베지어 곡선
- 점과 점 사이의 선형 보간(Lerp, Linear interpolation)을 이용해 그려내는 곡선
1차 베지어 곡선
-
Linear Curve
-
2개의 점
-
단순히 두 점 사이의 선형 보간을 통해, 직선을 그린다.
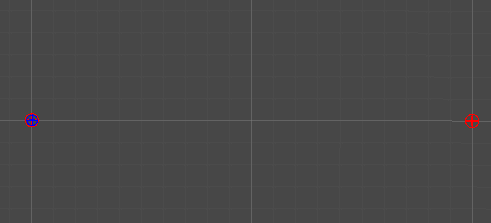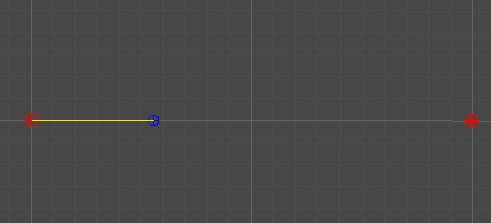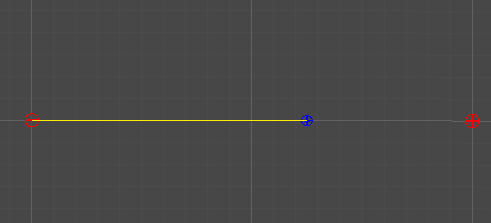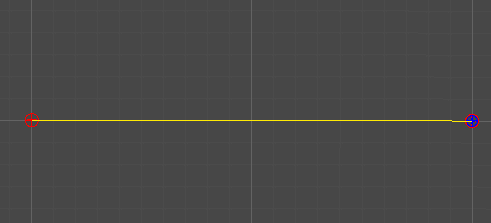
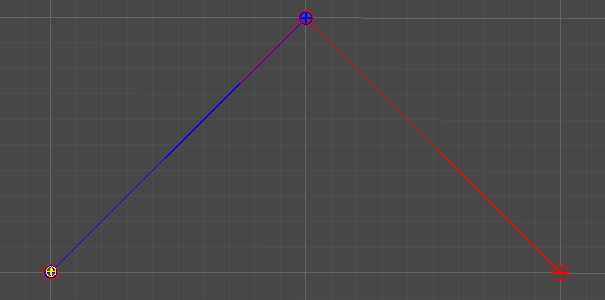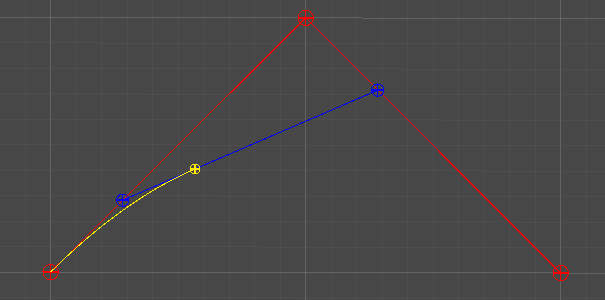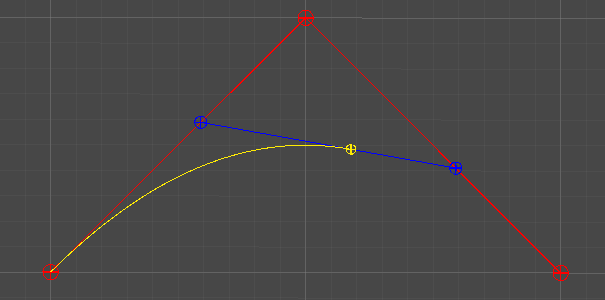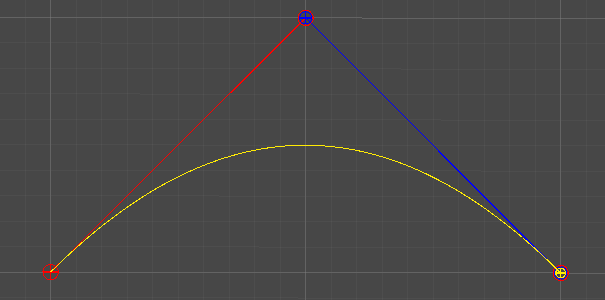
