooldown <= 0f)
{
currentCooldown = shootingInterval;
Shoot();
}
}
public void Shoot()
{
GameObject clone = Instantiate(cannonBallPrefab, transform.position, Quaternion.identity);
CannonBall ball = clone.GetComponent<CannonBall>();
ball.Shoot(transform.forward * force, explosionRange, explosionForce);
}
}
[5] Explode 커널 구현
폭발 중심 위치로부터 구 범위 내의 먼지를 밀쳐내는 기능을 별도의 커널로 작성한다.
DustCompute.compute
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
#pragma kernel Explode
/* Explode */
float3 explosionPosition; // 폭발 중심 위치
float explosionSqrRange; // 폭발 반지름 - 제곱
float explosionForce; // 폭발 힘
void Explode (uint3 id : SV_DispatchThreadID)
{
uint i = id.x;
if(dustBuffer[i].isAlive == FALSE) return;
if(i >= dustCount) return;
float3 dustPos = dustBuffer[i].position; // 현재 프레임 먼지 위치
float3 centerToDust = (dustPos - explosionPosition); // 폭발 중심 -> 먼지
float sqrDist = SqrMagnitude(centerToDust); // 폭발 중심<-> 먼지 사이 거리 제곱
// 구형 범위 내에 포함되는 경우
if (sqrDist < explosionSqrRange)
{
float t = 1 - (sqrDist / explosionSqrRange);
float f = t * explosionForce;
float3 dir = normalize(centerToDust);
float3 F = dir * f;
float3 A = F / mass;
velocityBuffer[i] += A * deltaTime;
}
}
[6] 먼지 관리 컴포넌트
우선, 편의상 싱글톤 클래스로 정의한다.
그리고 다른 Cone들과 마찬가지로 Cannon 필드를 작성하며,
키보드 4 키를 눌러 선택할 수 있게 한다.
Cannon에 의해 투사체를 발사하는 메소드 Explode()를 작성하며,
이 메소드 내에서는 Explode 커널에 필요한 변수 값들을 전달하고, 해당 커널을 실행한다.
DustManager.cs
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
// 싱글톤
public static DustManager Instance => _instance;
private static DustManager _instance;
private void Awake()
{
_instance = this;
}
// 다른 커널들과 동일한 방식의 kernelID 등의 내용은 생략 //
public void Explode(in Vector3 position, in float sqrRange, in float force)
{
dustCompute.SetVector("explosionPosition", position);
dustCompute.SetFloat("explosionSqrRange", sqrRange);
dustCompute.SetFloat("explosionForce", force);
dustCompute.Dispatch(kernelExplode, kernelGroupSizeX, 1, 1);
}
[7] 실행 결과
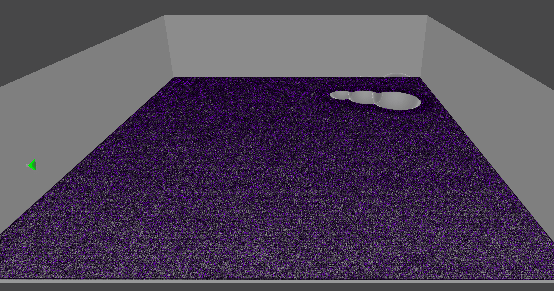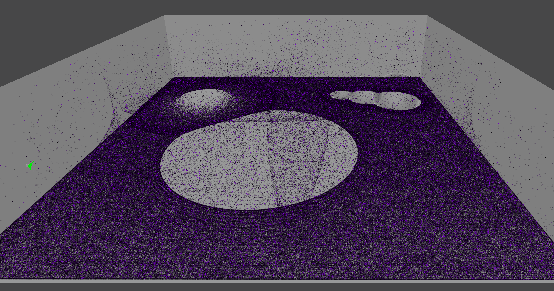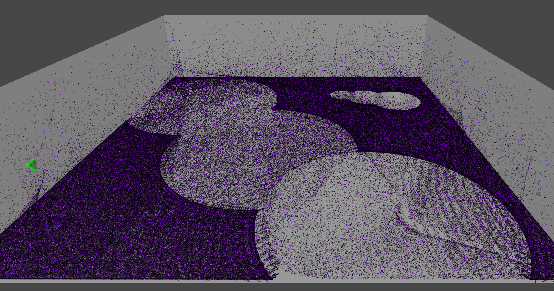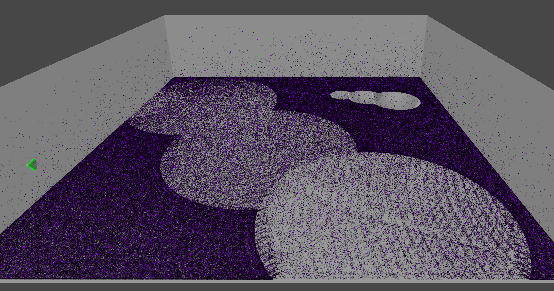

[8] 폭발 이펙트 추가

16. Box(AABB) Collision 구현
…
Sphere Collider의 정의에 필요한 데이터는 위치(float3)와 반지름(float)이다.
반면 Box Collider를 정의하기 위해 필요한 데이터는 위치(float3)와 크기(float3) 또는 최소 지점(float3)과 최대 지점(float3)이다.
이 중에서 최소 지점과 최대 지점을 통해 Box Collider를 정의한다.
[1] DustCollider 클래스 수정
컴퓨트 쉐이더에서 전달할 데이터를 제네릭을 통해 콜라이더마다 정의할 수 있도록, 아래와 같이 수정한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
public abstract class DustCollider<T> : MonoBehaviour
{
public abstract T Data { get; }
// ...
}
[2] DustBoxCollider 클래스 작성
유니티 엔진의 Bounds 구조체와 호환되는 MinMaxBounds 구조체를 작성하고,
이를 Data로 사용하는 DustBoxCollider 클래스를 작성한다.
트랜스폼의 스케일을 기반으로 콜라이더 영역이 정의된다.
DustBoxCollider.cs
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
/// <summary>
/// Box Collider를 위한 Min-Max 데이터
/// </summary>
public struct MinMaxBounds
{
public Vector3 min;
public Vector3 max;
public static MinMaxBounds FromBounds(in Bounds bounds)
{
MinMaxBounds mmb = default;
mmb.min = bounds.min;
mmb.max = bounds.max;
return mmb;
}
}
public class DustBoxCollider : DustCollider<MinMaxBounds>
{
public override MinMaxBounds Data
{
get
{
Bounds b = default;
b.center = transform.position;
b.extents = transform.lossyScale * 0.5f;
return MinMaxBounds.FromBounds(b);
}
}
}
[3] 제네릭 ColliderSet 클래스 작성
기존의 SphereColliderSet 클래스를 제네릭화하여,
Data를 정의하기만 하면 앞으로 작성할 모든 콜라이더를 같은 방식으로 관리할 수 있도록 한다.
DustManager.cs
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
private class ColliderSet<TCol, TData> where TCol : DustCollider<TData>
{
/* Collider */
private ComputeBuffer colliderBuffer;
private List<TCol> colliders;
/* Data */
private TData[] dataArray;
private int dataCount;
private int dataStride;
/* Compute Shader, Compute Buffer */
private ComputeShader computeShader;
private int shaderKernel; // Update Kernel
private string bufferName;
private string countVariableName;
public ColliderSet(ComputeShader computeShader, int shaderKernel, string bufferName, string countVariableName, int dataStride)
{
this.colliders = new List<TCol>(4);
this.dataArray = new TData[4];
this.computeShader = computeShader;
this.shaderKernel = shaderKernel;
this.bufferName = bufferName;
this.countVariableName = countVariableName;
this.dataStride = dataStride;
this.dataCount = 0;
colliderBuffer = new ComputeBuffer(1, 4); // 기본 값
computeShader.SetBuffer(shaderKernel, bufferName, colliderBuffer);
computeShader.SetInt(countVariableName, 0);
}
~ColliderSet()
{
ReleaseBuffer();
}
private void ReleaseBuffer()
{
if (colliderBuffer != null)
colliderBuffer.Release();
}
private void ExpandDataArray()
{
TData[] newArray = new TData[this.dataArray.Length * 2];
Array.Copy(this.dataArray, newArray, this.dataArray.Length);
this.dataArray = newArray;
}
/// <summary> 컴퓨트 버퍼의 데이터를 새롭게 갱신하고 컴퓨트 쉐이더에 전달 </summary>
private void ReallocateBuffer()
{
ReleaseBuffer();
if (dataCount == 0) return;
colliderBuffer = new ComputeBuffer(dataCount, dataStride);
computeShader.SetInt(countVariableName, dataCount);
UpdateColliderData();
}
/// <summary> 배열 내부의 콜라이더 데이터만 갱신하여 컴퓨트 쉐이더에 전달 </summary>
public void UpdateColliderData()
{
if (dataArray.Length < dataCount)
ExpandDataArray();
for (int i = 0; i < dataCount; i++)
{
dataArray[i] = colliders[i].Data;
}
colliderBuffer.SetData(dataArray, 0, 0, dataCount);
computeShader.SetBuffer(shaderKernel, bufferName, colliderBuffer);
}
public void AddCollider(TCol collider)
{
if (colliders.Contains(collider)) return;
dataCount++;
colliders.Add(collider);
ReallocateBuffer();
}
public void RemoveCollider(TCol collider)
{
if (!colliders.Contains(collider)) return;
dataCount--;
colliders.Remove(collider);
ReallocateBuffer();
}
}
[4] Collider API 작성
콜라이더에서 호출하기 위한 DustManager의 메소드들을 공통 기능 Add, Update, Remove로 묶어 제네릭화한다.
그리고 각 콜라이더 메소드에서는 간단히 호출할 수 있도록 한 줄씩만 작성해주면 된다.