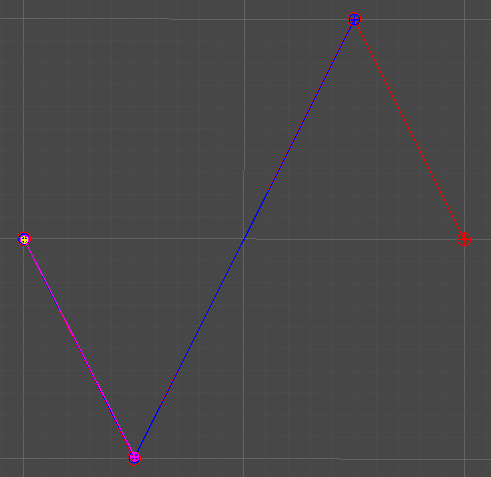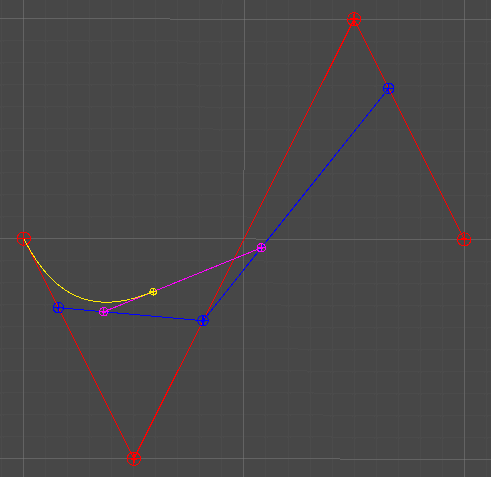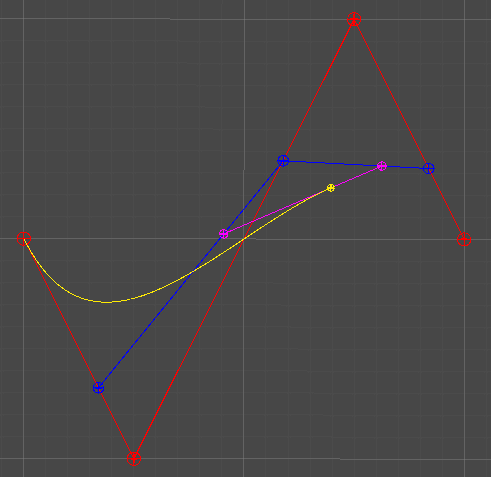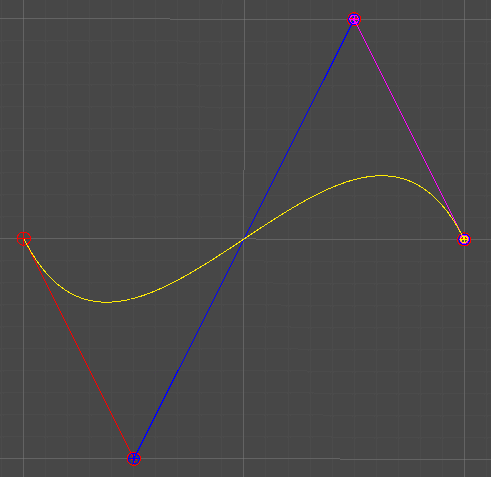
2차 베지어 곡선
-
Quadratic Curve
-
3개의 점 P0, P1, P2
-
Lerp(P0, P1, t)를 통해 보간된 지점 P01을 구한다.
-
Lerp(P1, P2, t)를 통해 보간된 지점 P02를 구한다.
-
P01, P02 역시 동일하게 보간하여, P012 = Lerp(P01, P02, t)를 구한다.
-
t = [0, 1]의 변화에 따라 그려지는 P012의 궤적에 따라 곡선이 그려진다.