DustManager.cs
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
private ColliderSet<DustSphereCollider, Vector4> sphereColliderSet;
private ColliderSet<DustBoxCollider, MinMaxBounds> boxColliderSet;
/* Generic Collider Methods */
private void AddCollider<TCol, TData>(Func<ColliderSet<TCol, TData>> getter, TCol collider) where TCol : DustCollider<TData>
{
var colSet = getter();
if (colSet == null)
{
afterInitJobQueue.Enqueue(() => getter().AddCollider(collider));
}
else
{
colSet.AddCollider(collider);
}
}
/// <summary> ColliderSet의 내부 컴퓨트 버퍼 갱신 </summary>
private void UpdateCollider<TCol, TData>(ColliderSet<TCol, TData> set) where TCol : DustCollider<TData>
{
if (set != null)
set.UpdateColliderData();
}
/// <summary> ColliderSet에서 Collider 제거 </summary>
private void RemoveCollider<TCol, TData>(ColliderSet<TCol, TData> set, TCol collider) where TCol : DustCollider<TData>
{
if (set != null)
set.RemoveCollider(collider);
}
/* Sphere Collider */
public void AddSphereCollider(DustSphereCollider collider)
{
AddCollider(() => sphereColliderSet, collider);
}
public void UpdateSphereCollider()
{
UpdateCollider(sphereColliderSet);
}
public void RemoveSphereCollider(DustSphereCollider collider)
{
RemoveCollider(sphereColliderSet, collider);
}
/* Box Collider */
public void AddBoxCollider(DustBoxCollider collider)
{
AddCollider(() => boxColliderSet, collider);
}
public void UpdateBoxCollider()
{
UpdateCollider(boxColliderSet);
}
public void RemoveBoxCollider(DustBoxCollider collider)
{
RemoveCollider(boxColliderSet, collider);
}
[5] AABB 충돌 감지
AABB와 Dust(Sphere)의 충돌 감지는 간단하다.
DustCompute.compute
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
// 구체와 육면체(AABB)의 충돌 여부 검사
// AABB : Axis Aligned Bounding Box
// S : 구체의 위치
// r : 구체의 반지름
bool SphereToAABBIntersection(float3 S, float r, Bounds aabb)
{
// Future Works : 최적화
// [1] AABB까지의 최단지점 계산
float3 C = S;
if (C.x < aabb.min.x) C.x = aabb.min.x;
else if (C.x > aabb.max.x) C.x = aabb.max.x;
if (C.y < aabb.min.y) C.y = aabb.min.y;
else if (C.y > aabb.max.y) C.y = aabb.max.y;
if (C.z < aabb.min.z) C.z = aabb.min.z;
else if (C.z > aabb.max.z) C.z = aabb.max.z;
// [2] 거리 비교
return SqrMagnitude(C - S) <= r * r;
}
[6] AABB 충돌 처리
AABB를 먼지의 반지름만큼 각 면을 확장시켜, 레이캐스트를 통해 검사한다.
그리고 Sphere Collider와 마찬가지로 반사 벡터를 계산하여
먼지의 다음 프레임 위치와 속도를 변경 적용한다.
DustCompute.compute
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
// Box(AABB) Collider에 충돌 검사하여 먼지 위치 및 속도 변경
// - cur : 현재 프레임에서의 위치
// - next : 다음 프레임에서의 위치 [INOUT]
// - velocity : 현재 이동 속도 [INOUT]
// - dustRadius : 먼지 반지름
// - box : Box 영역 범위
// - elasticity : 탄성력 계수(0 ~ 1) : 충돌 시 보존되는 운동량 비율
void DustToAABBCollision(float3 cur, inout float3 next, inout float3 velocity,
float dustRadius, Bounds box, float elasticity, inout bool handled)
{
/*
[흐름]
1. 레이의 xyz 성분 각각 부호를 판단하여 큐브의 평면 후보 6개를 3개로 줄인다.
2. 레이를 평면 3개(먼지 반지름 고려하여 확장)에 차례로 캐스트하여 접점을 구한다.
3. 얻은 접점이 각각의 면 범위 내에 있다면 해당 위치를 충돌지점으로 결정한다.
4. 레이와 속도 벡터에 대해 반사 벡터와 반사 속도를 구한다.
5. 탄성력을 적용하여 다음 위치와 다음 속도를 결정한다.
*/
// 먼지 반지름 고려하기
float3 boxMin = box.min - dustRadius;
float3 boxMax = box.max + dustRadius;
/* 지역변수 */
float3 ray = next - cur;
float3 contact = 0;
half3 raySign = (ray >= 0);
int flag = FLAG_ERROR; // XYZ 선택 플래그
/* 큐브 6면에 캐스트하여 충돌 지점 구하기 */
//if(flag == FLAG_ERROR)
{
if(raySign.x > 0) contact = RaycastToPlaneYZ(cur, next, boxMin.x);
else contact = RaycastToPlaneYZ(cur, next, boxMax.x);
if(InRange2(contact.yz, boxMin.yz, boxMax.yz))
flag = FLAG_X;
}
if(flag == FLAG_ERROR)
{
if(raySign.y > 0) contact = RaycastToPlaneXZ(cur, next, boxMin.y);
else contact = RaycastToPlaneXZ(cur, next, boxMax.y);
if(InRange2(contact.xz, boxMin.xz, boxMax.xz))
flag = FLAG_Y;
}
if(flag == FLAG_ERROR)
{
if(raySign.z > 0) contact = RaycastToPlaneXY(cur, next, boxMin.z);
else contact = RaycastToPlaneXY(cur, next, boxMax.z);
if(InRange2(contact.xy, boxMin.xy, boxMax.xy))
flag = FLAG_Z;
}
/* 최종 계산 */
float rayLen = length(ray);
float inLen = length(contact - cur); // 입사 벡터 길이
float rfLen = (rayLen - inLen) * elasticity; // 반사 벡터 길이(탄성 적용)
float3 rfRay = Reverse(ray, flag) * (rfLen / rayLen); // 반사 벡터
float3 rfVel = Reverse(velocity, flag) * elasticity; // 반사 속도 벡터(탄성 적용)
/* 변경사항 적용 */
next = contact + rfRay;
velocity = rfVel;
handled = true;
}
[7] Update 커널 수정
Sphere Collider와 마찬가지로, 반복문을 이용해 Box Collider들의 충돌을 계산한다.
여기서 한 가지 처리를 더해주는데, 바로 bool 타입의 CollisionFlag이다.
기존에는 한 프레임 내에서 여러 콜라이더에 의해 충돌이 발생할 수 있었지만
그렇게 되면 콜라이더가 겹친 위치에서 양측 콜라이더의 충돌 처리에 의해
서로 반대 방향으로 동일한 속도로 이동하려고 하다보니
두 방향 중 어느쪽으로도 완전히 이동하지 못하고 제자리에서 무한히 진동하는 현상이 발생한다.
따라서 이를 막기 위해 충돌 시 CollisionFlag를 true로 설정하고
이번 프레임에 충돌 처리가 발생했는지 여부를 검사하여
한 프레임 내에서는 단 하나의 콜라이더에 의한 충돌이 가능하도록 수정한다.
DustCompute.compute
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
RWStructuredBuffer<bool> collisionFlagBuffer; // 이번 프레임 충돌 처리 여부
RWStructuredBuffer<Bounds> boxColliderBuffer;
uint boxColliderCount;
void Update (uint3 id : SV_DispatchThreadID)
{
// ...
float3 currPos = dustBuffer[i].position;
float3 nextPos = currPos + velocityBuffer[i] * deltaTime;
// 이번 프레임 충돌 처리 완료 여부 초기화
collisionFlagBuffer[i] = false;
// [1] Sphere Colliders
for(uint scIndex = 0; scIndex < sphereColliderCount; scIndex++)
{
// 이번 프레임에 이미 충돌한 경우, 더이상 충돌 처리하지 않음
if(collisionFlagBuffer[i] == true) continue;
// ...
}
// [2] Box Colliders
for(uint bcIndex = 0; bcIndex < boxColliderCount; bcIndex++)
{
if(collisionFlagBuffer[i] == true) continue;
Bounds box = boxColliderBuffer[bcIndex];
if(CheckBoxIntersection(nextPos, radius, box))
{
CalculateBoxCollision(currPos, nextPos, velocityBuffer[i], radius, box, elasticity, collisionFlagBuffer[i]);
}
}
// [Last] 월드 영역 제한(Box)
// ...
// 다음 위치 적용
dustBuffer[i].position = nextPos;
}
[8] 실행 결과
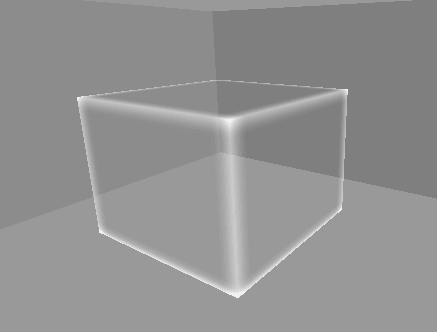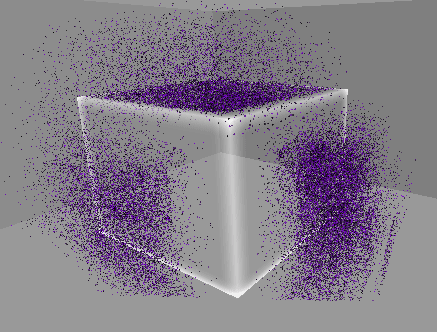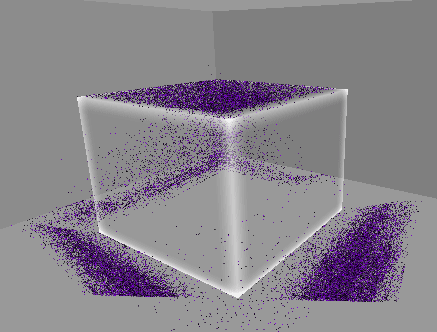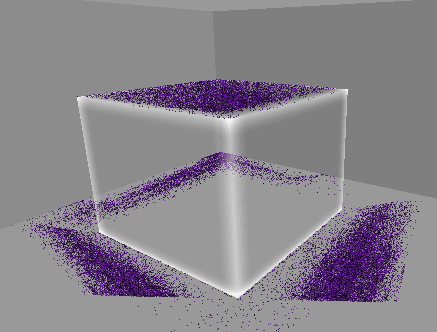
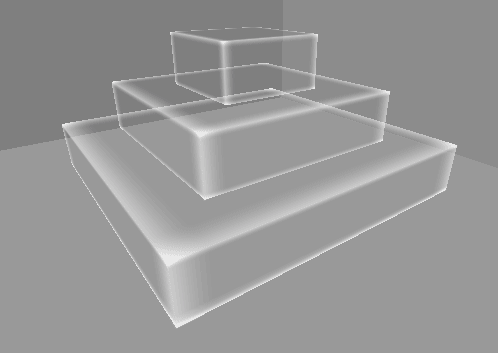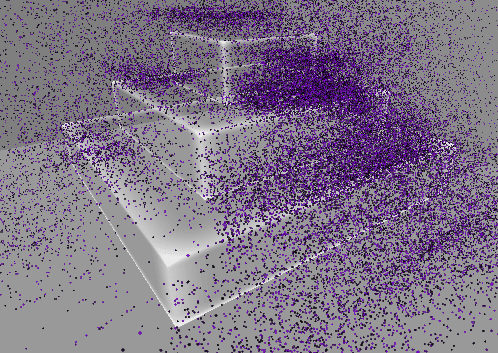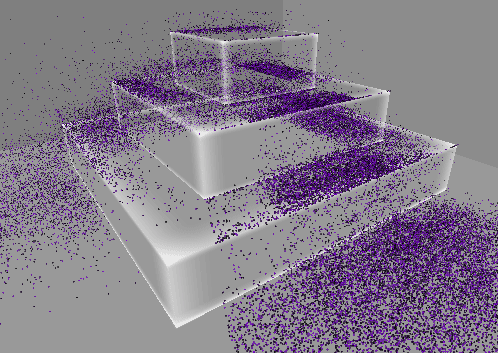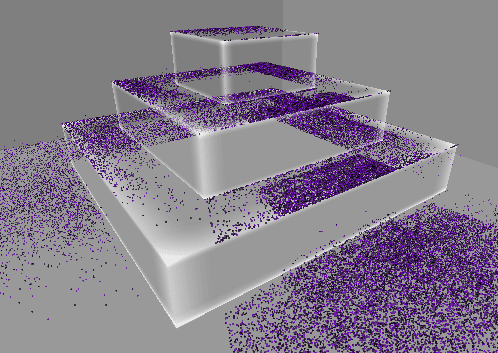
추가 : 타임스케일 변경 기능, deltaTime 수정
…
[1] DustManager
DustManager 컴포넌트에 게임 진행 속도를 조절할 수 있는 기능을 추가한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
[Header("Game")]
[Range(0, 1f)]
[SerializeField] private float timescale = 1f;
private void Update()
{
Time.timeScale = timescale;
// ...