Calculation Method
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
public Transform pointA;
public Transform pointB;
public Transform pointC;
private Vector3[] curvePoints;
/// <summary> 베지어 커브 내의 지점들 미리 계산 </summary>
private void CalculateCurvePoints(int count)
{
Vector3 pA = pointA.position;
Vector3 pB = pointB.position;
Vector3 pC = pointC.position;
curvePoints = new Vector3[count + 1];
float unit = 1.0f / count;
int i = 0; float t = 0f;
for (; i < count + 1; i++, t += unit)
{
float u = (1 - t);
float t2 = t * t;
float u2 = u * u;
curvePoints[i] =
pA * u2 +
pB * (t * u * 2) +
pC * t2
;
}
}
3차 베지어 곡선
-
Cubic Curve
-
4개의 점 P0, P1, P2, P3
-
2차 베지어 곡선과 같은 방식으로 인접한 점 두 개를 선형 보간하고, 얻어낸 점들을 다시 선형보간하기를 반복하여 최종적으로 하나의 점을 구한다.
-
최종 결과로 얻어낸 점의 이동궤적에 따라 곡선이 그려진다.
Calculation Method
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
public Transform pointA;
public Transform pointB;
public Transform pointC;
public Transform pointD;
private Vector3[] curvePoints;
/// <summary> 베지어 커브 내의 지점들 미리 계산 </summary>
private void CalculateCurvePoints(int count)
{
Vector3 pA = pointA.position;
Vector3 pB = pointB.position;
Vector3 pC = pointC.position;
Vector3 pD = pointD.position;
curvePoints = new Vector3[count + 1];
float unit = 1.0f / count;
int i = 0; float t = 0f;
for (; i < count + 1; i++, t += unit)
{
float t2 = t * t;
float t3 = t * t2;
float u = (1 - t);
float u2 = u * u;
float u3 = u * u2;
curvePoints[i] =
pA * u3 +
pB * (t * u2 * 3) +
pC * (t2 * u * 3) +
pD * t3
;
}
}
일반화
-
Bezier Spline
-
일반화된 공식을 이용하여, n차 베지어 곡선을 그려낸다.
-
점 (n + 1)개를 이용한다.
-
예 : 6차 베지어 곡선 B(6) -> 점 7개
-
공식 :
- n : 차수
- t : 0 ~ 1
- Pi : (i + 1)번째 점의 위치
예시 : 4차 베지어 곡선
- 점 5개 사용

예시 : 6차 베지어 곡선
- 점 7개 사용

Calculation Method
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
public Transform[] points;
private Vector3[] curvePoints;
private void CalculateCurvePoints(int count)
{
if (points == null || points.Length < 2) return;
curvePoints = new Vector3[count + 1];
float unit = 1.0f / count;
ref Transform[] P = ref points;
int n = P.Length - 1;
int[] C = GetCombinationValues(n); // nCi
float[] T = new float[n + 1]; // t^i
float[] U = new float[n + 1]; // (1-t)^i
// Iterate curvePoints : 0 ~ count(200)
int k = 0; float t = 0f;
for (; k < count + 1; k++, t += unit)
{
curvePoints[k] = Vector3.zero;
T[0] = 1f;
U[0] = 1f;
T[1] = t;
U[1] = 1f - t;
// T[i] = t^i
// U[i] = (1 - t)^i
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
T[i] = T[i - 1] * T[1];
U[i] = U[i - 1] * U[1];
}
// Iterate Bezier Points : 0 ~ n(number of points - 1)
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
{
curvePoints[k] += C[i] * T[i] * U[n - i] * P[i].position;
}
}
}
Math Methods
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
private int[] GetCombinationValues(int n)
{
int[] arr = new int[n + 1];
for (int r = 0; r <= n; r++)
{
arr[r] = Combination(n, r);
}
return arr;
}
private int Factorial(int n)
{
if (n == 0 || n == 1) return 1;
if (n == 2) return 2;
int result = n;
for (int i = n - 1; i > 1; i--)
{
result *= i;
}
return result;
}
private int Permutation(int n, int r)
{
if (r == 0) return 1;
if (r == 1) return n;
int result = n;
int end = n - r + 1;
for (int i = n - 1; i >= end; i--)
{
result *= i;
}
return result;
}
private int Combination(int n, int r)
{
if (n == r) return 1;
if (r == 0) return 1;
// C(n, r) == C(n, n - r)
if (n - r < r)
r = n - r;
return Permutation(n, r) / Factorial(r);
}