}
[2] 컴퓨트 쉐이더
게임 진행 속도가 다르더라도 물리 시뮬레이션은 일관성 있게 진행되어야 한다.
지금까지 가속도에 의한 속도 계산은 모두 \(v = a \cdot \Delta t\) 꼴로 작성되어 있는데,
‘순간적 충격에 의한 속도 변화’의 경우 이는 일관성 없는 결과를 보여주게 된다.
예를 들어 폭발 기능을 구현하는 Explode 커널의 경우
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
void Explode (uint3 id : SV_DispatchThreadID)
{
// ...
if (sqrDist < explosionSqrRange)
{
// ...
float3 F = dir * f;
float3 A = F / mass;
velocityBuffer[i] += A * deltaTime;
}
}
위와 같이 Δv = a * deltaTime 꼴인데,
이건 사실 타임스케일 변동이 없더라도 문제가 될수 있는 부분이다.
게임 루프의 deltaTime에 의존하기 때문에
극단적인 예시로 deltaTime = 0.0001인 경우에 Explode가 발생하면
먼지는 아주 미세하게 움직일 수 있다.
따라서 순간적 충격이 발생하는 물리 연산의 경우,
deltaTime 대신 고정된 임의의 Δt를 정의하여 사용하도록 한다.
1
#define CONSTANT_DELTA_TIME 0.02
현재 물리 연산을 구현하는 커널 목록은 다음과 같다.
Update(): 프레임 기반 실시간 가속도/속도/이동 계산VacuumUp(): 원뿔 범위 먼지 흡수Emit(): 먼지 방출(발사)BlowWind(): 먼지 밀쳐내기Explode(): 구형 범위 순간 폭발
이 중에서 일시적인 가속에 의한 순간 속도 변화가 발생하는 커널은
Emit, BlowWind, Explode 커널로,
해당 커널 함수들 내의 A * deltaTime 계산을 모두 A * CONST_DELTA_TIME으로 변경한다.
[3] 실행 결과
[3-1] deltaTime, timescale = 1
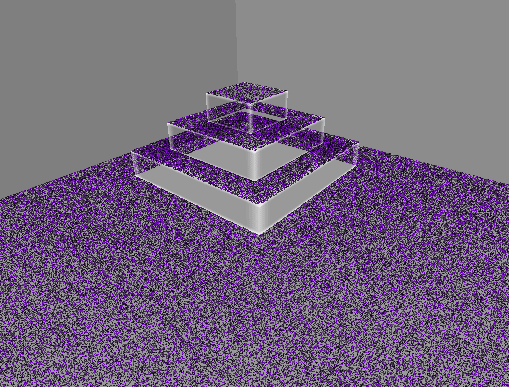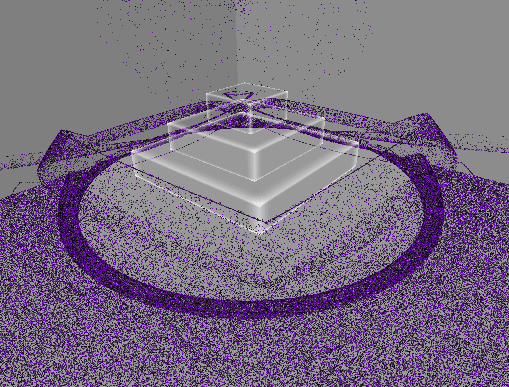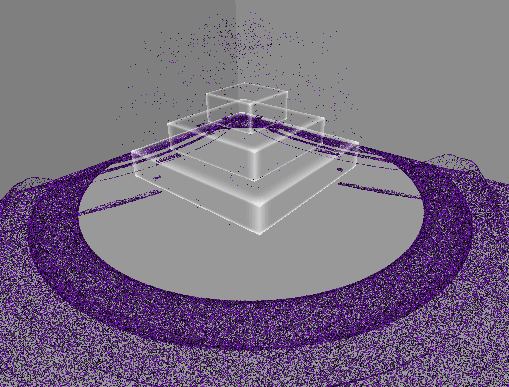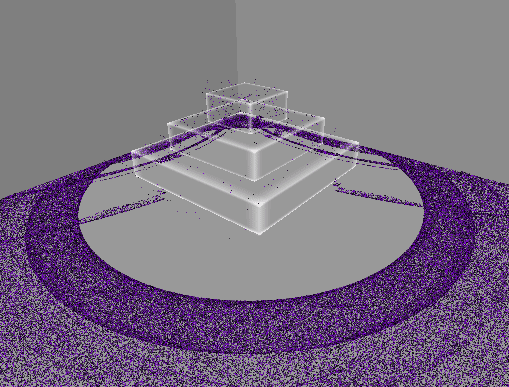
[3-2] deltaTime, timescale = 0.2

[3-3] CONST_DELTA_TIME, timescale = 0.2

17. Box(OBB) Collision 구현
…
[1] OBB란?
OBB는 Oriented Bounding Box의 약자로,
AABB처럼 마주보는 두 면끼리는 서로 평행하지만
모든 면이 공간의 축에 평행한 AABB와는 다르게 자유롭게 회전이 적용된 상자의 형태를 지닌다.
쉽게 말해, 회전 변환이 적용된 AABB라고 보면 된다.
[2] OBB 충돌 구현 방법
OBB는 AABB보다 구현이 어렵다.
특히나 3차원에서는 2차원보다 더 어렵고 번거롭다.
그래서 이걸 비교적 간단하게 구현할 수 있는 방법이 있는데,
바로 공간 변환을 이용하는 것이다.
큐브의 기본 형태는 중심 좌표가 (0, 0, 0), 모든 모서리의 길이가 1인 AABB이다.
모든 OBB는 이 기본 큐브를 위치, 회전, 크기 변환을 수행하여 만들 수 있다.
그러므로 OBB 충돌체의 데이터는 변환 행렬만 있으면 된다.
먼지를 AABB에 충돌시킬 때,
입력은 현재 프레임의 먼지 위치 벡터, 다음 프레임의 먼지 위치 벡터, 속도 벡터,
출력은 다음 프레임의 먼지 위치 벡터, 속도 벡터다.
세 개의 입력 벡터를 월드-로컬 공간 변환하여 콜라이더의 로컬 공간에서 AABB 충돌을 계산하고,
얻어낸 두 개의 출력 벡터를 다시 로컬-월드 공간변환하는 방식으로
기존의 AABB 충돌 계산을 이용해 OBB 충돌을 구현할 수 있다.
[3] 클래스 수정
제네릭으로 구현했던 ColliderSet 클래스에서 제네릭을 제거한다.
대신 모든 콜라이더가 컴퓨트 버퍼로 전달할 데이터를 변환 행렬로 통일한다.
컴퓨트 쉐이더의 각 스레드에서 매번 역행렬을 계산하는 것은 굉장히 손해이므로,
로컬-월드 변환 행렬과 월드-로컬 변환 행렬을 모두 전달한다.
그리고 충돌을 계산하는 콜라이더의 로컬 공간에서 먼지의 스케일을 재조정할 필요가 있는데,
변환 행렬에서 스케일을 따로 추출하기 위해 계산하는 것 역시 손해이므로 스케일 값도 함께 전달한다.
ColliderSet.cs
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
private class ColliderSet
{
private struct ColliderData
{
public Matrix4x4 localToWorld;
public Matrix4x4 worldToLocal;
public Vector3 scale;
public ColliderData(DustCollider collider)
{
localToWorld = collider.transform.localToWorldMatrix;
worldToLocal = collider.transform.worldToLocalMatrix;
scale = collider.transform.lossyScale;
}
}
/* Collider */
private ComputeBuffer colliderBuffer;
private List<DustCollider> colliders;
/* Data */
private ColliderData[] dataArray;
private int dataCount;
/* Compute Shader, Compute Buffer */
private ComputeShader computeShader;
private int shaderKernel; // Update Kernel
private string bufferName;
private string countVariableName;
public ColliderSet(ComputeShader computeShader, int shaderKernel, string bufferName, string countVariableName)
{
this.colliders = new List<DustCollider>(4);
this.dataArray = new ColliderData[4];
this.computeShader = computeShader;
this.shaderKernel = shaderKernel;
this.bufferName = bufferName;
this.countVariableName = countVariableName;
this.dataCount = 0;
colliderBuffer = new ComputeBuffer(1, 4); // 기본 값
computeShader.SetBuffer(shaderKernel, bufferName, colliderBuffer);
computeShader.SetInt(countVariableName, 0);
}
~ColliderSet()
{
ReleaseBuffer();
}
private void ReleaseBuffer()
{
if (colliderBuffer != null)
colliderBuffer.Release();
}
private void ExpandDataArray()
{
ColliderData[] newArray = new ColliderData[this.dataArray.Length * 2];
Array.Copy(this.dataArray, newArray, this.dataArray.Length);
this.dataArray = newArray;
}
/// <summary> 컴퓨트 버퍼의 데이터를 새롭게 갱신하고 컴퓨트 쉐이더에 전달 </summary>
private void ReallocateBuffer()
{
ReleaseBuffer();
if (dataCount == 0) return;
colliderBuffer = new ComputeBuffer(dataCount, sizeof(float) * 35);
computeShader.SetInt(countVariableName, dataCount);
UpdateColliderData();
}
/// <summary> 배열 내부의 콜라이더 데이터만 갱신하여 컴퓨트 쉐이더에 전달 </summary>
public void UpdateColliderData()
{
if (dataArray.Length < dataCount)
ExpandDataArray();
for (int i = 0; i < dataCount; i++)
{
dataArray[i] = new ColliderData(colliders[i]);
}
colliderBuffer.SetData(dataArray, 0, 0, dataCount);
computeShader.SetBuffer(shaderKernel, bufferName, colliderBuffer);
}
public void AddCollider(DustCollider collider)
{
if (colliders.Contains(collider)) return;
dataCount++;
colliders.Add(collider);
ReallocateBuffer();
}
public void RemoveCollider(DustCollider collider)
{
if (!colliders.Contains(collider)) return;
dataCount--;
colliders.Remove(collider);
ReallocateBuffer();
}
}
DustManager.cs
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
private ColliderSet sphereColliderSet;
private ColliderSet boxColliderSet;
/// <summary> ColliderSet에 새로운 Collider 추가 </summary>
private void AddCollider(Func<ColliderSet> getter, DustCollider collider)
{
var colSet = getter();
if (colSet == null)
{
afterInitJobQueue.Enqueue(() => getter().AddCollider(collider));
}
else
{
colSet.AddCollider(collider);
}
}
/// <summary> ColliderSet의 내부 컴퓨트 버퍼 갱신 </summary>
private void UpdateCollider(ColliderSet set)
{
if (set != null)
set.UpdateColliderData();
}
/// <summary> ColliderSet에서 Collider 제거 </summary>
private void RemoveCollider(ColliderSet set, DustCollider collider)
{
if (set != null)
set.RemoveCollider(collider);
}
[4] 컴퓨트 쉐이더 수정
DustCompute.compute
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
struct ColliderTransform
{
float4x4 localToWorld;
float4x4 worldToLocal;
float3 scale;
};
RWStructuredBuffer<ColliderTransform> sphereColliderBuffer;
uint sphereColliderCount;
RWStructuredBuffer<ColliderTransform> boxColliderBuffer;
uint boxColliderCount;
// AABB로 근사시킨 먼지를 기본 AABB(-0.5 ~ 0.5)와 교차 검사
bool DustToDefaultAABBIntersection(float3 pos, float3 scale)
{
if (pos.x + scale.x < -0.5) return false;
if (pos.y + scale.y < -0.5) return false;
if (pos.z + scale.z < -0.5) return false;
if (pos.x - scale.x > 0.5) return false;
if (pos.y - scale.y > 0.5) return false;
if (pos.z - scale.z > 0.5) return false;
return true;
}
void Update (uint3 id : SV_DispatchThreadID)
{
// ...
float3 currPos = dustBuffer[i].position;
float3 nextPos = currPos + velocityBuffer[i] * deltaTime;
// 이번 프레임 충돌 처리 완료 여부 초기화
collisionFlagBuffer[i] = false;
// [1] Sphere Colliders
for(uint scIndex = 0; scIndex < sphereColliderCount; scIndex++)
{
if(collisionFlagBuffer[i] == true) continue;
float4 sphere;
sphere.xyz = mul(sphereColliderBuffer[scIndex].localToWorld, float4(0, 0, 0, 1)).xyz;
sphere.w = sphereColliderBuffer[scIndex].scale.x * 0.5;
if(SphereToSphereIntersection(float4(nextPos, radius), sphere))
{
DustToSphereCollision(currPos, nextPos, velocityBuffer[i], radius, sphere, bounciness, collisionFlagBuffer[i]);
}
}
// [2] Box Colliders(OBB)
for(uint bcIndex = 0; bcIndex < boxColliderCount; bcIndex++)
{
if(collisionFlagBuffer[i] == true) continue;
Bounds box = DEFAULT_BOX_COLLIDER;
float4x4 WtL = boxColliderBuffer[bcIndex].worldToLocal;
float3 localNextPos = mul(WtL, float4(nextPos, 1)).xyz;
// 박스 로컬 스페이스에서의 먼지 스케일 계산
float3 localDustRadius = radius.xxx / boxColliderBuffer[bcIndex].scale;
// 박스 콜라이더의 로컬 스페이스에서 먼지 교차 검사(AABB-AABB)
if(DustToDefaultAABBIntersection(localNextPos, localDustRadius))
{
float3 localCurrPos = mul(WtL, float4(currPos, 1)).xyz;
float3 localVelocity = mul(WtL, float4(velocityBuffer[i], 0)).xyz;
// 박스 콜라이더의 로컬 스페이스에서 충돌 처리
DustToAABBCollision(localCurrPos, localNextPos, localVelocity, localDustRadius, box, bounciness, collisionFlagBuffer[i]);
float4x4 LtW = boxColliderBuffer[bcIndex].localToWorld;
nextPos = mul(LtW, float4(localNextPos, 1)).xyz;
velocityBuffer[i] = mul(LtW, float4(localVelocity, 0)).xyz;
}
}
// [Last] 월드 영역 제한(Box)
// ...
// 다음 위치 적용
dustBuffer[i].position = nextPos;
}
[5] 실행 결과
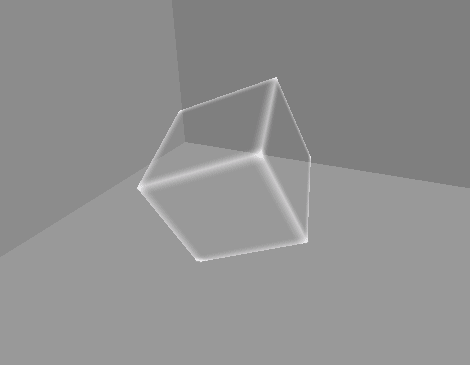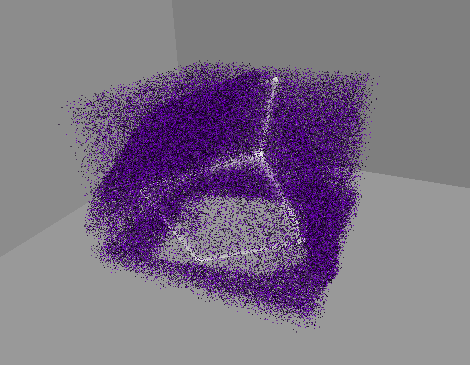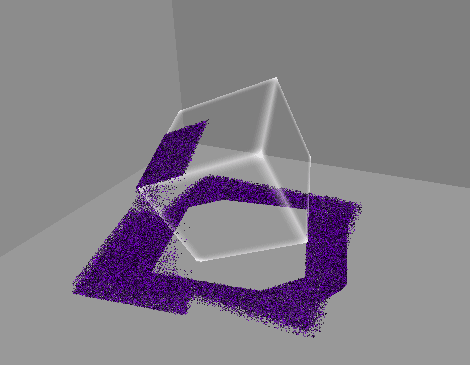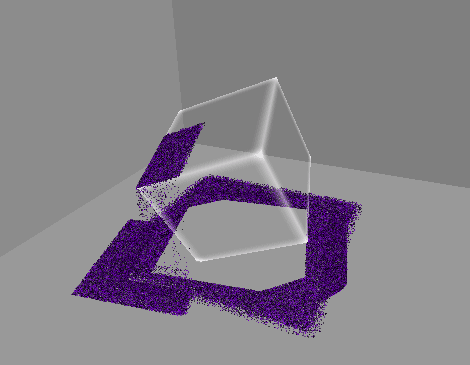
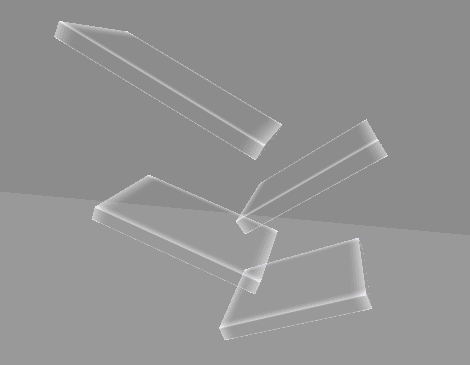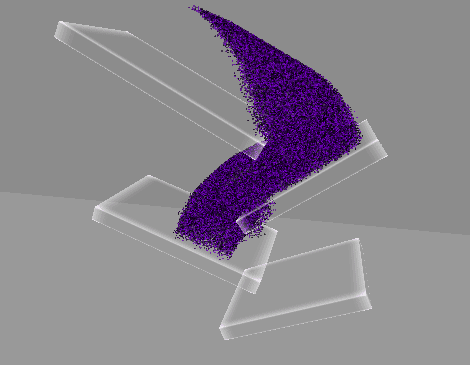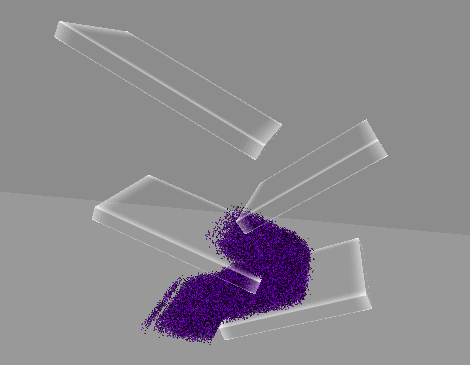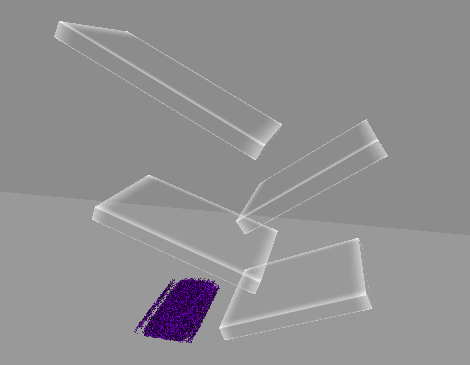
0. 글로벌 효과 구현
…
- 월드 내에 존재하는 모든 먼지에 적용되는 효과
- 바람
- 용권풍
- ..
0. 조작 개선
…
- WASD 이동
- Shift 달리기
- Ctrl 하강
- Space 상승
- Tab 모드 변경(흡수/방출/폭발 투사체), 원뿔 색상도 변경(Cyan/Yellow)/원기둥(Red)?
- Q/E 각도 변경
- Z/C 힘 변경
-
ESC 옵션 GUI 표시/미표시
- 옵션을 모두 조절할 수 있는 GUI 제공
- 중력을 3D로 조절할 수 있게 변경
0. 예쁘게 만들기
…
- 예쁜 방 꾸미기
- 예쁜 모델링 적용하기
- 미니 게임 만들기